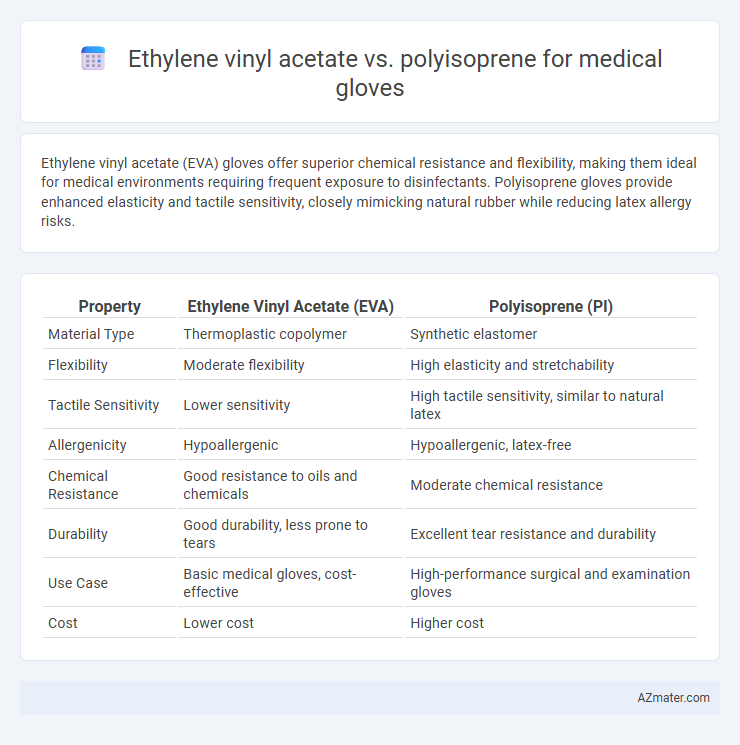
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gloves offer superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for medical environments requiring frequent exposure to disinfectants. Polyisoprene gloves provide enhanced elasticity and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural rubber while reducing latex allergy risks.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyisoprene (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic copolymer | Synthetic elastomer |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High elasticity and stretchability |
| Tactile Sensitivity | Lower sensitivity | High tactile sensitivity, similar to natural latex |
| Allergenicity | Hypoallergenic | Hypoallergenic, latex-free |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Durability | Good durability, less prone to tears | Excellent tear resistance and durability |
| Use Case | Basic medical gloves, cost-effective | High-performance surgical and examination gloves |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyisoprene are prominent materials in medical glove manufacturing, each offering distinct benefits in terms of flexibility, durability, and allergenic potential. EVA provides superior chemical resistance and hypoallergenic properties, making it suitable for tasks requiring extended chemical exposure. Polyisoprene, resembling natural rubber latex in elasticity and fit, offers enhanced tactile sensitivity and comfort without the risk of latex allergies, positioning it as a preferred choice for medical professionals.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer commonly used in medical gloves for its excellent flexibility, clarity, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring dexterity and durability. EVA gloves provide significant tensile strength and resistance to punctures and tears, enhancing protection in medical environments. Compared to Polyisoprene, EVA offers hypoallergenic properties with reduced risk of latex sensitivity, catering to healthcare settings where allergy concerns are paramount.
Overview of Polyisoprene
Polyisoprene medical gloves offer superior elasticity and sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex while providing excellent barrier protection against pathogens. These gloves exhibit low allergenic potential due to the absence of latex proteins, making them ideal for healthcare settings requiring hypoallergenic options. Their durability and comfortable fit enhance tactile performance, crucial for precise medical procedures compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate alternatives.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gloves exhibit greater tensile strength and enhanced flexibility compared to polyisoprene gloves, making them suitable for medical applications requiring durability and comfort. Polyisoprene gloves provide superior elongation at break and higher elasticity, offering better tactile sensitivity and fit during intricate medical procedures. The mechanical performance of EVA emphasizes puncture resistance, while polyisoprene excels in resilience and soft texture, influencing glove selection based on specific clinical needs.
Biocompatibility and Allergic Reactions
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) medical gloves exhibit excellent biocompatibility with minimal risk of allergic reactions due to their hypoallergenic nature and absence of latex proteins. In contrast, polyisoprene gloves, while latex-free and providing similar elasticity, carry a low risk of Type IV latex allergy due to residual proteins, though they are generally well-tolerated in sensitive patients. Both materials offer safe alternatives to latex, but EVA's inert chemical properties make it particularly suitable for patients with severe latex sensitivities or contact dermatitis concerns.
Barrier Protection Effectiveness
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) medical gloves provide excellent chemical resistance and durability, enhancing barrier protection against a wide range of contaminants and pathogens. Polyisoprene gloves offer superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, ensuring a secure fit that minimizes the risk of micro-tears and enhances overall protection against biological hazards. Comparative studies reveal that while EVA gloves excel in chemical barrier effectiveness, polyisoprene gloves are preferred for protection against viruses and bacteria due to their resilience and snug fit.
Comfort and Fit for Healthcare Workers
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) medical gloves offer moderate stretch and cushioning, providing comfort but with less elasticity compared to polyisoprene gloves. Polyisoprene gloves closely mimic natural latex in flexibility and fit, delivering superior tactile sensitivity and conforming snugly to the hand, which reduces hand fatigue during prolonged use. Healthcare workers often prefer polyisoprene for its latex-free, comfortable fit that balances durability and softness, essential for tasks requiring precision and extended wear.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) medical gloves are produced using a dip molding process involving the heating and mixing of EVA copolymer resins, which are then dipped onto ceramic or metal hand molds, followed by curing and drying to achieve elasticity and durability. Polyisoprene gloves are manufactured through a similar dipping technique but require precise control of polymerization and coagulation steps due to the natural rubber's chemical sensitivity, ensuring enhanced elasticity and tactile sensitivity. The EVA process offers faster curing times and reduced sensitivity to temperature variations, whereas polyisoprene demands meticulous vulcanization and leaching processes to eliminate proteins and improve biocompatibility.
Cost and Availability in the Medical Industry
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gloves typically offer a lower production cost compared to polyisoprene gloves, making them a more budget-friendly option for large-scale medical use. Polyisoprene gloves, known for their high elasticity and latex-free composition, are often more expensive due to complex manufacturing processes and limited raw material supply. In terms of availability, EVA gloves are generally easier to procure in bulk within the medical industry, while polyisoprene gloves may face supply constraints due to specialized demand and raw material scarcity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gloves demonstrate lower biodegradability compared to polyisoprene gloves, which are derived from natural rubber and exhibit superior compostability and reduced environmental footprint. Polyisoprene gloves, produced from renewable resources, offer enhanced sustainability due to their reduced reliance on petrochemicals and better end-of-life degradation characteristics. EVA gloves, typically synthesized from fossil fuels, contribute to higher carbon emissions and waste persistence, making polyisoprene a preferred choice for eco-friendly medical glove applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyisoprene for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com