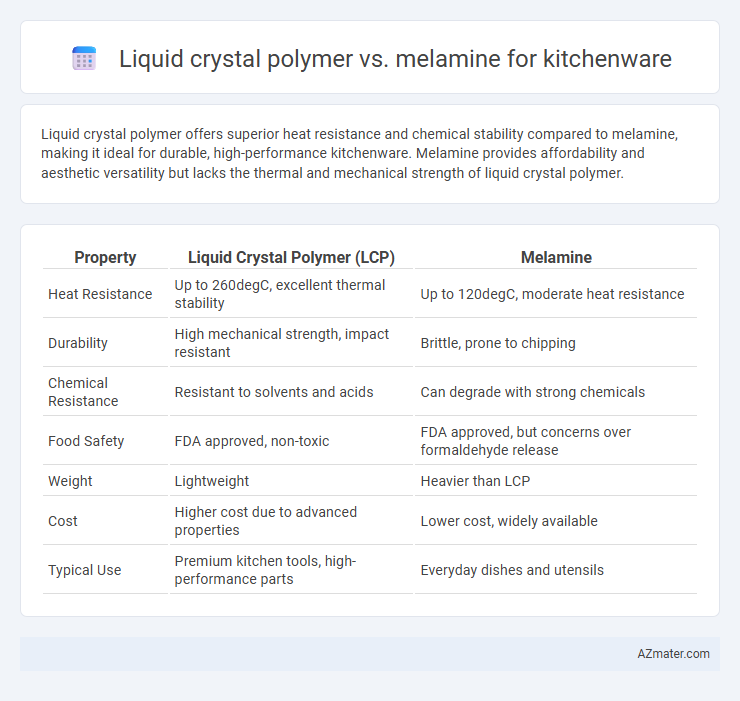
Liquid crystal polymer offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to melamine, making it ideal for durable, high-performance kitchenware. Melamine provides affordability and aesthetic versatility but lacks the thermal and mechanical strength of liquid crystal polymer.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Melamine |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 260degC, excellent thermal stability | Up to 120degC, moderate heat resistance |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, impact resistant | Brittle, prone to chipping |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and acids | Can degrade with strong chemicals |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, non-toxic | FDA approved, but concerns over formaldehyde release |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than LCP |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Use | Premium kitchen tools, high-performance parts | Everyday dishes and utensils |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer and Melamine
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for durable kitchenware components. Melamine, a thermosetting plastic, is widely used in kitchenware for its lightweight nature, affordability, and resistance to heat and stains, though it is less durable under high-temperature conditions compared to LCP. Both materials offer distinct advantages in kitchenware manufacturing, with LCP providing superior durability and melamine offering cost-effective, aesthetically versatile options.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits a highly ordered molecular structure with rigid rod-like polymer chains that align to form liquid crystalline phases, enhancing its mechanical strength and thermal stability. Melamine, composed primarily of melamine-formaldehyde resin, features a cross-linked three-dimensional network structure that provides excellent hardness and resistance to heat and chemicals but lacks the molecular alignment seen in LCPs. The distinct chemical compositions--aromatic polyamide chains in LCPs versus nitrogen-rich melamine-formaldehyde polymers--directly influence their performance, with LCPs offering superior durability and stability in extreme kitchenware applications compared to melamine.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal resistance withstanding continuous temperatures up to 260degC, making it highly suitable for high-heat kitchenware applications. Melamine, while durable for everyday use, has a lower heat tolerance, typically up to 100degC, and may degrade or release harmful substances when exposed to higher temperatures. The exceptional heat tolerance of LCP ensures better performance and safety in cooking utensils and tools exposed to extreme heat compared to melamine products.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to melamine, making it highly resistant to wear, impact, and deformation under high stress. LCP's molecular structure provides exceptional heat resistance and chemical stability, allowing kitchenware to maintain integrity through frequent use and exposure to hot liquids. In contrast, melamine is more prone to cracking and chipping over time, especially with exposure to high heat and heavy mechanical stress.
Safety and Food-Contact Suitability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and low moisture absorption, making it highly suitable for food-contact kitchenware that demands durability and safety. Melamine, while popular for its aesthetic appeal and affordability, can release formaldehyde-based compounds when exposed to high temperatures, raising concerns about its food-contact safety, especially with hot foods or microwaving. LCP's inert properties and compliance with stringent FDA and EU food safety regulations position it as a safer alternative for long-term kitchenware use.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior design flexibility for kitchenware due to its excellent moldability and ability to maintain precise shapes, enabling intricate and modern designs. Melamine provides a wide range of vibrant colors and glossy finishes that enhance aesthetic appeal but is limited in complex geometries compared to LCP. While LCP supports innovative, sleek kitchenware designs with robust mechanical properties, melamine remains popular for its classic look and cost-effective color variety.
Dishwasher and Microwave Compatibility
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) kitchenware offers excellent dishwasher and microwave compatibility due to its high thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation, making it ideal for repeated washing and microwave heating. Melamine kitchenware, while durable for everyday use, is generally not microwave-safe as it can warp or release harmful substances when heated, and it may degrade faster under dishwasher conditions. Choosing LCP ensures greater longevity and safety for kitchenware frequently used in dishwashers and microwaves.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) used in kitchenware offer high durability and heat resistance but pose recycling challenges due to complex chemical structures and limited industrial recycling facilities. Melamine kitchenware, while popular for its affordability and design versatility, is less environmentally friendly because it is made from formaldehyde-based resins that are difficult to recycle and may release toxins when disposed of improperly. Choosing kitchenware materials with higher recyclability rates and lower environmental footprints supports sustainable consumption and waste management efforts.
Cost Considerations for Kitchenware Application
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) kitchenware typically comes with a higher upfront cost compared to melamine due to its advanced material properties and superior durability. Melamine offers a budget-friendly option ideal for everyday use, but it may require more frequent replacement due to susceptibility to chipping and heat damage. Cost considerations should weigh the long-term savings from LCP's longevity against melamine's initial affordability in kitchenware applications.
Conclusion: Which Material is Best for Kitchenware?
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance kitchenware that requires long-term use and exposure to heat and harsh cleaning agents. Melamine is valued for its affordability, vibrant design options, and lightweight nature but lacks the thermal resilience and longevity of LCP, often leading to wear and potential health concerns over time. For kitchenware demanding durability and safety under extreme conditions, liquid crystal polymer emerges as the better material choice.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Melamine for Kitchenware
 azmater.com
azmater.com