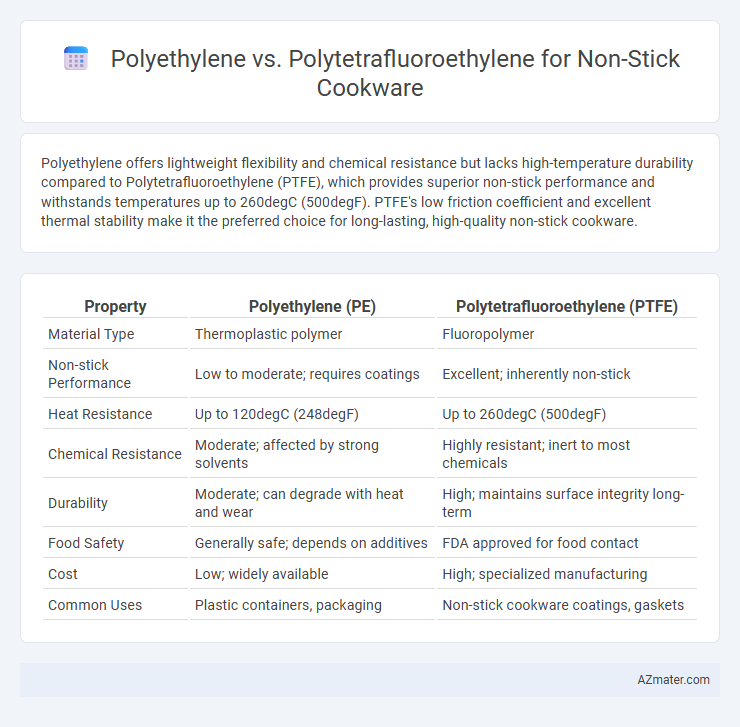
Polyethylene offers lightweight flexibility and chemical resistance but lacks high-temperature durability compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which provides superior non-stick performance and withstands temperatures up to 260degC (500degF). PTFE's low friction coefficient and excellent thermal stability make it the preferred choice for long-lasting, high-quality non-stick cookware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Fluoropolymer |
| Non-stick Performance | Low to moderate; requires coatings | Excellent; inherently non-stick |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; affected by strong solvents | Highly resistant; inert to most chemicals |
| Durability | Moderate; can degrade with heat and wear | High; maintains surface integrity long-term |
| Food Safety | Generally safe; depends on additives | FDA approved for food contact |
| Cost | Low; widely available | High; specialized manufacturing |
| Common Uses | Plastic containers, packaging | Non-stick cookware coatings, gaskets |
Introduction: Polyethylene and Polytetrafluoroethylene in Non-stick Cookware
Polyethylene and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are polymers used in non-stick cookware for their unique properties. Polyethylene offers good chemical resistance and affordability but lacks the high heat tolerance and superior non-stick performance of PTFE. PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, provides exceptional non-stick capabilities and high thermal stability, making it the preferred choice for durable, high-quality non-stick cookware coatings.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyethylene features a simple, repeating ethylene monomer structure (-CH2-CH2-)n, resulting in a flexible, semi-crystalline polymer with high chemical resistance and low melting point. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) consists of carbon atoms fully fluorinated (-CF2-CF2-)n, creating a highly stable, non-reactive polymer with exceptional heat resistance and an extremely low coefficient of friction. PTFE's electronegative fluorine atoms provide superior non-stick properties, chemical inertness, and thermal stability compared to polyethylene, making it more suitable for high-performance non-stick cookware.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior heat resistance and thermal stability compared to polyethylene, making it the preferred choice for non-stick cookware. PTFE can withstand continuous temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) without degradation, while polyethylene typically deforms at temperatures above 80-100degC (176-212degF). This thermal resilience enables PTFE-coated cookware to maintain a durable non-stick surface under high-heat cooking conditions.
Non-stick Performance and Surface Characteristics
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior non-stick performance due to its extremely low surface energy, enabling effortless food release and minimal residue buildup. Polyethylene, while more affordable, lacks the same level of chemical inertness and heat resistance, resulting in lower durability and stickier surfaces over time. PTFE's smooth, fluorinated polymer surface resists scratches and high temperatures up to 260degC, whereas polyethylene surfaces are more prone to wear and melting under intense cooking conditions.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polyethylene (PE) is commonly used in food contact applications due to its inert nature and compliance with FDA and EFSA safety standards, ensuring it poses minimal risk of chemical migration into food. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known by the brand name Teflon, is celebrated for its superior non-stick properties but requires careful manufacturing controls to avoid exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a substance restricted by major regulatory bodies for food contact materials. Both materials meet stringent food safety regulations when properly processed, but PTFE's thermal stability demands adherence to temperature limits to prevent degradation and potential release of harmful fumes.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior durability and scratch resistance compared to polyethylene when used in non-stick cookware, maintaining its non-stick properties under high temperatures and rigorous cleaning. Polyethylene tends to degrade faster and is more susceptible to surface damage, reducing the cookware's lifespan and performance. PTFE coatings resist abrasion and chemical wear more effectively, ensuring prolonged usability and safer cooking experiences.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Polyethylene cookware typically requires gentle cleaning with mild detergents to avoid surface wear, as its lower heat resistance can cause deformation under high temperatures. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for its superior non-stick properties, allows effortless cleaning with minimal residue, resisting staining and buildup from foods like eggs and sauces. PTFE's chemically inert surface demands less frequent maintenance and can be cleaned effectively with soft sponges, whereas polyethylene surfaces may degrade faster if abrasive scrubbers or harsh chemicals are used.
Cost-effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyethylene offers a highly cost-effective solution for non-stick cookware due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability in global markets. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for superior non-stick properties and chemical resistance, commands a higher price point and is less abundant, affecting its overall market presence. The balance between affordability and performance drives consumer preference, with polyethylene favored for budget-conscious cookware and PTFE dominating premium product segments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene (PE) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability for non-stick cookware. Polyethylene, a widely recyclable thermoplastic, has a lower environmental footprint due to its easier processing and biodegradability under certain conditions. In contrast, PTFE, known for its superior non-stick properties, poses recycling challenges and potential environmental risks due to the release of toxic fluorinated compounds during manufacture and disposal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Material for Non-stick Cookware
Polyethylene offers affordability and moderate non-stick properties suitable for light cooking, while polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior non-stick performance and durability, making it ideal for high-heat and frequent use. PTFE-based cookware, such as Teflon, resists sticking and is chemically inert, ensuring safer cooking with less oil. Selecting the ideal material depends on cooking habits and budget, with PTFE preferred for professional-grade non-stick cookware and polyethylene serving well in budget-friendly, low-temperature applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com