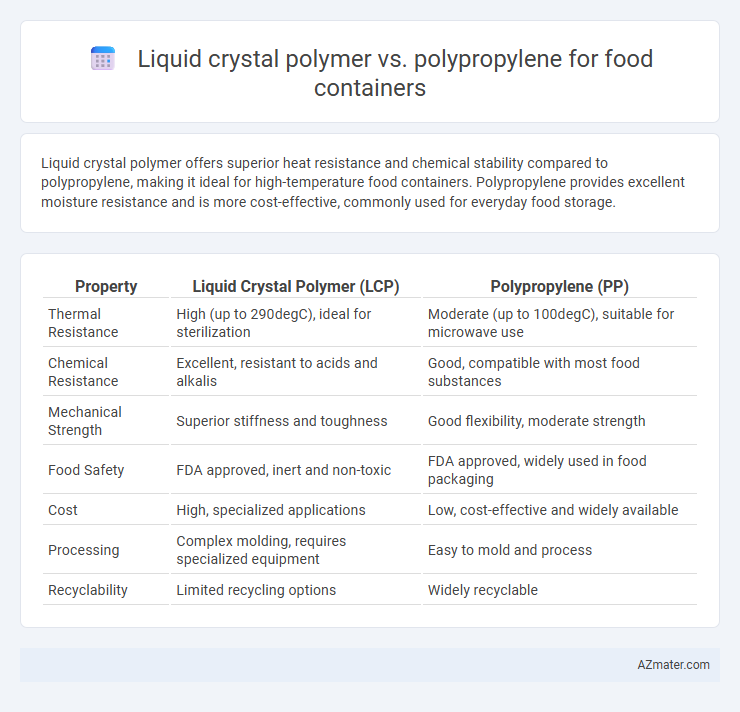
Liquid crystal polymer offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for high-temperature food containers. Polypropylene provides excellent moisture resistance and is more cost-effective, commonly used for everyday food storage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 290degC), ideal for sterilization | Moderate (up to 100degC), suitable for microwave use |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to acids and alkalis | Good, compatible with most food substances |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior stiffness and toughness | Good flexibility, moderate strength |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, inert and non-toxic | FDA approved, widely used in food packaging |
| Cost | High, specialized applications | Low, cost-effective and widely available |
| Processing | Complex molding, requires specialized equipment | Easy to mold and process |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) and Polypropylene (PP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for advanced food container applications that require durability and safety. Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used food-grade plastic characterized by its excellent moisture resistance, heat tolerance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in disposable and reusable food containers. Both materials offer unique benefits for food storage, with LCP providing superior mechanical properties and PP excelling in versatility and affordability.
Chemical Structure and Composition of LCP and PP
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) features rigid, rod-like molecular chains that align to form highly ordered crystalline structures, offering exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability for food containers. Polypropylene (PP) consists of flexible, saturated hydrocarbon chains with a semi-crystalline structure, providing good chemical inertness and lightweight properties. The difference in molecular rigidity and crystallinity between LCP and PP influences their barrier performance and durability in food packaging applications.
Thermal Stability: LCP vs Polypropylene
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability compared to polypropylene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 260degC, whereas polypropylene typically withstands up to 110-130degC before deformation. LCP's high melting point and minimal thermal expansion make it ideal for sterilization and microwave applications in food containers. In contrast, polypropylene's lower thermal threshold limits its use to less demanding thermal environments, impacting long-term durability and safety under high heat.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and rigidity compared to polypropylene (PP), making it more resistant to deformation and impact under stress. LCP's tensile strength ranges from 150 to 300 MPa, while polypropylene typically offers tensile strength around 30 to 40 MPa, highlighting LCP's superior load-bearing capacity in food container applications. The enhanced thermal stability and stiffness of LCP contribute to its durability during repeated use and exposure to varying temperatures, outperforming polypropylene in maintaining structural integrity.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, making it highly suitable for food containers requiring stringent food safety standards. LCP complies with FDA and EU regulations for food contact materials, ensuring minimal risk of chemical migration and contamination. Polypropylene is widely accepted for food storage due to its inert nature and FDA-approved status, though it has lower heat resistance and may not perform as reliably in high-temperature applications.
Barrier Properties: Odor, Moisture, and Gas Resistance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior barrier properties compared to polypropylene (PP) for food containers, exhibiting enhanced resistance to odor transmission, moisture ingress, and gas permeability. LCP's highly ordered molecular structure creates a dense barrier that minimizes gas exchange and prevents contamination, preserving food freshness for longer periods. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and widely used, demonstrates lower performance in blocking odors and moisture, making LCP a preferred choice for high-barrier food packaging applications requiring stringent protection.
Durability and Longevity in Food Storage
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for long-term food storage applications. LCP's high tensile strength and thermal stability ensure minimal deformation and degradation under repeated use and exposure to heat, unlike polypropylene, which tends to warp and degrade over time. This enhanced longevity of LCP containers makes them a reliable choice for preserving food quality and safety during extended storage periods.
Microwave and Dishwasher Compatibility
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making it highly microwave and dishwasher safe without warping or leaching harmful substances. Polypropylene, while commonly used for food containers, may deform or release chemicals under prolonged microwave heating and frequent dishwasher cycles. LCP containers provide enhanced durability and maintain food safety standards better during repeated microwave and dishwasher use.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene (PP), but its environmental impact is higher due to complex production processes and limited recycling infrastructure. Polypropylene, widely used in food containers, is more environmentally friendly given its lower energy production requirements and broad recyclability in municipal programs. The recyclability of PP supports circular economy initiatives, while LCP's current recycling options are scarce, hindering sustainable waste management for food packaging.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP) but comes at a significantly higher cost, limiting its widespread use in food containers. Polypropylene is more cost-effective, widely available, and commonly used in food packaging due to its low price and ease of processing. Market availability of polypropylene is extensive, making it the preferred choice for manufacturers focused on affordability and scalability, whereas LCP remains niche with specialized applications and limited supplier options.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com