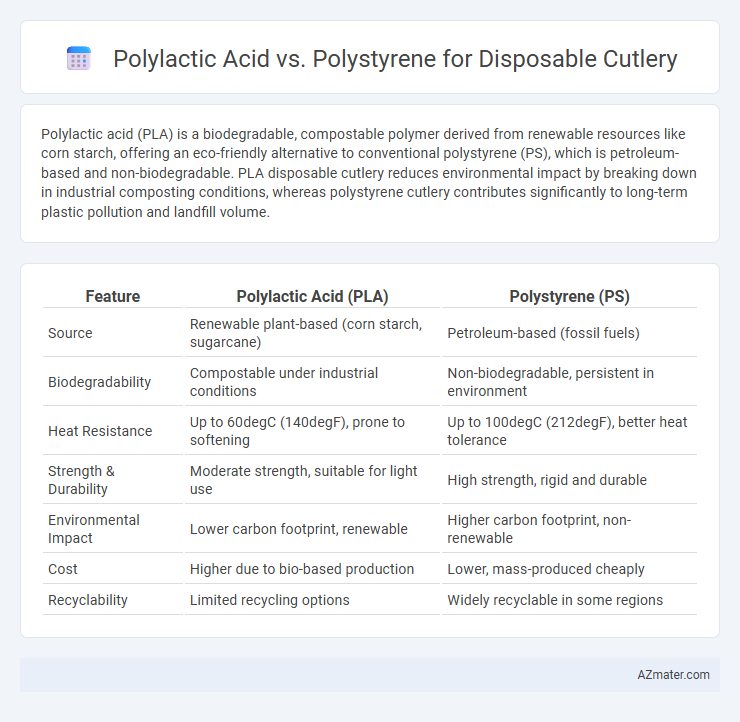
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable, compostable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering an eco-friendly alternative to conventional polystyrene (PS), which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA disposable cutlery reduces environmental impact by breaking down in industrial composting conditions, whereas polystyrene cutlery contributes significantly to long-term plastic pollution and landfill volume.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based (corn starch, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based (fossil fuels) |
| Biodegradability | Compostable under industrial conditions | Non-biodegradable, persistent in environment |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60degC (140degF), prone to softening | Up to 100degC (212degF), better heat tolerance |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate strength, suitable for light use | High strength, rigid and durable |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, renewable | Higher carbon footprint, non-renewable |
| Cost | Higher due to bio-based production | Lower, mass-produced cheaply |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Widely recyclable in some regions |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) and polystyrene (PS) represent two primary materials used for disposable cutlery, each with distinct environmental and performance characteristics. PLA, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and compostability, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based polystyrene, known for its rigidity and low cost but poor environmental impact. The material selection in disposable cutlery balances factors such as durability, cost-effectiveness, environmental footprint, and consumer safety.
What is Polylactic Acid (PLA)?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, widely used in disposable cutlery for its eco-friendly properties. PLA offers a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics like polystyrene by decomposing into natural elements under industrial composting conditions. Its biocompatibility and lower carbon footprint make PLA a preferred material for environmentally conscious single-use utensils.
What is Polystyrene (PS)?
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, widely used in disposable cutlery due to its rigidity, clarity, and low cost. It is a petroleum-based plastic known for its ease of molding into various shapes but has limited biodegradability, contributing to environmental concerns. Polystyrene's non-biodegradable nature contrasts with polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable alternative derived from renewable resources like corn starch, making PLA a more sustainable choice for disposable cutlery.
Environmental Impact: PLA vs Polystyrene
Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery offers a significant environmental advantage over polystyrene by being biodegradable and compostable under industrial conditions, reducing plastic pollution and landfill waste. Polystyrene, derived from petroleum, is non-biodegradable and persists in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to microplastic contamination and harmful effects on wildlife. PLA's carbon footprint is lower due to its biobased origins from renewable resources like corn starch, whereas polystyrene relies on fossil fuels and energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
Biodegradability and Compostability Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers superior biodegradability and compostability compared to polystyrene, as PLA is derived from renewable resources like corn starch and can decompose fully in industrial composting facilities within 1 to 3 months. Polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic, resists biodegradation and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to long-term pollution and landfill accumulation. The compostability advantage of PLA supports eco-friendly disposable cutlery solutions by reducing environmental impact and enhancing waste management sustainability.
Performance and Durability in Everyday Use
Polylactic acid (PLA) disposable cutlery offers biodegradability and compostability but generally exhibits lower heat resistance and brittleness compared to polystyrene, which delivers superior rigidity and durability under heat and pressure. In everyday use, polystyrene cutlery withstands repeated contact with hot foods and liquids without deforming, making it more reliable for longer meals or takeaway scenarios. PLA cutlery may crack or soften when exposed to hot substances, limiting its performance in high-temperature environments despite its environmental benefits.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polylactic acid (PLA) disposable cutlery is favored for safety and health as it is derived from renewable resources, is biodegradable, and poses minimal risk of leaching harmful chemicals when exposed to heat or acidic foods. Polystyrene (PS), commonly used in disposable cutlery, may release styrene monomers, considered possible carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), especially when heated, raising concerns about chemical exposure. Choosing PLA cutlery reduces potential toxicological risks and supports safer food contact practices, making it a preferable option for health-conscious consumers.
Cost Analysis for Manufacturers
Polylactic acid (PLA) incurs higher production costs due to raw material prices and processing complexity compared to polystyrene, which benefits from low-cost petrochemical sources and established manufacturing infrastructure. Polystyrene disposable cutlery is more cost-effective for large-scale manufacturers seeking minimal expenses, while PLA's biodegradability commands premium pricing that can be offset by eco-conscious market demand and regulatory incentives. Cost analysis must factor in lifecycle expenses, including waste management and potential taxes on non-biodegradable plastics, influencing long-term manufacturer profitability.
Regulations and Compliance Issues
Polylactic acid (PLA) disposable cutlery benefits from stringent global regulations promoting biodegradability, as it meets ASTM D6400 and EN 13432 compostability standards, aiding compliance with EU Single-Use Plastics Directive 2019/904. Polystyrene cutlery faces increasing restrictions due to its non-biodegradable nature and classification under various bans on single-use plastics in regions like California and the European Union. Businesses must navigate evolving regulatory landscapes favoring PLA to avoid penalties and ensure sustainable product lifecycle compliance.
Future Trends in Disposable Cutlery Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) is gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to polystyrene in disposable cutlery due to its biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Emerging technologies in biodegradable polymers and advances in composting facilities are expected to further increase PLA adoption, driven by stricter regulations on single-use plastics worldwide. Innovations in material blends and improved manufacturing processes aim to enhance the durability and heat resistance of PLA, positioning it as the future standard for eco-friendly disposable cutlery materials.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polystyrene for Disposable Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com