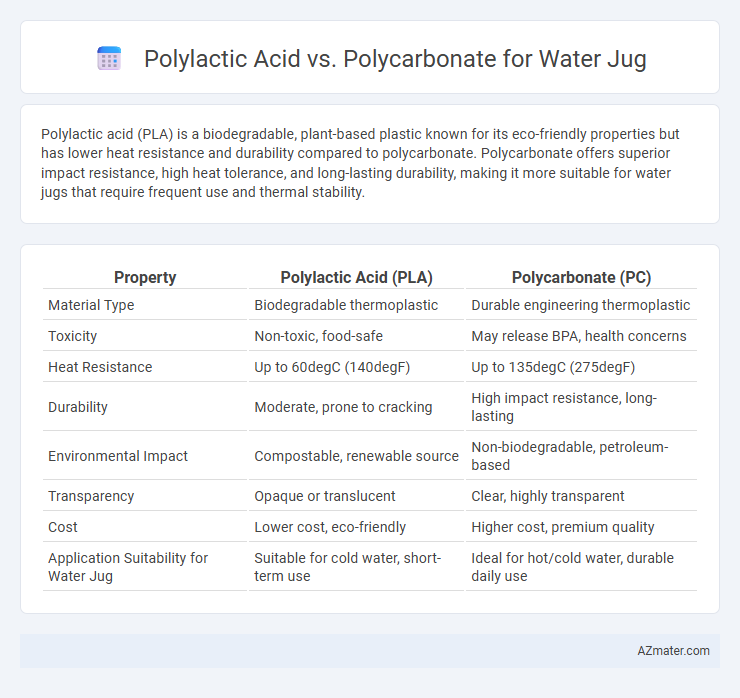
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable, plant-based plastic known for its eco-friendly properties but has lower heat resistance and durability compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance, high heat tolerance, and long-lasting durability, making it more suitable for water jugs that require frequent use and thermal stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic | Durable engineering thermoplastic |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, food-safe | May release BPA, health concerns |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60degC (140degF) | Up to 135degC (275degF) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High impact resistance, long-lasting |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable, renewable source | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear, highly transparent |
| Cost | Lower cost, eco-friendly | Higher cost, premium quality |
| Application Suitability for Water Jug | Suitable for cold water, short-term use | Ideal for hot/cold water, durable daily use |
Introduction to Water Jug Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) and polycarbonate are two common materials used for water jugs, each offering distinct advantages based on composition and durability. PLA, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, making it suitable for eco-conscious consumers. Polycarbonate, a petroleum-based plastic known for its high impact resistance and clarity, provides superior durability and long-term reuse potential in water jug applications.
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable, bio-based polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics. Its natural origin and compostability contribute to reduced environmental impact compared to polycarbonate, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA offers good clarity and safety for water containment but typically has lower heat resistance and durability than polycarbonate, affecting its long-term performance in water jugs.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, high-impact-resistant thermoplastic often used for water jugs due to its clarity and toughness. It exhibits excellent heat resistance and is BPA-free, making it suitable for safe water storage and repeated use. Compared to polylactic acid (PLA), PC provides superior durability and longevity, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers moderate mechanical strength, making it suitable for lightweight water jugs but less resistant to impact and bending compared to polycarbonate (PC), which exhibits superior tensile strength and durability. Polycarbonate's high impact resistance and flexibility provide enhanced crack and breakage prevention under stress, ideal for long-term, heavy-duty water jug applications. PLA, while biodegradable and environmentally friendly, generally lacks the robust mechanical properties of polycarbonate, limiting its use in high-stress or high-impact environments.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers moderate thermal resistance with a melting point around 150-160degC but tends to deform at temperatures above 60degC, making it less suitable for hot water storage. Polycarbonate (PC) excels in thermal stability, maintaining integrity at temperatures up to 135degC and often higher, providing superior durability for water jugs exposed to heat. The inherent heat resistance and toughness of polycarbonate make it a preferred material for applications requiring repeated exposure to hot liquids and dishwasher safety.
Food Safety and Health Implications
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering excellent food safety due to its non-toxic and compostable nature, making it ideal for water jugs intended for single-use or short-term storage. Polycarbonate (PC), although durable and heat-resistant, contains bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical linked to health risks such as hormonal disruptions when leached into beverages, raising concerns for long-term food contact applications. Choosing PLA over PC for water jugs reduces exposure to harmful chemicals and supports environmental sustainability, aligning with increasing consumer demand for safe, eco-friendly food containers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a compostable bioplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering a lower carbon footprint and enhanced biodegradability compared to polycarbonate (PC), which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA's environmental impact is significantly reduced through its ability to break down in industrial composting facilities, unlike PC that contributes to long-term plastic pollution due to its persistent nature. Sustainability efforts favor PLA for water jugs because of its renewable sourcing and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, while PC provides superior durability but poses greater challenges in recycling and environmental degradation.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polylactic acid (PLA) water jugs generally offer lower material costs due to their renewable, plant-based origins, but they require careful processing to maintain structural integrity and thermal resistance during manufacturing. Polycarbonate (PC) water jugs typically have higher raw material costs but provide superior durability, high impact resistance, and easier molding with injection technology, resulting in faster production cycles. Manufacturers must weigh PLA's eco-friendly appeal and biodegradability against PC's cost efficiency in mass production and long-term performance.
User Experience and Practicality
Polylactic acid (PLA) water jugs offer a biodegradable and environmentally friendly option, with a lighter weight that enhances portability but tend to have lower heat resistance and durability compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate water jugs provide superior impact resistance, high clarity, and excellent heat tolerance, making them ideal for long-term use and frequent handling. Users seeking sustainability and ease of disposal may prefer PLA, while those prioritizing toughness and longevity benefit more from polycarbonate materials.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Water Jugs
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability and environmental sustainability, making it ideal for eco-friendly water jugs, while polycarbonate (PC) provides superior durability, impact resistance, and heat tolerance for long-lasting performance. For disposable or short-term use, PLA's compostable nature is advantageous, but polycarbonate water jugs excel in reusable applications requiring strength and clarity. Selecting between PLA and polycarbonate depends on balancing environmental impact with durability requirements for specific water jug use cases.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polycarbonate for Water Jug
 azmater.com
azmater.com