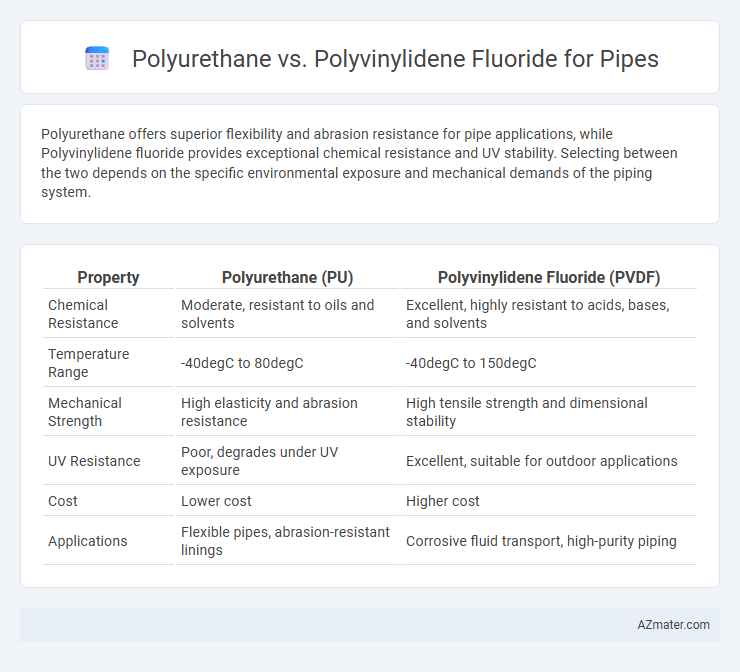
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance for pipe applications, while Polyvinylidene fluoride provides exceptional chemical resistance and UV stability. Selecting between the two depends on the specific environmental exposure and mechanical demands of the piping system.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, resistant to oils and solvents | Excellent, highly resistant to acids, bases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High elasticity and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and dimensional stability |
| UV Resistance | Poor, degrades under UV exposure | Excellent, suitable for outdoor applications |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Flexible pipes, abrasion-resistant linings | Corrosive fluid transport, high-purity piping |
Overview of Polyurethane and Polyvinylidene Fluoride
Polyurethane offers excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and toughness, making it ideal for dynamic or high-wear pipe applications in industries like automotive and construction. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and UV resistance, which is crucial for piping systems in aggressive chemical processing and outdoor environments. Both materials serve distinct roles based on environmental exposure and mechanical demands, influencing their selection for specialized pipeline applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyurethane (PU) pipes consist of repeating urethane linkages formed from polyols and diisocyanates, offering a flexible and elastomeric molecular structure ideal for abrasion resistance and elasticity. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes are composed of semi-crystalline fluoropolymer chains with strong carbon-fluorine bonds that provide exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability. The distinct chemical compositions result in PU pipes excelling in mechanical flexibility while PVDF pipes exhibit superior resistance to aggressive chemicals and UV degradation.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to polyurethane (PU) pipes, making them ideal for high-pressure applications and environments requiring exceptional impact resistance. PVDF offers higher tensile strength, greater abrasion resistance, and enhanced stiffness, resulting in longer service life under mechanical stress. Polyurethane pipes provide flexibility and moderate mechanical durability but typically fall short of PVDF's robustness in demanding industrial settings.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyurethane pipes exhibit excellent abrasion resistance and maintain flexibility under varying temperatures, offering a lifespan of up to 10-15 years in demanding environments. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes demonstrate superior chemical resistance and UV stability, often lasting 20-30 years with minimal degradation in corrosive or outdoor conditions. PVDF's enhanced durability in aggressive chemical settings contrasts with polyurethane's robustness against mechanical wear, making PVDF preferred for long-term chemical applications.
Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyurethane, especially against strong acids, bases, and organic solvents. Polyurethane shows excellent abrasion resistance but is more prone to degradation when exposed to harsh chemicals and solvents over time. PVDF's molecular structure offers enhanced durability and stability in aggressive chemical environments, making it ideal for industrial piping applications requiring long-term chemical resistance.
Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior temperature and pressure tolerance compared to polyurethane, withstanding continuous temperatures up to 150degC and pressure ratings exceeding 5000 psi. Polyurethane typically operates effectively within a temperature range of -40degC to 80degC and pressure limits around 3000 psi. The chemical stability and high melting point of PVDF make it preferred for applications requiring harsh environmental resistance and high mechanical stress.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Polyurethane pipes offer superior flexibility and ease of installation, requiring minimal jointing and allowing for quick modifications or repairs in complex piping systems. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes demand more precise fittings and specialized tools due to their rigidity and chemical resistance, which can extend installation time and complexity. Maintenance for polyurethane involves regular inspections for abrasion and UV damage, while PVDF pipes require less frequent attention due to their outstanding chemical inertness and resistance to environmental degradation.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Polyurethane pipes generally offer lower upfront costs compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes, making them attractive for budget-sensitive projects. PVDF pipes, while more expensive initially, provide superior chemical resistance and longer service life, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Careful cost analysis should weigh the initial investment against lifecycle savings to determine the most economical choice for specific industrial applications.
Typical Applications in Piping Systems
Polyurethane pipes are commonly utilized in industries requiring high abrasion resistance and flexibility, such as pneumatic conveying systems and slurry transport, due to their impact resistance and elasticity. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes excel in chemical processing and pharmaceutical applications, offering exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low permeability to corrosive fluids. Selecting between polyurethane and PVDF pipes depends on operational demands, with polyurethane suited for mechanical stress environments and PVDF preferred for aggressive chemical and high-purity fluid handling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane pipes offer advantages in biodegradability and lower toxicity during production compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which is derived from fluorinated polymers with persistent environmental pollutants. PVDF excels in chemical resistance and durability, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste but poses challenges in recycling and emits harmful fluorinated compounds if incinerated improperly. Choosing polyurethane supports sustainability through better end-of-life degradation, while PVDF prioritizes long-term durability with trade-offs in environmental persistence and recyclability.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com