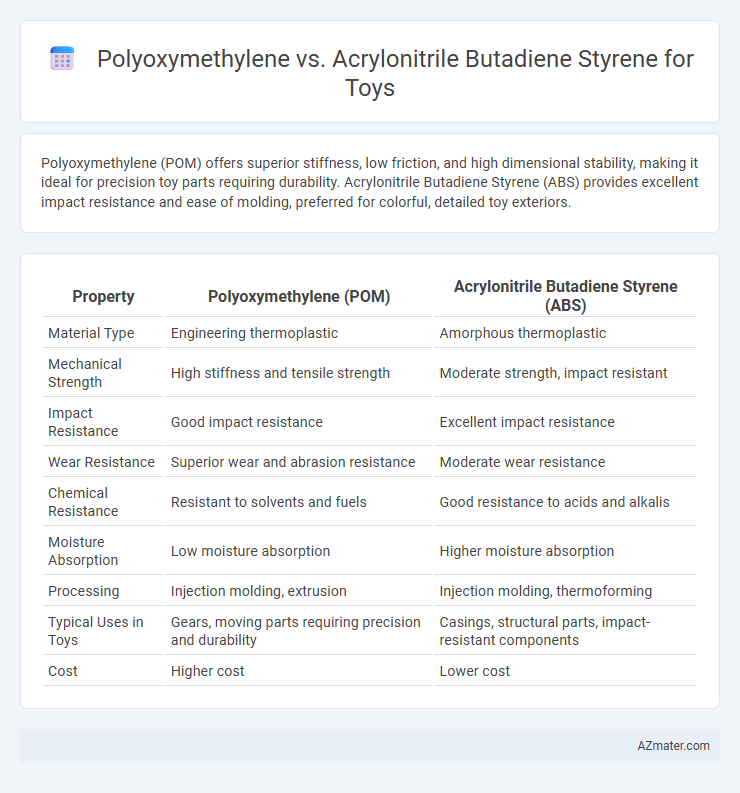
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior stiffness, low friction, and high dimensional stability, making it ideal for precision toy parts requiring durability. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, preferred for colorful, detailed toy exteriors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering thermoplastic | Amorphous thermoplastic |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and tensile strength | Moderate strength, impact resistant |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Excellent impact resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear and abrasion resistance | Moderate wear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and fuels | Good resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Higher moisture absorption |
| Processing | Injection molding, extrusion | Injection molding, thermoforming |
| Typical Uses in Toys | Gears, moving parts requiring precision and durability | Casings, structural parts, impact-resistant components |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a thermoplastic polymer noted for its high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for precision toy components requiring durability and smooth mechanical performance. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a common thermoplastic polymer favored in toy manufacturing for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of molding into complex shapes with vibrant colors. Both materials offer unique properties that influence toy safety, longevity, and aesthetic appeal, with POM excelling in mechanical parts and ABS widely used in outer shells and colorful designs.
Material Properties: POM vs ABS
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength, stiffness, and wear resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for durable toy components that require high precision and longevity. ABS provides excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, which benefits toy designs needing complex shapes and vibrant color options. While POM excels in low friction applications and chemical resistance, ABS is preferred for its cost-effectiveness and better thermal stability during the manufacturing process.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it more suitable for toys requiring high durability and impact resistance. POM's tensile strength ranges between 60-70 MPa, while ABS typically offers 40-50 MPa, enhancing the toy's ability to withstand rough handling. The higher stiffness and fatigue resistance of POM also contribute to longer-lasting, safer toy components under repetitive stress.
Safety and Toxicity for Toys
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high dimensional stability and low toxicity, making it a safe choice for toys due to its resistance to chemical leaching and minimal allergenic potential. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is widely used in toys for durability and impact resistance but may release trace amounts of styrene, raising concerns about long-term exposure and toxicity in sensitive children. Regulatory compliance such as ASTM F963 and EN 71 standards ensures both materials meet strict safety criteria, however, POM tends to have a safer chemical profile for direct and prolonged contact in children's products.
Colorability and Aesthetic Versatility
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers limited colorability due to its inherent natural opacity and tendency to favor neutral tones, resulting in less aesthetic versatility for toys. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) excels in colorability, allowing vibrant, glossy finishes and a wide palette of hues, enhancing the visual appeal and design flexibility of toys. ABS's superior aesthetic versatility makes it a preferred choice for toys requiring customized, eye-catching appearances.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers exceptional dimensional stability and low friction, making it easier to machine and mold with high precision for toy components requiring tight tolerances. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and can be processed with injection molding at lower temperatures, facilitating faster cycle times and cost-efficient mass production in toy manufacturing. The choice between POM and ABS depends on balancing precision and mechanical performance with production scalability in toy manufacturing processes.
Durability and Lifespan in Play Environments
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for toys subjected to frequent mechanical stress and impact, ensuring a longer lifespan in active play environments. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides good toughness and impact resistance but can degrade faster under continuous exposure to UV light and harsh play conditions. The high stiffness and low friction of POM contribute to enhanced durability, while ABS's ease of molding and colorability supports diverse toy designs with moderate longevity.
Cost-Effectiveness for Toy Production
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior dimensional stability and wear resistance, making it a durable choice for high-quality toy components, though its higher material and processing costs can impact overall budget constraints. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and ease of molding with lower production costs, making it highly cost-effective for mass-produced toys. In cost-effectiveness analysis, ABS typically enables greater scalability and reduced expenses in toy manufacturing without compromising safety and aesthetics.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and durability for toys but presents challenges in recycling due to limited industrial recycling streams and longer degradation periods. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is more widely recycled, supported by established municipal recycling programs, and has a lower environmental footprint during processing. Both materials are thermoplastics; however, ABS's greater recyclability and availability of reprocessing facilities make it a more environmentally favorable option for toy manufacturing.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Toy Applications
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior rigidity, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for precise, durable toy components. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides better impact resistance and ease of molding, suited for toys requiring vibrant colors and complex shapes. For toy applications demanding mechanical strength and wear resistance, POM is the best choice, whereas ABS excels in aesthetic versatility and impact toughness.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com