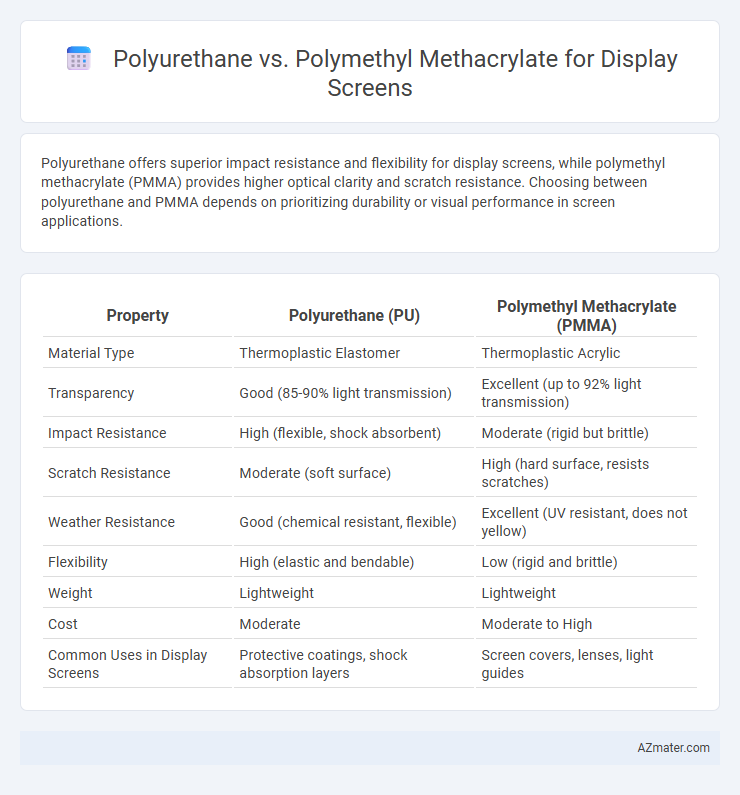
Polyurethane offers superior impact resistance and flexibility for display screens, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides higher optical clarity and scratch resistance. Choosing between polyurethane and PMMA depends on prioritizing durability or visual performance in screen applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Thermoplastic Acrylic |
| Transparency | Good (85-90% light transmission) | Excellent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | High (flexible, shock absorbent) | Moderate (rigid but brittle) |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate (soft surface) | High (hard surface, resists scratches) |
| Weather Resistance | Good (chemical resistant, flexible) | Excellent (UV resistant, does not yellow) |
| Flexibility | High (elastic and bendable) | Low (rigid and brittle) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Common Uses in Display Screens | Protective coatings, shock absorption layers | Screen covers, lenses, light guides |
Introduction to Display Screen Materials
Polyurethane and Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) are widely used materials for display screens due to their distinctive optical and mechanical properties. Polyurethane offers high flexibility, impact resistance, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it suitable for touch-sensitive and flexible displays. Polymethyl Methacrylate provides superior clarity, UV resistance, and hardness, commonly employed in rigid screens requiring high transparency and durability.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and impact absorption, making it ideal for use as a protective layer on display screens. Its high elasticity and superior scratch resistance provide durable protection while maintaining optical clarity, essential for touchscreen sensitivity. Compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), PU offers enhanced durability and shock absorption, reducing the risk of screen damage from drops or impacts.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic glass, is a transparent thermoplastic widely used for display screens due to its excellent optical clarity, high light transmittance (up to 92%), and superior weather resistance. It offers good scratch resistance compared to polyurethane but is more brittle, with lower impact resistance and flexibility. PMMA's lightweight nature and UV stability make it a preferred choice for outdoor displays and protective screens requiring long-term durability and visual performance.
Optical Clarity: PU vs PMMA
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity compared to polyurethane (PU), with light transmittance rates typically exceeding 92%, making it ideal for high-definition display screens. PU, while more flexible and impact-resistant, generally has lower transparency due to its molecular structure, resulting in slight haze or reduced light transmission around 85-90%. The choice between PMMA and PU depends on balancing optical clarity requirements with mechanical durability for display applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Polyurethane offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it highly durable against drops and deformation for display screens. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent scratch resistance and clarity but is more brittle and prone to cracking under stress compared to polyurethane. Choosing polyurethane enhances long-term durability for rugged use, while PMMA is optimal for applications prioritizing surface hardness and optical clarity.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
Polyurethane exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for display screens requiring durability and resilience under stress. PMMA offers excellent optical clarity but is more rigid and prone to cracking upon impact, limiting its use in flexible or high-impact environments. The inherent elasticity and toughness of polyurethane allow it to absorb shocks effectively, extending the lifespan of touchscreens and protective covers in mobile devices.
UV Stability and Weathering
Polyurethane exhibits superior UV resistance and weathering durability compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for outdoor display screens exposed to harsh sunlight and fluctuating environmental conditions. PMMA tends to yellow and degrade under prolonged UV exposure, compromising optical clarity and mechanical integrity over time. Polyurethane's enhanced formulation provides long-term protection against UV-induced brittleness and color distortion, ensuring consistent performance and display quality.
Cost Analysis: PU vs PMMA
Polyurethane (PU) generally offers lower raw material costs and enhanced impact resistance compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it a cost-effective choice for budget-sensitive display screen applications. PMMA, while more expensive upfront due to higher material and processing costs, provides superior optical clarity and UV resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, PU may reduce initial investment, whereas PMMA supports durability and performance benefits that can justify its premium price in high-end displays.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane and Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for display screens. Polyurethane, derived from petrochemicals, often involves toxic isocyanates and displays limited recyclability, leading to higher ecological footprints. PMMA is more recyclable and can be produced from bio-based methacrylates, offering advantages in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting circular economy practices in screen manufacturing.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Polyurethane offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for rugged, touch-sensitive display screens frequently used in industrial and wearable devices. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), known for its superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, suits high-visibility display applications like smartphones and tablets where image sharpness is crucial. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability needs against optical performance to optimize screen functionality and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Display Screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com