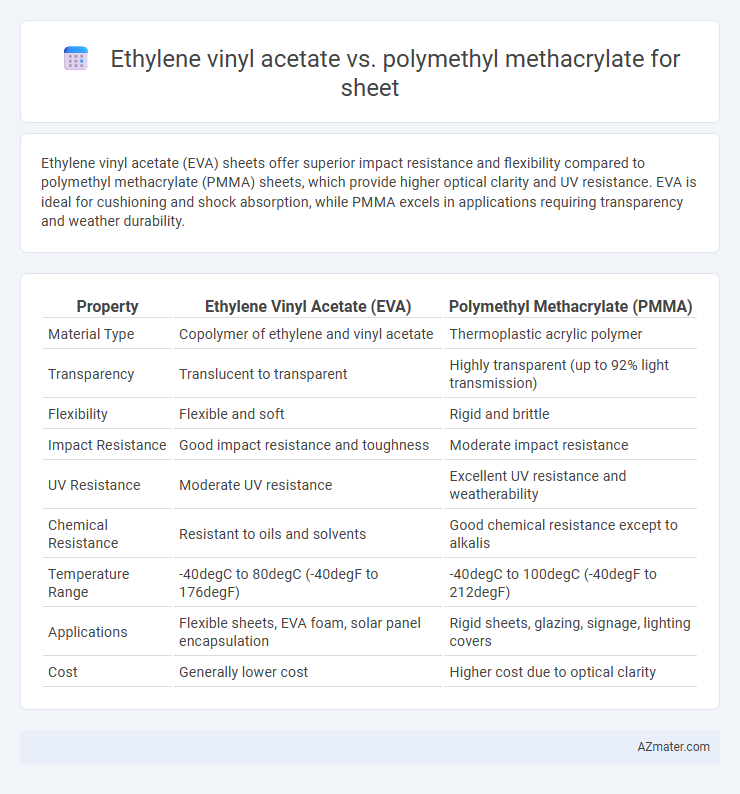
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets offer superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets, which provide higher optical clarity and UV resistance. EVA is ideal for cushioning and shock absorption, while PMMA excels in applications requiring transparency and weather durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Thermoplastic acrylic polymer |
| Transparency | Translucent to transparent | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Flexibility | Flexible and soft | Rigid and brittle |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance and toughness | Moderate impact resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance | Excellent UV resistance and weatherability |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Good chemical resistance except to alkalis |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC (-40degF to 176degF) | -40degC to 100degC (-40degF to 212degF) |
| Applications | Flexible sheets, EVA foam, solar panel encapsulation | Rigid sheets, glazing, signage, lighting covers |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to optical clarity |
Introduction to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) and Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) Sheets
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets are characterized by their excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and transparency, making them ideal for applications requiring cushioning and durability. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets provide superior optical clarity, UV resistance, and rigidity, commonly used in signage, skylights, and protective barriers. Both EVA and PMMA offer unique physical and chemical properties tailored to specific industrial and commercial uses.
Chemical Structure and Material Composition
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) consists of a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, featuring flexible chains with polar acetate groups that enhance impact resistance and elasticity. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a rigid thermoplastic composed of polymerized methyl methacrylate monomers, characterized by a glassy structure providing high clarity and hardness. The chemical composition of EVA leads to superior flexibility and UV resistance, while PMMA's acrylic backbone imparts toughness and optical transparency ideal for sheet applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets exhibit superior flexibility, higher elongation at break, and better impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets, which are stiffer with higher tensile strength and greater hardness. PMMA offers excellent rigidity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and optical clarity, whereas EVA's lower modulus and enhanced toughness suit cushioning and vibration-damping uses. The mechanical properties of EVA sheets include a tensile strength typically around 8-25 MPa and elongation over 400%, while PMMA sheets exhibit tensile strengths of 70-80 MPa with elongation limited to about 2-5%.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets offer excellent optical clarity with light transmission rates typically ranging from 85% to 90%, making them suitable for applications requiring moderate transparency and flexibility. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic, provides superior optical clarity with light transmission values up to 92%-93%, often surpassing glass in clarity and allowing for high-definition visibility. While EVA balances durability and clarity, PMMA excels in light transmission and scratch resistance, making it ideal for precision optical uses and glazing.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets exhibit superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets, making EVA ideal for applications requiring high shock absorption and elasticity. PMMA, though more rigid and less impact-resistant, offers excellent clarity and hardness, suited for protective covers where stiffness is prioritized over flexibility. The choice between EVA and PMMA sheets depends on the balance needed between flexibility and resilience versus transparency and structural rigidity.
Processing and Fabrication Methods
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets are processed primarily through extrusion and compression molding, offering flexibility and ease of thermoforming, which makes them suitable for applications requiring impact resistance and elasticity. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets are typically fabricated using injection molding or thermoforming, providing a rigid, glass-like finish with superior optical clarity but requiring careful temperature control to prevent cracking during processing. The fabrication of EVA allows for easier heat sealing and lamination compared to PMMA, which often demands precise machining or laser cutting due to its brittleness and hardness.
Weatherability and UV Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets exhibit excellent flexibility and impact resistance but have moderate weatherability and UV resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA sheets offer superior UV resistance, exceptional clarity, and long-lasting weatherability, making them ideal for outdoor applications requiring prolonged exposure to sunlight. EVA is more suitable for applications where flexibility and shock absorption are prioritized, while PMMA excels in environments demanding robust durability against UV degradation.
Typical Applications in Industry
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets are widely used in packaging, footwear, and solar panel encapsulation due to their flexibility, impact resistance, and excellent clarity. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets, known for superior optical transparency and weather resistance, are preferred in automotive lighting, signage, and architectural glazing. Both materials serve distinct industrial purposes based on performance requirements in clarity, durability, and environmental exposure.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets generally offer greater cost-effectiveness compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making EVA a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. PMMA sheets, while more expensive, provide superior optical clarity and durability, justifying their higher price in industries where performance outweighs cost. Economic considerations often balance EVA's affordability and flexibility against PMMA's higher initial investment but longer lifespan and better resistance to environmental factors.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) sheets exhibit superior sustainability due to their lower energy requirements during production and higher recyclability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which relies heavily on fossil fuel-based raw materials and emits more volatile organic compounds (VOCs). EVA's biodegradability and non-toxic byproducts enhance its environmental profile, whereas PMMA's resistance to degradation contributes to long-term environmental persistence and microplastic pollution. Choosing EVA reduces carbon footprint and supports circular economy principles, making it a more environmentally responsible option for sheet applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com