Biodegradable plastics decompose naturally within months, reducing landfill waste compared to polystyrene, which can persist for hundreds of years and releases toxic chemicals when burned. Biodegradable cups also lower carbon footprints and promote sustainable waste management, unlike polystyrene cups that contribute significantly to environmental pollution.
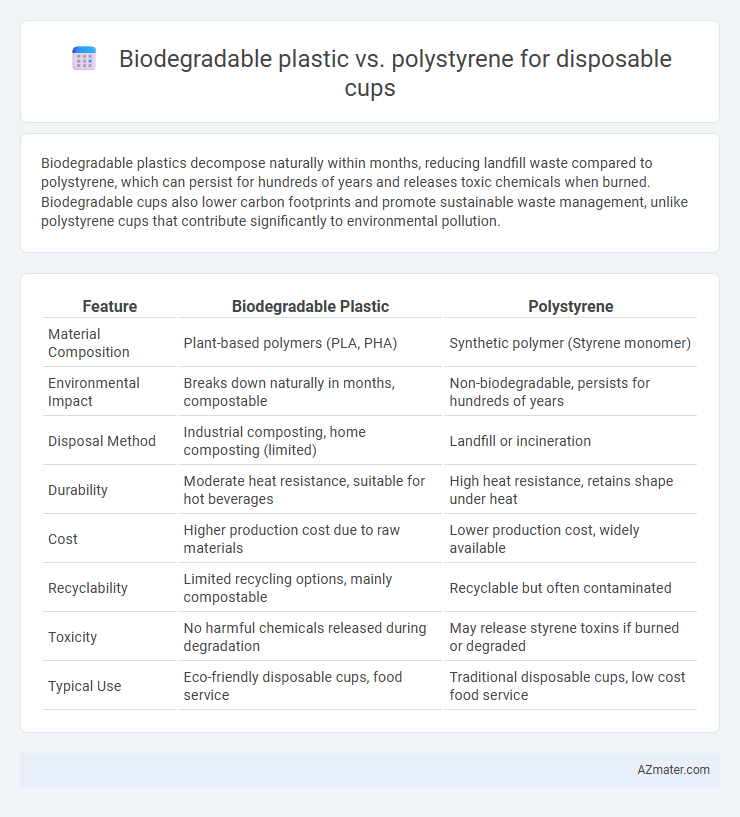
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biodegradable Plastic | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant-based polymers (PLA, PHA) | Synthetic polymer (Styrene monomer) |
| Environmental Impact | Breaks down naturally in months, compostable | Non-biodegradable, persists for hundreds of years |
| Disposal Method | Industrial composting, home composting (limited) | Landfill or incineration |
| Durability | Moderate heat resistance, suitable for hot beverages | High heat resistance, retains shape under heat |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to raw materials | Lower production cost, widely available |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options, mainly compostable | Recyclable but often contaminated |
| Toxicity | No harmful chemicals released during degradation | May release styrene toxins if burned or degraded |
| Typical Use | Eco-friendly disposable cups, food service | Traditional disposable cups, low cost food service |
Introduction to Disposable Cup Materials
Disposable cups are primarily made from materials such as biodegradable plastics and polystyrene, each offering distinct environmental and functional properties. Biodegradable plastics, derived from renewable sources like cornstarch or sugarcane, decompose more rapidly under industrial composting conditions, reducing landfill impact. Polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic, provides excellent insulation and strength but poses significant environmental challenges due to its long degradation time and difficulty in recycling.
What is Biodegradable Plastic?
Biodegradable plastic is made from natural materials such as cornstarch or sugarcane, designed to break down through microbial activity into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass within a specific timeframe, minimizing environmental impact. Unlike traditional polystyrene, which can persist in landfills for hundreds of years, biodegradable plastic cups decompose within months under industrial composting conditions. This capability makes biodegradable plastic an eco-friendly alternative for disposable cups, reducing plastic pollution and supporting sustainable waste management practices.
Overview of Polystyrene in Disposable Cups
Polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic polymer widely used in disposable cups due to its excellent insulation properties, lightweight nature, and low cost. It provides effective thermal resistance, keeping beverages hot or cold while preventing heat transfer to the user's hand. However, polystyrene is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution, with limited recycling options compared to biodegradable alternatives.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable Plastic vs Polystyrene
Biodegradable plastic disposable cups decompose naturally within months, significantly reducing landfill accumulation and microplastic pollution compared to polystyrene, which can persist for centuries and release harmful styrene compounds into soil and water. The production of biodegradable plastics often involves renewable resources, resulting in lower carbon emissions and less toxic waste than the petroleum-based process used for polystyrene. Although both materials impact the environment, biodegradable plastics offer a more sustainable solution by minimizing long-term ecological damage and supporting circular waste management practices.
Decomposition Rates and End-of-Life Scenarios
Biodegradable plastics used for disposable cups typically decompose within 6 months to 2 years under industrial composting conditions, significantly faster than polystyrene, which can persist in the environment for over 500 years. End-of-life scenarios for biodegradables include composting facilities that convert waste into nutrient-rich soil, while polystyrene cups often end up in landfills or incineration, contributing to long-term pollution and toxic emissions. The enhanced decomposition rate of biodegradable plastics reduces environmental impact and landfill volume compared to the slow degradation and limited recycling options of polystyrene.
Production Process and Resource Consumption
Biodegradable plastic disposable cups are produced through fermentation of renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, requiring less energy and emitting fewer greenhouse gases compared to polystyrene cups, which are synthesized from petroleum-based styrene monomers via polymerization processes with high chemical input. The production of polystyrene cups involves extensive use of non-renewable fossil fuels and releases harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. In contrast, biodegradable plastics use renewable biomass, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and offer a lower carbon footprint through more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Consumer Health and Safety Considerations
Biodegradable plastic disposable cups reduce exposure to harmful chemicals like styrene, which is a known neurotoxin present in polystyrene cups. Polystyrene cups can leach toxic substances, especially when containing hot liquids, posing risks such as endocrine disruption and respiratory issues. Choosing biodegradable plastics supports consumer health by minimizing toxic chemical migration and promoting safer drinking containers.
Cost Comparison: Biodegradable Plastic vs Polystyrene Cups
Biodegradable plastic cups generally incur higher initial costs compared to polystyrene cups, driven by raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes. Polystyrene cups remain more cost-effective due to inexpensive production and continuous economies of scale, often priced 20-40% lower than biodegradable alternatives. However, factoring in environmental regulations and potential disposal fees reveals that long-term cost benefits may favor biodegradable plastics despite their upfront premium.
Regulatory Policies and Market Trends
Regulatory policies increasingly favor biodegradable plastics over polystyrene due to stricter environmental standards aimed at reducing plastic pollution and promoting sustainable waste management. Market trends show a rising demand for biodegradable disposable cups driven by consumer preference for eco-friendly products and government incentives supporting biodegradable materials. Polystyrene faces growing restrictions and bans in various regions, prompting manufacturers to shift towards biodegradable alternatives to comply with evolving regulations and capture market growth.
Future Outlook: Sustainable Alternatives for Disposable Cups
Biodegradable plastics offer a promising sustainable alternative to traditional polystyrene in disposable cups, as their decomposition rates reduce environmental impact significantly. Innovations in materials such as polylactic acid (PLA) and cellulose-based bioplastics are driving increased adoption in the foodservice industry. Future outlooks emphasize scalability and cost-efficiency improvements, aiming to replace polystyrene entirely while meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Infographic: Biodegradable plastic vs Polystyrene for Disposable cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com