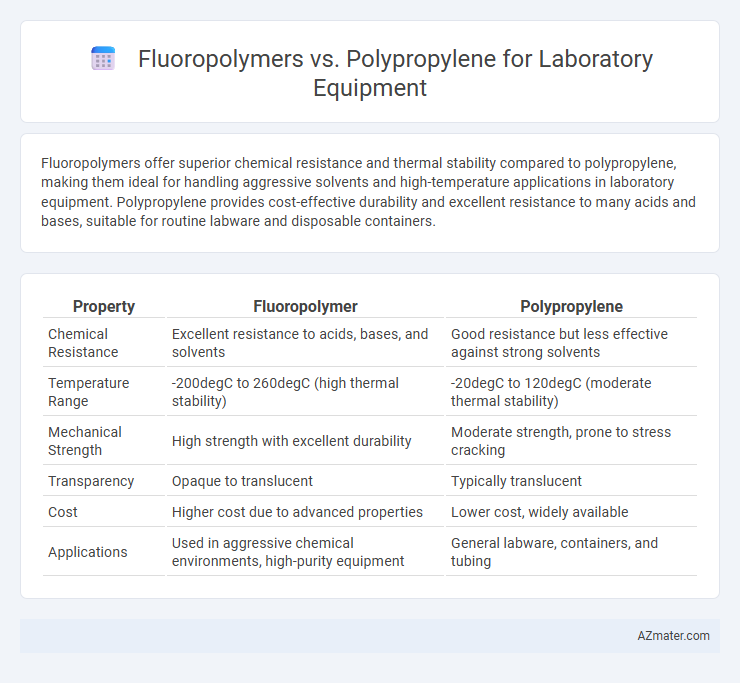
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for handling aggressive solvents and high-temperature applications in laboratory equipment. Polypropylene provides cost-effective durability and excellent resistance to many acids and bases, suitable for routine labware and disposable containers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance but less effective against strong solvents |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC (high thermal stability) | -20degC to 120degC (moderate thermal stability) |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength with excellent durability | Moderate strength, prone to stress cracking |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Typically translucent |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Used in aggressive chemical environments, high-purity equipment | General labware, containers, and tubing |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polypropylene in Laboratory Equipment
Fluoropolymers, known for exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, offer unparalleled performance in laboratory equipment exposed to aggressive solvents and corrosive environments. Polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic, provides cost-effective durability, excellent chemical resistance to many acids and bases, and is widely used for general-purpose lab containers and tubing. Choosing between fluoropolymer and polypropylene depends on specific laboratory requirements such as temperature tolerance, chemical compatibility, and budget constraints.
Chemical Resistance: Fluoropolymer vs Polypropylene
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, withstanding aggressive acids, bases, and solvents without degradation or loss of integrity. Polypropylene offers good resistance to many chemicals but can be compromised by strong oxidizers and organic solvents, limiting its use in highly corrosive environments. This makes fluoropolymers the preferred choice for laboratory equipment requiring durability against a broad spectrum of harsh chemicals.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Tolerance
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior thermal stability and can tolerate continuous temperatures up to 260degC, making them ideal for high-temperature laboratory applications. Polypropylene, with a maximum temperature tolerance around 110degC, is suitable for less demanding thermal environments but may deform or degrade under prolonged heat exposure. The chemical inertness and high melting point of fluoropolymers provide enhanced resistance to thermal degradation compared to polypropylene, ensuring reliability in rigorous lab settings.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for demanding laboratory environments requiring high durability and corrosion resistance. Polypropylene offers good mechanical properties with flexibility and impact resistance but tends to degrade under prolonged chemical exposure and elevated temperatures. The enhanced toughness and thermal stability of fluoropolymers ensure longer service life and consistent performance in harsh laboratory applications.
Ease of Cleaning and Sterilization
Fluoropolymer laboratory equipment offers superior chemical resistance and non-stick surfaces, enabling effortless cleaning and effective sterilization without degradation. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals, can absorb solvents and may retain residues, complicating thorough cleaning procedures. The choice between fluoropolymer and polypropylene depends on the required sterility standards and the frequency of exposure to harsh cleaning agents in laboratory settings.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, typically exhibit higher upfront costs due to their superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, which is more affordable and widely used for general laboratory equipment. Budget considerations must weigh the long-term durability and reduced maintenance costs of fluoropolymer materials against the lower initial investment but potentially shorter lifespan of polypropylene components. Cost analysis should factor in the specific chemical exposure, temperature requirements, and frequency of equipment replacement to optimize expenditure without compromising lab safety and performance.
Application Suitability in Laboratory Settings
Fluoropolymer materials such as PTFE are highly suitable for laboratory equipment due to their exceptional chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, making them ideal for handling aggressive solvents and corrosive reagents. Polypropylene offers excellent durability, low cost, and good resistance to many acids and bases, but it has lower thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to fluoropolymers, limiting its use in high-temperature or highly reactive environments. Laboratories focused on high-purity applications and demanding chemical processes typically favor fluoropolymer equipment for precise control and safety, while polypropylene is preferred for routine usage and less aggressive conditions.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Fluoropolymer laboratory equipment, such as PTFE and PFA, offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, meeting stringent safety standards like USP Class VI and ISO 10993 for biocompatibility. Polypropylene is commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and compliance with FDA 21 CFR 177 requirements but has lower resistance to aggressive solvents and limited thermal stability. Selecting fluoropolymer materials ensures enhanced safety in handling corrosive substances and maintains compliance with rigorous industry regulations for laboratory applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymers such as PTFE exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and durability but pose significant environmental challenges due to their persistence and difficulty in recycling, leading to long-term ecological accumulation. Polypropylene offers greater sustainability through easier recyclability and biodegradability under specific conditions, making it a more environmentally friendly choice for laboratory equipment disposal. Selecting polypropylene reduces greenhouse gas emissions and microplastic pollution compared to fluoropolymer alternatives, aligning with sustainable laboratory practices.
Final Recommendations: Choosing the Right Material
Fluoropolymer offers exceptional chemical resistance, temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and non-stick properties ideal for handling aggressive reagents in laboratory equipment. Polypropylene is lightweight, cost-effective, and suitable for applications with moderate chemical exposure and temperatures below 100degC. For high-performance applications requiring superior durability and chemical inertness, fluoropolymer is recommended, while polypropylene is best for general-purpose use where budget and ease of fabrication are priorities.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polypropylene for Laboratory Equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com