Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance and UV protection, making them ideal for active lifestyles, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses provide excellent optical clarity but are more prone to scratches and less impact-resistant. Polycarbonate is lighter and thinner compared to PMMA, enhancing comfort for extended eyewear use.
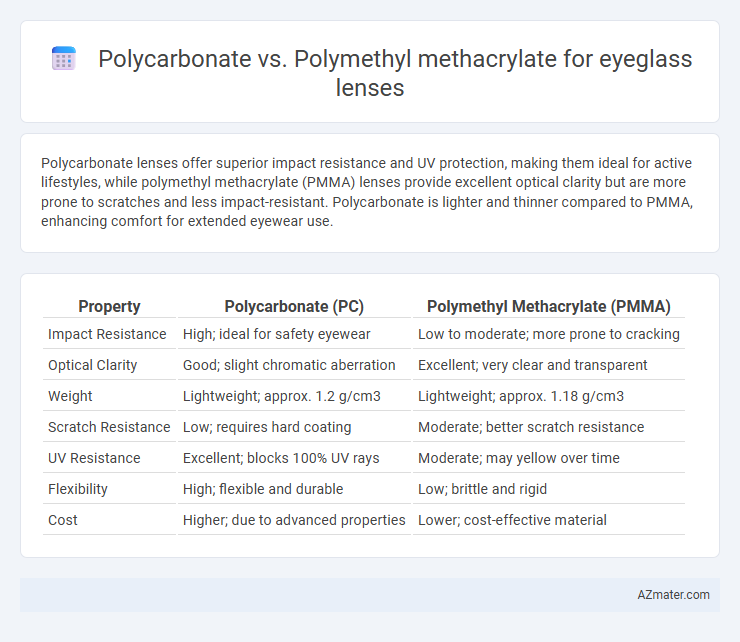
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High; ideal for safety eyewear | Low to moderate; more prone to cracking |
| Optical Clarity | Good; slight chromatic aberration | Excellent; very clear and transparent |
| Weight | Lightweight; approx. 1.2 g/cm3 | Lightweight; approx. 1.18 g/cm3 |
| Scratch Resistance | Low; requires hard coating | Moderate; better scratch resistance |
| UV Resistance | Excellent; blocks 100% UV rays | Moderate; may yellow over time |
| Flexibility | High; flexible and durable | Low; brittle and rigid |
| Cost | Higher; due to advanced properties | Lower; cost-effective material |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Polycarbonate and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are two primary materials used in eyeglass lenses, each offering distinct optical and physical properties. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and UV protection, making them ideal for safety and sports eyewear. Polymethyl methacrylate, also known as acrylic, offers high optical clarity and scratch resistance but lacks the toughness of polycarbonate, making it more suitable for budget-friendly and fashion eyeglasses.
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used in eyeglass lenses due to its superior shatterproof properties and lightweight nature. This material offers high optical clarity and UV protection, making it ideal for safety and everyday eyewear. Compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polycarbonate provides better impact resistance and flexibility, enhancing lens longevity and wearer comfort.
What is Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)?
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic commonly used as an alternative to glass in eyeglass lenses due to its lightweight and high optical clarity. PMMA lenses offer excellent scratch resistance but lack impact resistance compared to polycarbonate lenses, making them more prone to shattering upon impact. The material is favored for its low cost and high transparency, though it is less flexible and more brittle than polycarbonate in eyewear applications.
Optical Clarity: Polycarbonate vs PMMA
Polycarbonate lenses offer high impact resistance but have slightly lower optical clarity compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides superior light transmission and minimal distortion. PMMA lenses exhibit a refractive index around 1.49, resulting in excellent visual sharpness and color accuracy, whereas polycarbonate's refractive index of approximately 1.58 can introduce minor chromatic aberrations. For applications prioritizing optical clarity, PMMA remains the preferred material despite its lower impact resistance relative to polycarbonate.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making them ideal for high-impact environments and sports eyewear. While PMMA lenses provide good optical clarity and scratch resistance, they are more prone to cracking or shattering under sudden impact. Polycarbonate's molecular structure grants enhanced durability and flexibility, reducing breakage risk and extending the lifespan of eyeglass lenses in daily use.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Polycarbonate lenses weigh approximately 30% less than polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses, making them significantly lighter and more comfortable for extended wear. The reduced weight of polycarbonate lenses decreases pressure on the nose and ears, enhancing overall comfort and reducing fatigue. PMMA lenses, while rigid, are heavier and less impact-resistant, often leading to less comfort during prolonged use.
UV Protection Capabilities
Polycarbonate lenses provide superior UV protection, blocking 100% of UVA and UVB rays due to their inherent chemical composition, making them highly effective for eyeglass lenses. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses offer moderate UV protection but require additional coatings to achieve comparable UV-blocking performance. For optimal UV safety in eyewear, polycarbonate is preferred for its built-in UV filtering capabilities without compromising lens clarity or weight.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs PMMA
Polycarbonate eyeglass lenses generally cost more than polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses due to their superior impact resistance and lightweight properties. PMMA lenses offer a budget-friendly option with good optical clarity but lack the durability and scratch resistance provided by polycarbonate. The higher initial cost of polycarbonate lenses is often offset by their longer lifespan and enhanced protection, making them cost-effective for active users.
Suitability for Prescription and Non-prescription Lenses
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance and are thinner and lighter, making them highly suitable for both prescription and non-prescription eyeglass lenses, especially for active lifestyles and children's eyewear. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent optical clarity but lacks the durability and impact resistance required for prescription lenses, limiting its use primarily to non-prescription sunglasses or fashion eyewear. The choice between polycarbonate and PMMA depends on the need for robustness and lens thickness versus optical performance in non-prescription applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Lens Material
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance and lightweight comfort, making them ideal for active lifestyles and children's eyewear, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses provide better optical clarity and scratch resistance at a lower cost. Selecting the right lens material depends on balancing durability, visual performance, and budget, with polycarbonate favored for safety and PMMA chosen for cost-effective vision correction. Consumers should prioritize their specific needs such as lens strength requirements, clarity preferences, and price sensitivity when deciding between these two materials.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com