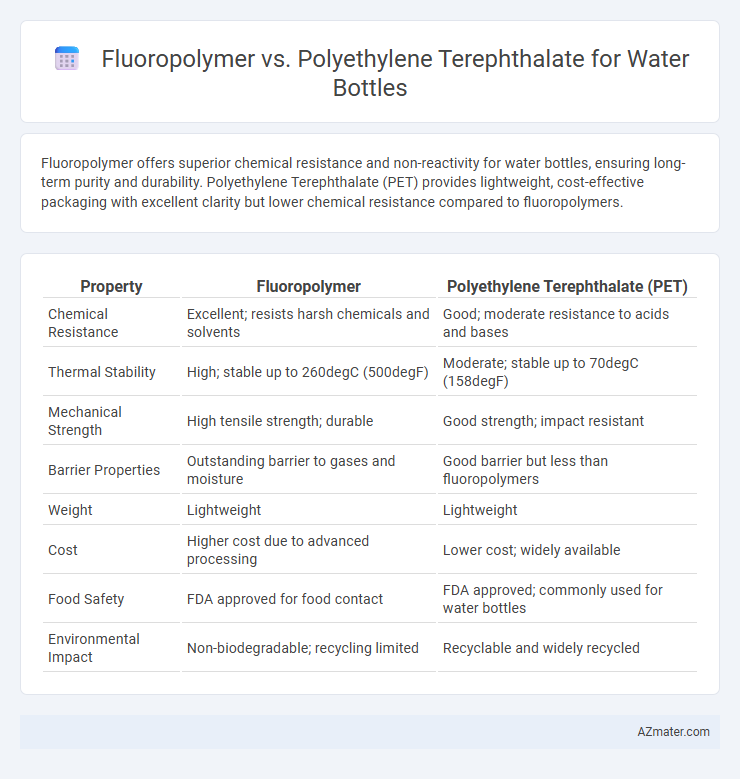
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance and non-reactivity for water bottles, ensuring long-term purity and durability. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) provides lightweight, cost-effective packaging with excellent clarity but lower chemical resistance compared to fluoropolymers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; resists harsh chemicals and solvents | Good; moderate resistance to acids and bases |
| Thermal Stability | High; stable up to 260degC (500degF) | Moderate; stable up to 70degC (158degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength; durable | Good strength; impact resistant |
| Barrier Properties | Outstanding barrier to gases and moisture | Good barrier but less than fluoropolymers |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Lower cost; widely available |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved; commonly used for water bottles |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; recycling limited | Recyclable and widely recycled |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Fluoropolymers are high-performance polymers characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds that provide exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and excellent temperature stability, making them suitable for demanding applications like water bottle liners and coatings. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, lightweight nature, and excellent clarity, commonly employed in water bottle manufacturing due to its affordability and recyclability. The fundamental differences between fluoropolymers and PET influence their mechanical properties, chemical inertness, and suitability in various water bottle designs.
Chemical Structure and Material Composition
Fluoropolymers, composed of carbon-fluorine bonds, exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and low surface energy, making them highly hydrophobic and inert compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), which is a polyester consisting of repeating ethylene terephthalate units derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. The strong C-F bonds in fluoropolymers create a stable and non-reactive surface ideal for protecting against chemical leaching, whereas PET's ester linkages are more susceptible to hydrolysis under extreme pH or temperature conditions. Material composition differences impact durability and safety in water bottles, with fluoropolymers providing superior chemical stability and PET offering lightweight and cost-effective mechanical strength.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Fluoropolymer water bottles exhibit superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, ensuring long-lasting durability under extreme conditions compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). PET bottles, while lightweight and cost-effective, tend to degrade faster when exposed to UV light and repeated physical stress, reducing their overall lifespan. The enhanced molecular structure of fluoropolymers provides extended resistance to cracking, staining, and chemical breakdown, making them a more durable choice for reusable water bottles.
Water Safety and Taste Retention
Fluoropolymer water bottles offer superior chemical resistance, preventing leaching of harmful substances and ensuring water safety compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which can degrade over time and release trace chemicals. Fluoropolymers exhibit excellent non-stick and inert properties, preserving the original taste of water without imparting any plastic aftertaste commonly associated with PET bottles. The enhanced durability and stability of fluoropolymer materials make them ideal for long-term water storage while maintaining purity and freshness.
Resistance to Chemicals and Staining
Fluoropolymer exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals including acids, bases, and solvents, making it highly durable against staining and degradation in water bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), while resistant to many common beverages, is more susceptible to staining and chemical erosion over time, especially from acidic or oily substances. The chemical inertness of fluoropolymers ensures prolonged clarity and hygiene, whereas PET may require more frequent replacement due to discoloration and chemical wear.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Fluoropolymers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and durability but pose significant environmental challenges due to their persistence and difficulty in recycling, leading to long-term pollution concerns. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) stands out for its high recyclability, widespread collection infrastructure, and lower ecological footprint, making it a more sustainable choice for water bottles. While PET contributes less to microplastic release and can be efficiently repurposed into new containers, fluoropolymers often require specialized disposal methods due to their resistance to degradation.
Weight, Portability, and Design Flexibility
Fluoropolymer water bottles offer superior weight reduction and enhanced portability due to their lightweight molecular structure, making them ideal for active lifestyles and travel. Their exceptional chemical resistance allows for sleek, durable designs with greater flexibility in shapes and colors compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which tends to be heavier and less adaptable in design. PET bottles, while more rigid and economical, often sacrifice ergonomic design options and portability benefits inherent to fluoropolymers.
Cost Analysis: Production and Consumer Pricing
Fluoropolymer water bottles typically incur higher production costs due to complex manufacturing processes and expensive raw materials, resulting in a consumer price premium compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles. PET, favored for its low-cost production and recyclability, offers a cost-effective option for mass-market water bottles with significantly lower retail prices. The durability and chemical resistance of fluoropolymers justify their elevated costs in niche markets, while PET dominates mainstream segments due to affordability and scalability.
Common Applications in Water Bottles
Fluoropolymer water bottles are favored for their exceptional chemical resistance, non-stick surface, and durability, making them ideal for acidic or reactive beverage storage. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is widely used in disposable and recyclable water bottles due to its clarity, lightweight nature, and affordability, suitable for mass production and cold liquids. While fluoropolymer bottles excel in specialized applications requiring high performance, PET bottles dominate in everyday hydration solutions for consumption convenience.
Choosing the Best Material for Water Bottles: Key Considerations
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for water bottles exposed to harsh environments or acidic beverages, while Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) provides lightweight, clear, and cost-effective options with excellent oxygen barrier properties suitable for everyday use. Choosing the best material depends on factors such as temperature stability, impact resistance, and environmental footprint, with PET being more recyclable and fluoropolymers demonstrating enhanced longevity but higher production costs. Evaluate usage scenarios, including temperature fluctuations, potential chemical exposure, and sustainability goals, to determine the optimal material for water bottle applications.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyethylene Terephthalate for Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com