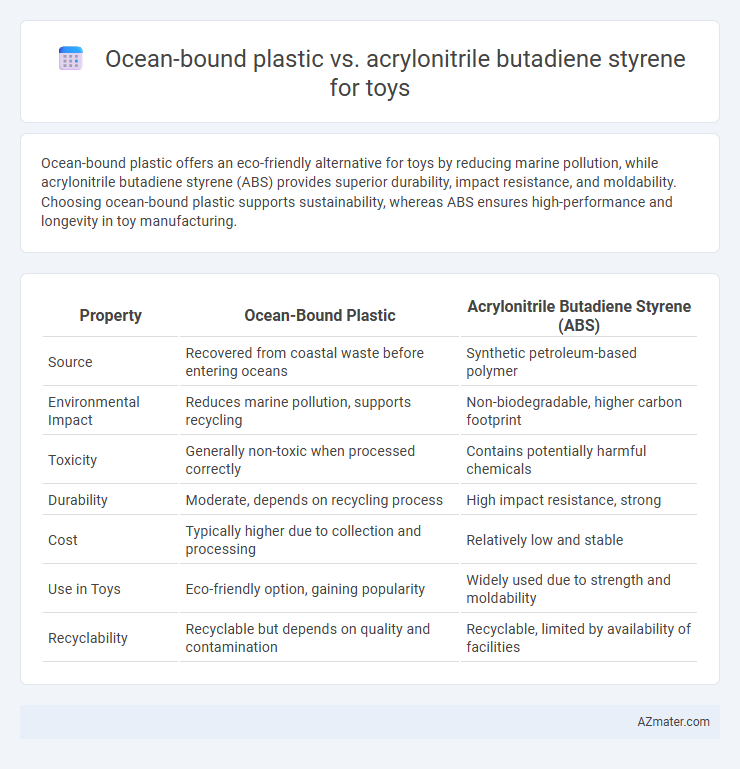
Ocean-bound plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative for toys by reducing marine pollution, while acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior durability, impact resistance, and moldability. Choosing ocean-bound plastic supports sustainability, whereas ABS ensures high-performance and longevity in toy manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ocean-Bound Plastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered from coastal waste before entering oceans | Synthetic petroleum-based polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces marine pollution, supports recycling | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Toxicity | Generally non-toxic when processed correctly | Contains potentially harmful chemicals |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on recycling process | High impact resistance, strong |
| Cost | Typically higher due to collection and processing | Relatively low and stable |
| Use in Toys | Eco-friendly option, gaining popularity | Widely used due to strength and moldability |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but depends on quality and contamination | Recyclable, limited by availability of facilities |
Introduction: The Toy Industry’s Material Dilemma
The toy industry faces a critical material dilemma between using ocean-bound plastic and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Ocean-bound plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative by repurposing waste collected near coastal areas, reducing marine pollution and promoting sustainability. In contrast, ABS is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely favored for its strength and versatility but poses environmental concerns due to its petroleum-based origin and limited recyclability.
Understanding Ocean-Bound Plastic: Origins and Impacts
Ocean-bound plastic originates from waste materials collected within 50 kilometers of coastlines, posing significant environmental threats by entering marine ecosystems and harming aquatic life. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), a durable and recyclable thermoplastic commonly used in toys for its strength and impact resistance, ocean-bound plastic represents a sustainable alternative by repurposing waste and reducing ocean pollution. Utilizing ocean-bound plastic in toy manufacturing helps mitigate plastic waste accumulation and supports circular economy initiatives without compromising product quality and safety.
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a high-impact thermoplastic polymer commonly used in toy manufacturing due to its durability, strength, and ease of molding into complex shapes. It offers superior resistance to physical impacts and chemical corrosion compared to ocean-bound plastics derived from recycled marine debris, which are more environmentally friendly but may lack the structural integrity required for certain toy applications. ABS's consistent quality and safety standards make it a preferred material for producing high-performance toys that meet regulatory requirements.
Mechanical Properties: Comparing Durability and Strength
Ocean-bound plastic exhibits moderate tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for eco-friendly toys with reasonable durability. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) outperforms ocean-bound plastic in mechanical properties, offering higher impact resistance, superior toughness, and better dimensional stability under stress. ABS's enhanced durability and strength make it ideal for toys requiring rigorous mechanical performance and long-term use.
Environmental Footprint: Production and End-of-Life Analysis
Ocean-bound plastic, derived from waste collected near waterways, significantly reduces environmental footprint by diverting debris from oceans and lowering reliance on virgin fossil resources compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). Production of ABS involves energy-intensive petrochemical processes with higher greenhouse gas emissions, whereas ocean-bound plastic utilizes recycled materials, minimizing carbon footprint and raw material extraction. At end-of-life, ocean-bound plastic toys offer improved circularity through recycling or biodegradation potential, while ABS presents challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and limited recyclability, contributing to persistent plastic pollution.
Toy Safety Standards: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs ABS
Ocean-bound plastic and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are both materials used in toy manufacturing, but they differ significantly in terms of toy safety standards. ABS is a well-established, non-toxic thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and compliance with global toy safety regulations such as ASTM F963 and EN71. Ocean-bound plastic, while environmentally beneficial for reducing marine pollution, may require rigorous testing to ensure it meets safety standards related to toxicity, durability, and chemical leaching before being widely accepted for use in toys.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility in Toy Manufacturing
Ocean-bound plastic offers eco-friendly aesthetics with natural textures and color variations that enhance toy uniqueness, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior design flexibility due to its excellent moldability, enabling precise detailing and vibrant, consistent colors in toy production. The choice between ocean-bound plastic and ABS impacts both the visual appeal and customization options, driving innovation in sustainable and high-quality toy design.
Supply Chain and Economic Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable supply chain advantage by sourcing waste material from coastal areas before it enters the ocean, reducing environmental impact and often lowering raw material costs due to recycled content incentives. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) relies on petrochemical supply chains that are subject to price volatility and geopolitical risks, leading to fluctuating production costs and potential supply disruptions. Economically, ocean-bound plastic can improve brand value and meet rising consumer demand for eco-friendly toys, while ABS provides consistent material performance but faces increasing regulatory pressures and potential cost increases linked to fossil fuel dependency.
Brand Perceptions and Consumer Trends
Ocean-bound plastic toys are increasingly favored by eco-conscious consumers and brands aiming to enhance sustainability credentials, reflecting a growing trend toward environmentally friendly products. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), valued for its durability and versatile molding properties, remains popular in traditional toy manufacturing but faces criticism due to its reliance on fossil fuels and limited recyclability. Consumer perceptions are shifting, with a rising demand for transparent sourcing and reduced environmental impact, prompting brands to innovate using ocean-bound plastic to align with green marketing strategies and capture the eco-aware market segment.
Future Prospects: Toward Sustainable Toy Materials
Ocean-bound plastic offers a promising future as a sustainable toy material by directly addressing marine pollution and reducing reliance on virgin plastics, with increasing adoption in eco-conscious toy manufacturing. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), known for its durability and safety, faces sustainability challenges due to its petrochemical origin and lower recyclability. Innovations in bio-based ABS and improved recycling technologies are essential to enhance its environmental profile and compete with ocean-bound plastics in sustainable toy production.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com