Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable ties offer excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for general outdoor and indoor applications. Polyamide (nylon) cable ties provide superior tensile strength, flexibility, and heat resistance, ideal for demanding industrial environments requiring durability and long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
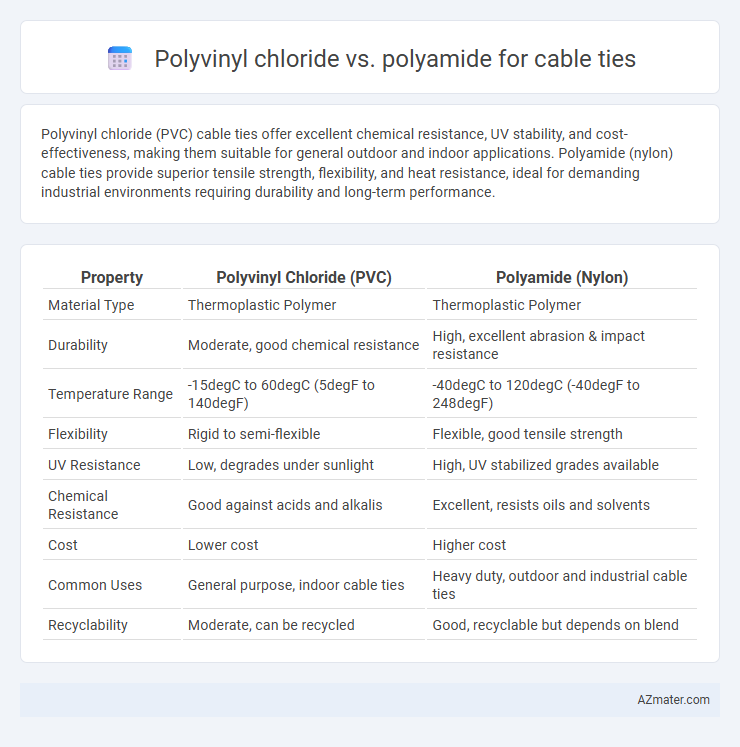
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Durability | Moderate, good chemical resistance | High, excellent abrasion & impact resistance |
| Temperature Range | -15degC to 60degC (5degF to 140degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Flexibility | Rigid to semi-flexible | Flexible, good tensile strength |
| UV Resistance | Low, degrades under sunlight | High, UV stabilized grades available |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Excellent, resists oils and solvents |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Uses | General purpose, indoor cable ties | Heavy duty, outdoor and industrial cable ties |
| Recyclability | Moderate, can be recycled | Good, recyclable but depends on blend |
Introduction to Cable Tie Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyamide (PA) are two primary materials used for cable ties, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific applications. PVC provides excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for general indoor wiring and bundling tasks. Polyamide, known for its superior strength, thermal stability, and UV resistance, is preferred in demanding environments, including outdoor and industrial settings.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a versatile plastic widely used for cable ties due to its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and affordability. It offers good flexibility and weather resistance, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications where moderate strength is required. PVC cable ties provide effective insulation and protection against UV rays, moisture, and abrasion, but typically have lower tensile strength compared to polyamide counterparts.
Overview of Polyamide (Nylon)
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers exceptional strength, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, making it a preferred material for high-performance cable ties. Its inherent resistance to chemicals, UV radiation, and temperature extremes ensures durability in demanding industrial and outdoor environments. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), nylon provides superior tensile strength and thermal stability, enhancing cable tie reliability in critical applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyamide cable ties exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) variants, offering higher tensile strength and better resistance to stress and impact. Polyamide's molecular structure provides enhanced durability and flexibility, making it ideal for heavy-duty and outdoor applications. In contrast, PVC cable ties typically have lower tensile strength and may become brittle under prolonged exposure to UV and extreme temperatures.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable ties exhibit excellent resistance to oils, acids, and alkalis, making them suitable for environments with moderate chemical exposure, while polyamide (nylon) cable ties offer superior resistance to hydrocarbons and solvents. PVC tends to degrade under prolonged UV exposure and extreme temperatures, whereas polyamide provides better thermal stability and resists embrittlement, although it can absorb moisture that affects its mechanical properties. Environmentally, PVC is less eco-friendly due to its chlorine content and difficulties in recycling, whereas polyamide is more biodegradable and recyclable, enhancing sustainability in cable tie applications.
Temperature Performance
Polyamide cable ties exhibit superior temperature resistance, functioning effectively between -40degC and 85degC, with some variants enduring up to 105degC, making them ideal for high-heat environments. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable ties typically operate within a narrower range of -20degC to 60degC, limiting their use in extreme temperature conditions. Polyamide's enhanced thermal stability ensures durability and maintains tensile strength under fluctuating temperatures, whereas PVC may become brittle or deform.
Flexibility and Durability
Polyamide cable ties offer superior flexibility and tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring robust durability and resistance to wear and temperature variations. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable ties provide moderate flexibility but tend to be less durable and more prone to brittleness under harsh environmental conditions. The choice between polyamide and PVC cable ties depends on the specific requirements for flexibility under stress and long-term durability in varying operational environments.
Cost and Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable ties offer a cost-effective solution with widespread availability due to large-scale production and extensive distribution networks. Polyamide (nylon) cable ties, although generally more expensive, provide superior mechanical strength and resistance to wear, often justifying the higher price in demanding applications. The choice between PVC and polyamide depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements, where PVC suits low-cost, general-purpose needs and polyamide fits high-performance, durable uses.
Typical Applications: PVC vs Polyamide
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable ties are commonly used in environments requiring UV resistance and chemical exposure resistance, making them ideal for outdoor electrical installations and automotive wiring. Polyamide cable ties excel in high-temperature applications and provide superior mechanical strength, suitable for industrial machinery, aerospace, and heavy-duty bundling. PVC offers flexibility and weatherability, whereas polyamide ensures durability and high tensile strength under harsh operational conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general-purpose cable ties in moderate environments. Polyamide (nylon) provides superior tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability, suitable for demanding applications exposed to high temperatures or harsh conditions. Selecting the right material hinges on the specific requirements of the application, balancing environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polyamide for Cable tie
 azmater.com
azmater.com