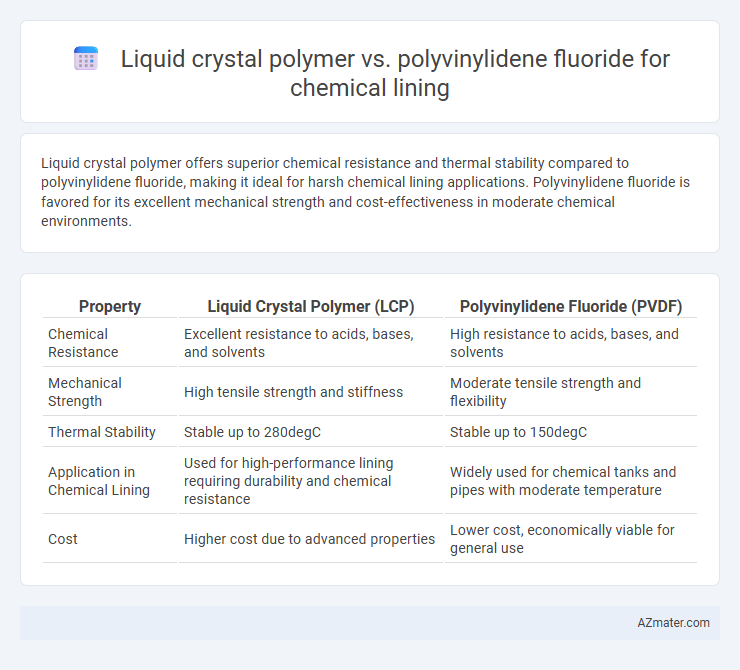
Liquid crystal polymer offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyvinylidene fluoride, making it ideal for harsh chemical lining applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride is favored for its excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness in moderate chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | High resistance to acids, bases, and solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate tensile strength and flexibility |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 280degC | Stable up to 150degC |
| Application in Chemical Lining | Used for high-performance lining requiring durability and chemical resistance | Widely used for chemical tanks and pipes with moderate temperature |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, economically viable for general use |
Introduction to Chemical Lining Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are prominent materials used for chemical lining due to their exceptional chemical resistance and mechanical properties. LCP offers superior thermal stability and dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments, whereas PVDF provides excellent resistance to acids, bases, and organic solvents with strong UV stability. Selection between LCP and PVDF depends on specific chemical exposure, temperature requirements, and mechanical stress considerations in industrial applications.
Overview of Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability, making it ideal for chemical lining applications. Unlike Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which offers good chemical resistance and flexibility, LCP provides superior dimensional stability and resistance to aggressive chemicals, including strong acids and solvents. LCP's unique molecular structure allows for precise, durable linings that excel in harsh chemical environments where long-term corrosion protection is critical.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer widely used in chemical lining due to its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability up to 150degC. PVDF offers superior resistance to acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments found in industrial applications. Compared to liquid crystal polymers, PVDF provides better flexibility and easier fabrication, while maintaining long-term durability in corrosive conditions.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: LCP vs PVDF
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior chemical resistance to strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments. PVDF offers excellent resistance to a broad range of chemicals including chlorine, halogens, and oxidative agents but may degrade under high-temperature exposure to strong bases, where LCP maintains stability. The choice between LCP and PVDF for chemical lining applications depends on specific exposure conditions, with LCP generally preferred for extreme chemical and thermal resistance requirements.
Mechanical Properties and Durability Analysis
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), including higher tensile strength, rigidity, and resistance to creep, making it ideal for demanding chemical lining applications. LCP also demonstrates enhanced durability against thermal degradation and chemical attack, providing longer service life in aggressive environments where PVDF may suffer from embrittlement or material fatigue. The crystalline structure of LCP contributes to its exceptional dimensional stability and wear resistance, outperforming PVDF in maintaining integrity under mechanical stress and corrosive conditions.
Temperature and Environmental Stability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior temperature resistance withstanding continuous use up to 260degC, whereas polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) typically handles temperatures up to 150degC. LCP offers exceptional chemical and UV resistance, ensuring long-term environmental stability in harsh industrial conditions, while PVDF provides good chemical resistance but may degrade under prolonged UV exposure. The high melting point and robust molecular structure of LCP make it ideal for high-temperature chemical linings requiring durability against thermal and environmental stress.
Ease of Processing and Installation
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior ease of processing for chemical lining due to its excellent thermal stability and fluidity, enabling precise molding and reduced cycle times. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is more flexible during installation, providing better adhesion and resistance to chemical permeation but requires careful handling to avoid stress-induced defects. Both materials balance ease of processing and installation differently, with LCP favored for high-precision applications and PVDF preferred for versatility and toughness in chemical environments.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), but its higher raw material and processing costs can significantly impact project budgets. PVDF provides a more cost-effective solution with adequate chemical resistance for many applications, leading to lower initial investment and maintenance expenses. Choosing between LCP and PVDF involves balancing long-term economic benefits against upfront cost considerations based on specific chemical environments and performance requirements.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for chemical lining applications in aggressive media within the semiconductor, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing industries. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides excellent corrosion resistance, UV stability, and ease of fabrication, widely used in piping, tanks, and linings for water treatment, chemical storage, and food processing sectors. Comparing both, LCP suits high-temperature and high-performance environments, while PVDF is preferred for cost-effective, versatile chemical protection in moderate conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Chemical Lining
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments and high-temperature applications in chemical lining. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides excellent resistance to solvents, acids, and bases, along with superior UV stability and flexibility, suitable for lining tanks and pipes exposed to varying outdoor conditions. Choosing the right material depends on specific chemical exposure, temperature range, mechanical stress, and environmental factors, with LCP favored for high-performance, demanding conditions and PVDF preferred for versatile, cost-effective applications.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Chemical Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com