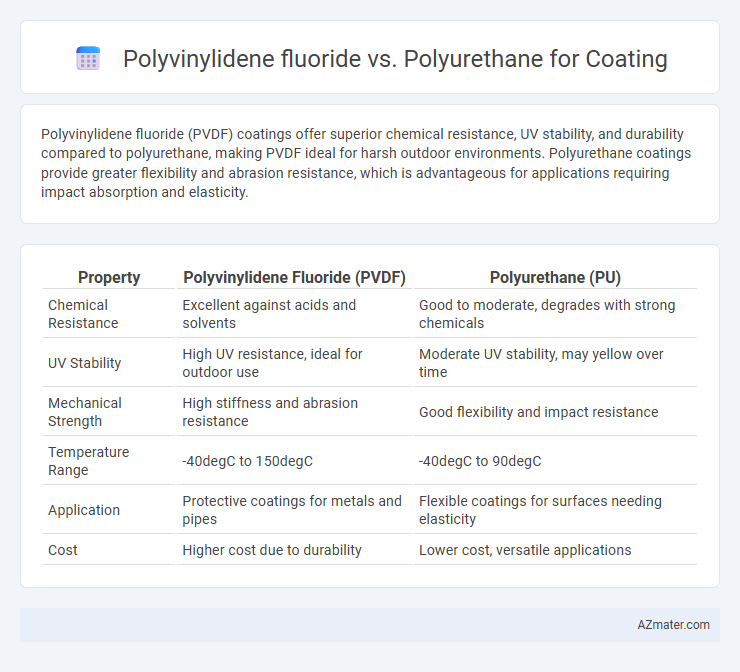
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings offer superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and durability compared to polyurethane, making PVDF ideal for harsh outdoor environments. Polyurethane coatings provide greater flexibility and abrasion resistance, which is advantageous for applications requiring impact absorption and elasticity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and solvents | Good to moderate, degrades with strong chemicals |
| UV Stability | High UV resistance, ideal for outdoor use | Moderate UV stability, may yellow over time |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and abrasion resistance | Good flexibility and impact resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 90degC |
| Application | Protective coatings for metals and pipes | Flexible coatings for surfaces needing elasticity |
| Cost | Higher cost due to durability | Lower cost, versatile applications |
Introduction to Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polyurethane
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and weather durability, making it ideal for industrial and architectural coatings. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer characterized by excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and strong adhesive properties, often used in protective and decorative coatings. Both materials offer distinct advantages depending on application requirements, with PVDF favored for long-term exterior durability and polyurethane for impact resistance and elasticity.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) features a highly fluorinated carbon backbone, providing exceptional chemical resistance and UV stability, whereas polyurethane (PU) consists of segmented polymers characterized by urethane linkages, which offer flexibility and abrasion resistance but are more susceptible to chemical degradation. The presence of strong carbon-fluorine bonds in PVDF results in superior inertness and durability in harsh environments, contrasting with the relatively more polar and reactive urethane groups in PU that enable diverse formulations but limit long-term chemical resilience. These structural differences determine their coating performance, with PVDF favored for outdoor, corrosive settings and PU preferred for applications requiring elasticity and impact tolerance.
Mechanical Properties Overview
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior mechanical strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for coatings requiring durability and long-term performance. Polyurethane offers exceptional flexibility, impact resistance, and elongation capabilities, suitable for coatings exposed to dynamic mechanical stresses and deformation. PVDF coatings maintain integrity under UV exposure and chemical corrosion, whereas polyurethane excels in environments demanding elasticity and wear resistance.
Weather and UV Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings exhibit exceptional weather and UV resistance due to their strong carbon-fluorine bonds, maintaining color stability and durability for over 20 years in extreme conditions. Polyurethane coatings offer good UV resistance but can degrade faster under prolonged sunlight exposure, resulting in chalking and discoloration within 5 to 10 years. PVDF is preferred for architectural applications requiring long-term resistance to harsh weather and UV radiation, while polyurethane is more suitable for applications with moderate UV exposure and flexibility needs.
Abrasion and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings exhibit superior chemical resistance, effectively protecting surfaces against acids, solvents, and UV degradation, making them ideal for harsh environments. Polyurethane coatings provide excellent abrasion resistance due to their toughness and flexibility, offering enhanced durability against mechanical wear and impact. Choosing between PVDF and polyurethane depends on specific application needs, prioritizing chemical stability or abrasion durability.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings exhibit superior thermal stability, maintaining performance at temperatures up to 150degC, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term exposure to heat and UV radiation. Polyurethane coatings offer enhanced flexibility and abrasion resistance but generally degrade faster under thermal stress, with optimal performance up to 80degC. PVDF's chemical resistance and excellent weathering properties provide a longer lifespan in harsh environments compared to polyurethane, which is preferred for impact resistance and elasticity.
Application Methods and Flexibility
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings are typically applied using spray, dip, or electrostatic methods, offering excellent chemical resistance and UV stability, making them ideal for harsh outdoor environments. Polyurethane coatings are often applied via brush, roller, or spray, providing superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, suitable for surfaces subject to movement or impact. PVDF exhibits limited elasticity, whereas polyurethane's higher flexibility supports substrates that experience deformation, enhancing coating durability in dynamic applications.
Common Industries and End Uses
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings are widely used in the architectural, chemical processing, and automotive industries due to their exceptional UV resistance, chemical stability, and durability. Polyurethane coatings find common application in footwear, furniture, and industrial machinery sectors, offering excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility. Both materials serve critical roles in protective and decorative coatings, with PVDF preferred for outdoor and harsh chemical environments, while polyurethane is favored for impact resistance and versatility in interior uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings demonstrate superior environmental resistance and long service life, reducing the frequency of recoating and lowering overall material consumption. Polyurethane coatings, while offering excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, may contribute to higher VOC emissions during application and shorter lifespan, increasing environmental burdens. PVDF's recyclability and lower toxicity enhance sustainability profiles compared to polyurethane, making it a preferred choice in eco-conscious industrial and architectural applications.
Cost Considerations and Longevity
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coatings typically incur higher initial costs compared to polyurethane (PU) but offer superior durability and resistance to UV exposure, chemicals, and weathering, reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Polyurethane coatings are more affordable upfront and provide excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but may require more frequent reapplication due to lower UV stability and chemical resistance. Evaluating total lifecycle cost, PVDF's enhanced longevity often results in better return on investment for industrial and architectural applications requiring long-term protection.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyurethane for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com