Polysulfone offers high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gears operating under high temperature and harsh conditions. Polyoxymethylene provides superior stiffness and low friction, ensuring precise gear performance in applications requiring dimensional stability and wear resistance.
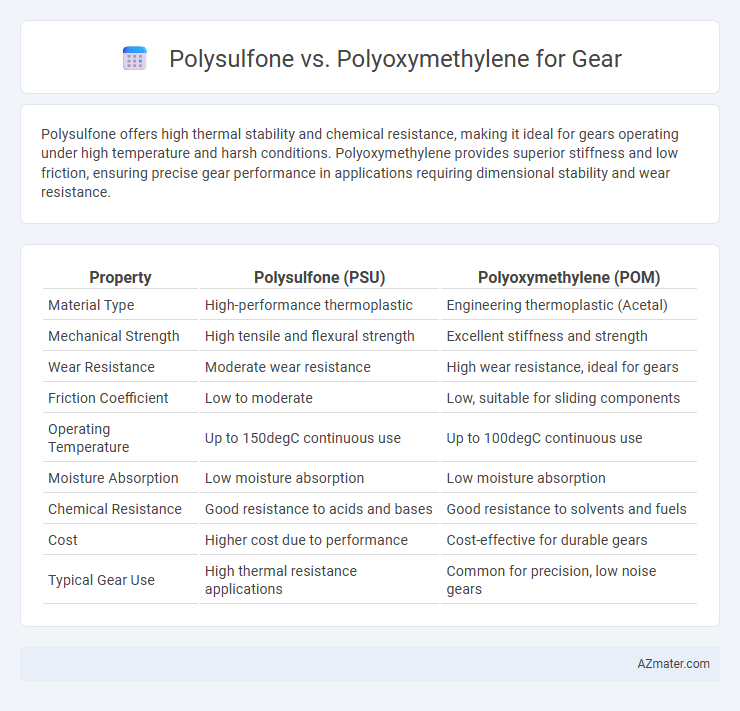
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic | Engineering thermoplastic (Acetal) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Excellent stiffness and strength |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | High wear resistance, ideal for gears |
| Friction Coefficient | Low to moderate | Low, suitable for sliding components |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 100degC continuous use |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Good resistance to solvents and fuels |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance | Cost-effective for durable gears |
| Typical Gear Use | High thermal resistance applications | Common for precision, low noise gears |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyoxymethylene
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability up to 150degC, and resistance to hydrolysis and oxidation, making it suitable for demanding gear applications. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, offers high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability with a melting point around 175degC, widely used in precision gear manufacturing. Both materials provide distinct benefits for gears, with polysulfone excelling in thermal and chemical resistance, while polyoxymethylene delivers superior wear resistance and low moisture absorption.
Material Properties Overview
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability with a heat deflection temperature around 190degC and high impact resistance, making it suitable for gears requiring durability under moderate mechanical stress and elevated temperatures. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, exhibits superior stiffness, low friction coefficients, and excellent dimensional stability with a melting point near 175degC, ideal for precision gears with high wear resistance and smooth operation. Both materials provide chemical resistance, but PSU outperforms POM in hydrolytic stability, while POM typically delivers better fatigue resistance and machinability for gear manufacturing.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibit distinct mechanical strengths influencing their suitability for gears; PSU offers higher tensile strength and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for high-load, high-temperature applications. POM provides superior stiffness, low friction, and excellent wear resistance, which are critical for precise, low-noise gear operation under moderate mechanical stress. The choice depends on balancing PSU's strength and temperature endurance against POM's durability and dimensional stability in gear manufacturing.
Wear and Friction Performance
Polysulfone exhibits superior wear resistance and maintains low friction coefficients under high load and temperature conditions, making it ideal for gears requiring durability and heat stability. Polyoxymethylene offers excellent dimensional stability and low friction but tends to have higher wear rates under abrasive or high-stress environments compared to polysulfone. For applications demanding longevity and minimal wear, polysulfone outperforms polyoxymethylene in maintaining gear integrity and reducing maintenance frequency.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits superior thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to 150degC, outperforming Polyoxymethylene (POM), which has a maximum continuous service temperature around 100degC. Chemically, polysulfone resists hydrolysis, strong acids, and bases, making it suitable for harsh environments, whereas polyoxymethylene shows vulnerability to acidic and oxidative conditions, limiting its chemical resistance. For gears requiring high thermal endurance and robust chemical resistance, polysulfone provides enhanced durability and performance compared to polyoxymethylene.
Machinability and Manufacturing Ease
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for precision gear applications requiring durability, but its machinability demands specialized tooling due to its toughness and tendency to generate heat. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, excels in manufacturability with excellent machinability, allowing high-speed cutting and tight tolerances in gear production, enhancing manufacturing ease and reducing cycle times. Choosing between polysulfone and POM hinges on balancing the required mechanical performance against the complexity and cost of machining processes.
Cost Considerations
Polysulfone offers higher thermal stability and impact resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polyoxymethylene, impacting budget constraints in gear manufacturing. Polyoxymethylene provides excellent stiffness and low friction at a more economical price point, making it suitable for large-scale production where cost efficiency is critical. Evaluating the trade-off between material performance and cost is essential for selecting the optimal polymer for gear applications.
Applications in Gear Manufacturing
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyoxymethylene (POM) are prominent thermoplastics widely used in gear manufacturing due to their high mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance. Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gears operating in high-temperature or aggressive environments such as automotive transmissions and industrial machinery. Polyoxymethylene provides exceptional dimensional stability and low friction, which is advantageous for precision gears in consumer electronics and small mechanical devices.
Durability and Longevity Assessment
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it highly durable under high-temperature and harsh environmental conditions for gear applications. Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides excellent wear resistance and low friction, enhancing gear longevity in moderate temperature scenarios with strong mechanical performance. Gear longevity dependent on operational environment favors polysulfone for durability in demanding conditions, while polyoxymethylene excels in maintaining dimensional stability and reducing maintenance in standard gear operations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Gears
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for gears in high-temperature environments with moderate mechanical stress. Polyoxymethylene provides superior stiffness, low friction, and high wear resistance, ideal for precision gears requiring high dimensional stability and low backlash. Selecting the right material depends on the specific gear application, balancing mechanical demands, thermal conditions, and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyoxymethylene for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com