Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high strength, durability, and heat resistance, making it ideal for functional 3D printing parts. Polylactic acid (PLA) is biodegradable, easier to print, and produces less odor, suited for environmentally friendly and detailed cosmetic models.
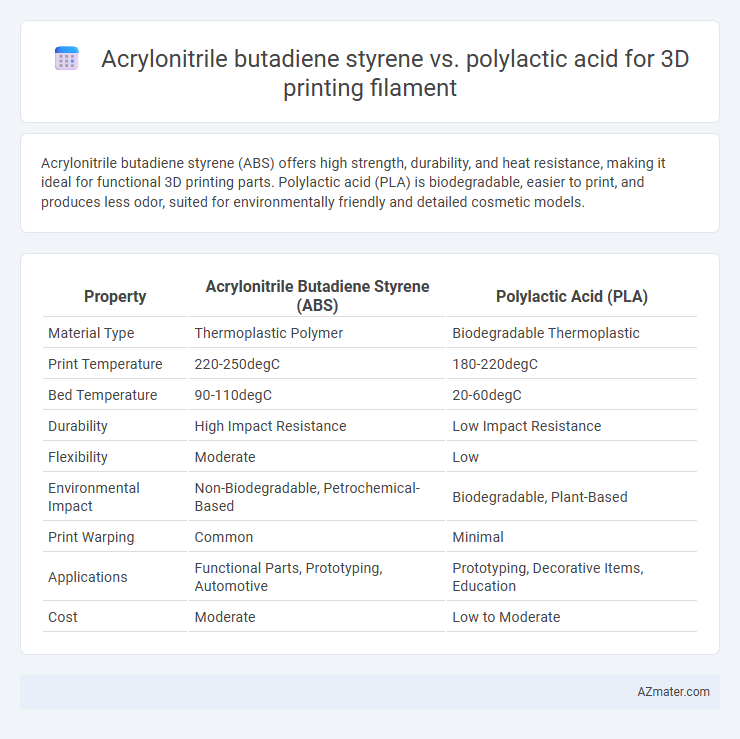
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Biodegradable Thermoplastic |
| Print Temperature | 220-250degC | 180-220degC |
| Bed Temperature | 90-110degC | 20-60degC |
| Durability | High Impact Resistance | Low Impact Resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Non-Biodegradable, Petrochemical-Based | Biodegradable, Plant-Based |
| Print Warping | Common | Minimal |
| Applications | Functional Parts, Prototyping, Automotive | Prototyping, Decorative Items, Education |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to ABS and PLA for 3D Printing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polylactic acid (PLA) are two of the most common thermoplastic filaments used in 3D printing. ABS offers high strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it ideal for functional prototypes and end-use parts, while PLA is biodegradable, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, and produces less warping during printing, making it user-friendly for beginners. The choice between ABS and PLA depends on the specific application requirements, such as mechanical performance, environmental impact, and ease of printing.
Material Composition and Sources
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based thermoplastic made from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering durability and heat resistance ideal for 3D printing applications requiring strength and impact resistance. Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, known for its eco-friendly attributes and ease of use in 3D printing with low warping tendencies. The contrasting sources and compositions influence not only environmental impact but also mechanical properties, making ABS favored for functional prototypes and PLA for visually detailed models.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers higher impact resistance and greater flexibility, making it ideal for functional parts requiring durability. Polylactic acid (PLA) features superior stiffness and tensile strength but is more brittle, suitable for aesthetic and low-stress applications. ABS withstands higher temperatures and mechanical stress, whereas PLA excels in precision and surface finish with lower thermal resistance.
Printing Temperature and Equipment Compatibility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) requires a printing temperature range between 220-250degC and is compatible with most FDM 3D printers equipped with heated beds to prevent warping. Polylactic acid (PLA) prints at a lower temperature range of 180-220degC, making it suitable for a broader range of 3D printers, including those without heated beds due to its minimal warping properties. ABS demands more controlled environments and equipment capable of maintaining higher temperatures, while PLA's compatibility with lower-temperature, less specialized printers enhances its accessibility for beginners and hobbyists.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a smooth, durable surface finish with a glossy appearance ideal for functional and high-strength 3D prints, while polylactic acid (PLA) provides a naturally glossy, vibrant finish that enhances intricate details and color vibrancy. ABS tends to better withstand post-processing techniques like sanding and painting, improving its aesthetic versatility compared to PLA, which is more prone to surface imperfections but excels in producing sharp, detailed visual elements. PLA's biodegradability and wide color range make it popular for decorative and display applications, whereas ABS is preferred for industrial-grade prototypes requiring robustness and refined mechanical appearance.
Strength, Durability, and Flexibility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior strength and durability compared to polylactic acid (PLA), making it ideal for functional parts that require impact resistance and long-term use. PLA, while less durable, provides better flexibility and ease of printing with lower warping and shrinkage, suited for detailed and less stress-prone models. ABS withstands higher temperatures and mechanical stress, whereas PLA is biodegradable but more brittle under load, influencing material choice based on application needs.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based thermoplastic known for its durability but has significant environmental drawbacks due to its non-biodegradability and the release of toxic fumes during printing. Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a biodegradable alternative that decomposes under industrial composting conditions, reducing long-term environmental impact. PLA's lower carbon footprint and biodegradability make it a more sustainable choice compared to ABS, which persists in landfills and contributes to plastic pollution.
Ease of Use and Printability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers higher durability and heat resistance but requires a heated bed and controlled printing environment to minimize warping, contributing to moderate ease of use. Polylactic acid (PLA) excels in ease of use with low printing temperature and minimal warping, making it highly suitable for beginners and detailed prints. ABS demands better ventilation due to fumes, whereas PLA is more environmentally friendly and emits less odor during printing.
Cost and Market Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) filament typically costs more than polylactic acid (PLA), reflecting its enhanced durability and heat resistance. PLA benefits from broader market availability due to its eco-friendly composition and ease of printing, making it a popular choice among hobbyists and beginners. ABS, while slightly less accessible, remains widely stocked in industrial applications and specialty 3D printing suppliers due to its superior mechanical properties.
Best Applications: Choosing Between ABS and PLA
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) excels in applications requiring high impact resistance, thermal stability, and durability, making it ideal for automotive parts, electronic housings, and functional prototypes. Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources, is perfect for biodegradable and detailed prints such as decorative items, educational models, and disposable prototypes due to its ease of printing and excellent surface finish. Selecting between ABS and PLA depends on the intended use: ABS suits demanding mechanical and thermal environments, while PLA fits eco-friendly, low-stress, and precision-focused projects.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polylactic acid for 3D printing filament
 azmater.com
azmater.com