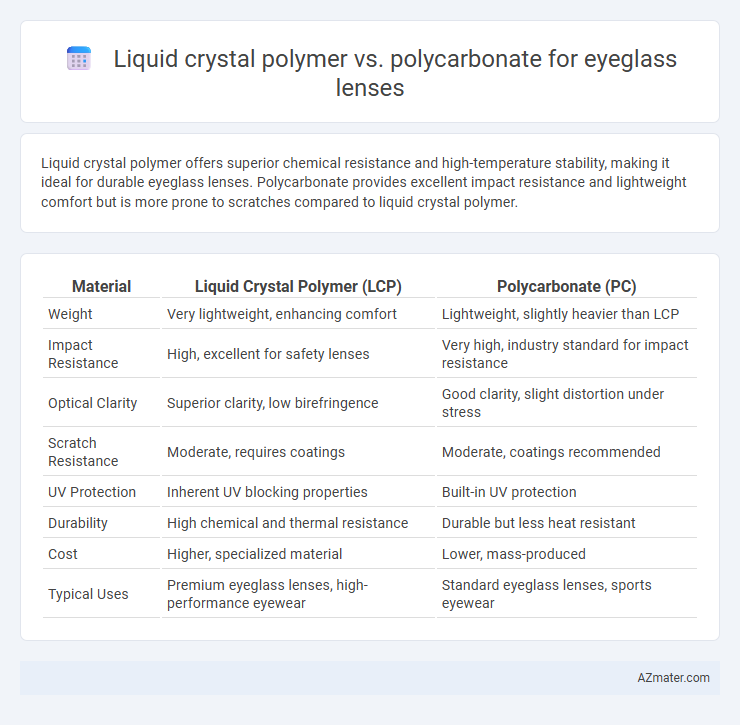
Liquid crystal polymer offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for durable eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate provides excellent impact resistance and lightweight comfort but is more prone to scratches compared to liquid crystal polymer.
Table of Comparison
| Material | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Very lightweight, enhancing comfort | Lightweight, slightly heavier than LCP |
| Impact Resistance | High, excellent for safety lenses | Very high, industry standard for impact resistance |
| Optical Clarity | Superior clarity, low birefringence | Good clarity, slight distortion under stress |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate, requires coatings | Moderate, coatings recommended |
| UV Protection | Inherent UV blocking properties | Built-in UV protection |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal resistance | Durable but less heat resistant |
| Cost | Higher, specialized material | Lower, mass-produced |
| Typical Uses | Premium eyeglass lenses, high-performance eyewear | Standard eyeglass lenses, sports eyewear |
Introduction: Liquid Crystal Polymer vs Polycarbonate Eyeglass Lenses
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) and polycarbonate are both popular materials for eyeglass lenses, each offering unique optical and physical properties. LCP lenses provide superior clarity, high chemical resistance, and excellent dimensional stability, making them ideal for precision eyewear. Polycarbonate lenses deliver strong impact resistance and lightweight comfort, favored for durability and safety in active lifestyles.
Material Composition and Properties
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass lenses are composed of highly ordered polymer chains that provide exceptional strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Polycarbonate lenses consist of a carbonate polymer with excellent impact resistance and lightweight properties but lower scratch resistance and thermal stability compared to LCP. The anisotropic molecular structure of LCP offers superior optical clarity and minimal birefringence, making it ideal for precision eyewear, while polycarbonate lenses are valued for affordability and durability in everyday use.
Optical Clarity and Visual Performance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) lenses offer superior optical clarity due to their high refractive index and minimal light distortion, enhancing visual sharpness compared to polycarbonate lenses. Polycarbonate lenses provide impact resistance but often have lower optical performance, with more chromatic aberration and slight blurriness in peripheral vision. For eyewear needing exceptional visual performance, LCP lenses outperform polycarbonate in delivering crisper, clearer vision.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) lenses exhibit superior durability and impact resistance compared to polycarbonate lenses due to their high tensile strength and chemical stability. Polycarbonate lenses, while well-known for impact resistance, often suffer from surface scratches and lower structural rigidity than LCP lenses. This makes LCP an increasingly preferred material for premium eyeglass lenses where long-lasting durability and enhanced impact protection are critical.
Weight and Comfort for Daily Wear
Liquid crystal polymer lenses are significantly lighter than polycarbonate lenses, reducing pressure on the nose and temples for enhanced all-day comfort. The high strength-to-weight ratio of liquid crystal polymer allows for thinner, more durable lenses without compromising optical clarity. Polycarbonate, while impact-resistant, tends to be heavier and may cause discomfort during prolonged wear compared to the ultra-light properties of liquid crystal polymer.
Scratch and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer eyeglass lenses exhibit superior scratch resistance compared to polycarbonate due to their highly organized molecular structure, which creates a harder, more durable surface. Chemical resistance is also enhanced in liquid crystal polymers, enabling better performance against solvents, oils, and cleaning agents that commonly degrade polycarbonate lenses. This makes liquid crystal polymer lenses a more resilient and long-lasting option for eyeglass wearers seeking enhanced durability and maintenance ease.
UV Protection Capabilities
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) lenses offer superior UV protection with higher absorption rates for harmful UV-A and UV-B rays compared to polycarbonate lenses. Polycarbonate lenses inherently block about 99% of UV rays but may require additional coatings to enhance full spectrum UV defense. The molecular structure of LCP allows for better UV filtering without compromising lens clarity, making it an optimal choice for UV-sensitive eyewear.
Cost and Affordability Factors
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) lenses typically cost more than polycarbonate lenses due to their advanced material properties and manufacturing complexity. Polycarbonate lenses offer a more affordable option with reasonable durability and impact resistance, making them popular for budget-conscious consumers. The lower production cost and wider availability of polycarbonate contribute to its cost-effectiveness compared to the premium-priced LCP lenses.
Suitability for Prescription and Specialty Lenses
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) lenses offer exceptional dimensional stability and high impact resistance, making them highly suitable for specialty lenses requiring thin, lightweight designs with precise optical performance. Polycarbonate lenses are widely preferred for prescription eyewear due to their excellent impact resistance and affordability, though they may exhibit slight chromatic aberration compared to LCP lenses. For prescription lenses demanding superior optical clarity and durability, especially in high-prescription or specialty applications, LCP provides a more advanced option despite higher cost.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Eyeglass Lens Material
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance, exceptional durability, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate lenses provide excellent impact resistance and affordability, with good optical clarity suitable for everyday use. Considering factors such as durability, weight, optical quality, and budget helps determine that LCP suits premium lenses demanding longevity and resilience, while polycarbonate remains a practical choice for cost-effective, impact-resistant eyewear.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com