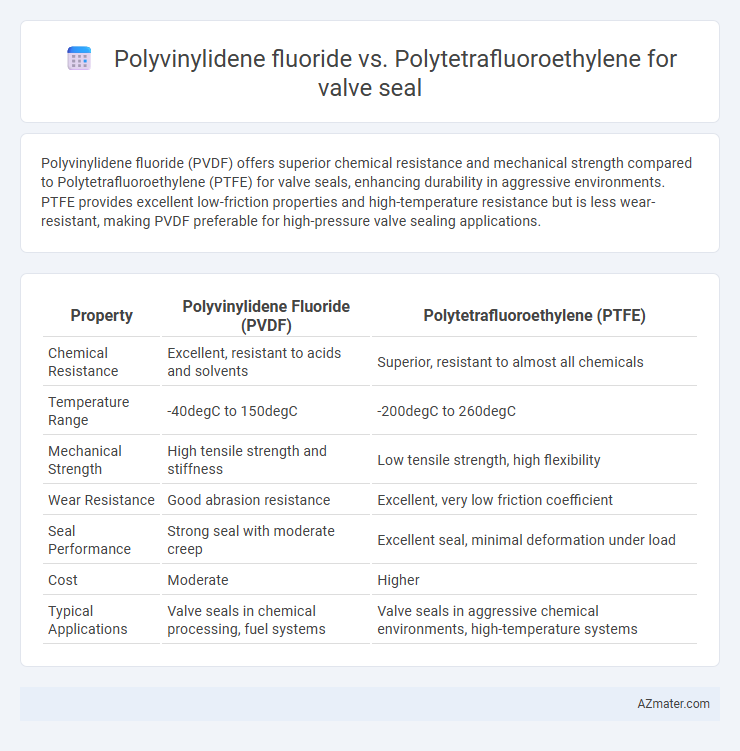
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for valve seals, enhancing durability in aggressive environments. PTFE provides excellent low-friction properties and high-temperature resistance but is less wear-resistant, making PVDF preferable for high-pressure valve sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to acids and solvents | Superior, resistant to almost all chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -200degC to 260degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Low tensile strength, high flexibility |
| Wear Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent, very low friction coefficient |
| Seal Performance | Strong seal with moderate creep | Excellent seal, minimal deformation under load |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Valve seals in chemical processing, fuel systems | Valve seals in aggressive chemical environments, high-temperature systems |
Introduction to Valve Seal Materials
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are key materials used in valve seal applications due to their chemical resistance and mechanical properties. PVDF offers higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, making it suitable for dynamic sealing environments, while PTFE excels in low friction and a wide temperature range, ensuring excellent sealing performance under extreme conditions. The selection between PVDF and PTFE depends on specific operational demands such as chemical exposure, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress in valve systems.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability, making it suitable for valve seal applications in aggressive environments. Compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), PVDF offers superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength while maintaining good resistance to solvents and UV radiation. Its semi-crystalline structure ensures durability in dynamic sealing conditions, providing reliable performance in industrial valves handling corrosive fluids.
Key Properties of PVDF for Valve Seals
PVDF offers superior chemical resistance and excellent mechanical strength, which ensures durability and reliability in valve seals exposed to harsh fluids. Its resistance to UV radiation and abrasion makes it ideal for long-term outdoor and industrial applications, reducing maintenance frequency. Additionally, PVDF's low permeability to gases and liquids enhances sealing efficiency, preventing leaks and ensuring optimal valve performance.
Understanding Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance and low friction properties, making it ideal for valve seals in aggressive environments. Its high thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 260degC, ensures reliable performance under extreme conditions. PTFE's non-reactive nature and excellent sealing capability minimize leakage and enhance valve longevity compared to materials like Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF).
Comparative Mechanical Strength: PVDF vs PTFE
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it more resistant to deformation and wear under high-pressure valve seal applications. PVDF's higher tensile strength and impact resistance enable longer service life and better maintenance of seal integrity in dynamic environments. PTFE, while offering excellent chemical resistance and low friction, generally has lower mechanical strength, limiting its use in high-stress valve seal scenarios.
Chemical Resistance in Valve Applications
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and solvents commonly encountered in valve seal applications, maintaining integrity under aggressive media. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior chemical inertness with unmatched resistance to nearly all chemicals, including strong oxidizers and harsh solvents, making it ideal for highly corrosive environments. The choice between PVDF and PTFE for valve seals depends on the specific chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical requirements, with PTFE favored for extreme chemical resistance and PVDF preferred for a balance of chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits high chemical resistance with temperature tolerance up to 150degC, making it suitable for moderate thermal environments in valve seals. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 260degC, which enhances its performance in high-temperature valve seal applications. PTFE's low friction and excellent thermal resistance make it the preferred choice for valves exposed to extreme heat and chemically aggressive media.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior wear resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for valve seals subjected to abrasive and corrosive environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits excellent longevity due to its low coefficient of friction and high thermal stability, reducing seal degradation over time. PVDF's enhanced mechanical strength combined with PTFE's exceptional inertness ensures optimal performance and extended service life in valve sealing applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Application Suitability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers a cost-effective valve seal solution with excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals and moderate temperatures. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior temperature tolerance and exceptional non-stick properties but comes at a higher material cost, justified by its suitability in extreme temperature, high-purity, and highly corrosive environments. Choosing between PVDF and PTFE hinges on balancing budget constraints with specific application requirements such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and durability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Valve Seals
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical resistance, high mechanical strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for valve seals in demanding chemical processing environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides unmatched thermal stability and low friction properties, suitable for valves operating under extreme temperatures and requiring minimal wear. Selecting the right material depends on operating temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, with PVDF favored for robust chemical compatibility and PTFE preferred for high-temperature resilience and low-friction sealing.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Valve seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com