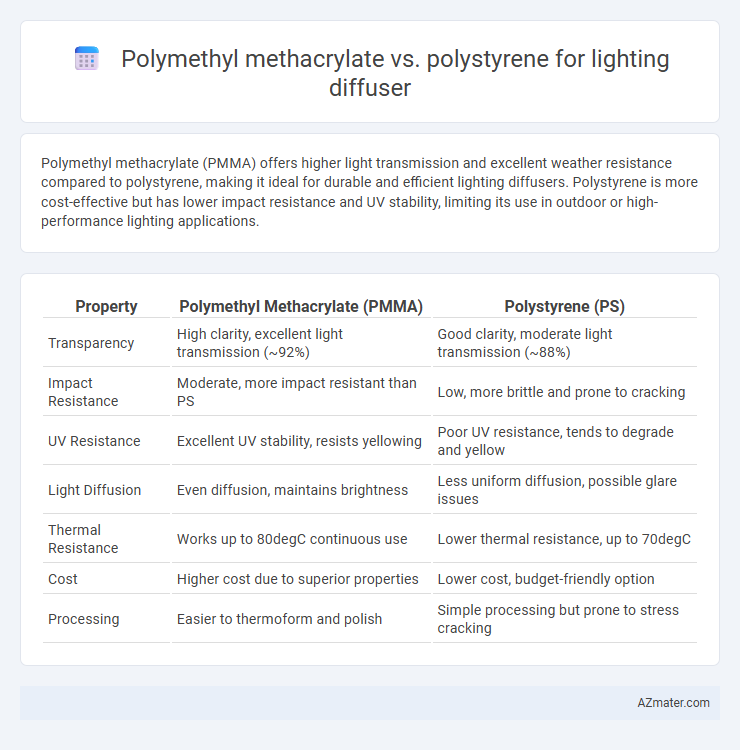
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers higher light transmission and excellent weather resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for durable and efficient lighting diffusers. Polystyrene is more cost-effective but has lower impact resistance and UV stability, limiting its use in outdoor or high-performance lighting applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High clarity, excellent light transmission (~92%) | Good clarity, moderate light transmission (~88%) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, more impact resistant than PS | Low, more brittle and prone to cracking |
| UV Resistance | Excellent UV stability, resists yellowing | Poor UV resistance, tends to degrade and yellow |
| Light Diffusion | Even diffusion, maintains brightness | Less uniform diffusion, possible glare issues |
| Thermal Resistance | Works up to 80degC continuous use | Lower thermal resistance, up to 70degC |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior properties | Lower cost, budget-friendly option |
| Processing | Easier to thermoform and polish | Simple processing but prone to stress cracking |
Introduction to Lighting Diffuser Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polystyrene are widely used materials for lighting diffusers due to their excellent optical properties and ease of fabrication. PMMA offers superior light transmission and greater UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or high-performance lighting applications. Polystyrene provides cost-effective diffusion with good impact resistance but generally exhibits lower durability and yellowing over time compared to PMMA.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its high light transmittance of approximately 92%, making it ideal for lighting diffuser applications where clarity and brightness are essential. PMMA offers superior weather resistance, UV stability, and impact strength compared to polystyrene, which tends to yellow and degrade under prolonged exposure to light. Its ease of fabrication and excellent optical properties contribute to enhanced diffusion uniformity and durability in lighting fixtures.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a transparent, lightweight thermoplastic commonly used in lighting diffusers due to its excellent optical clarity and cost-effectiveness. It offers good stiffness and ease of fabrication but has lower impact resistance and UV stability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PS is suitable for indoor lighting applications where budget constraints and ease of manufacturing are prioritized over long-term durability and weather resistance.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity with a light transmission rate of up to 92%, making it ideal for lighting diffusers requiring high transparency and vibrant light diffusion. Polystyrene (PS) exhibits lower light transmission, typically around 89%, and reduced clarity due to its higher haze factor, which can result in less crisp illumination. The enhanced clarity and light diffusion properties of PMMA contribute to more efficient and visually appealing lighting applications compared to polystyrene.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior durability and higher impact resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for lighting diffuser applications requiring long-lasting performance. PMMA exhibits excellent resistance to yellowing and mechanical stress, maintaining clarity over extended periods, while polystyrene tends to become brittle and discolored under UV exposure. For environments with potential impact or harsh conditions, PMMA ensures enhanced longevity and reliability in diffuser panels.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 100-110degC while polystyrene typically withstands only 70-80degC before deforming. PMMA's higher glass transition temperature (around 105degC) ensures better performance in lighting diffuser applications exposed to prolonged heat, reducing the risk of yellowing and warping. Polystyrene's lower heat resistance limits its use in high-temperature lighting environments, making PMMA the preferred material for durable and reliable diffuser components.
Cost Comparison: PMMA vs Polystyrene
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generally incurs a higher initial cost compared to polystyrene due to its superior optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for premium lighting diffusers. Polystyrene offers a more cost-effective solution with lower raw material and processing expenses, though its lower durability and susceptibility to yellowing might increase long-term replacement costs. Evaluating total lifecycle costs is crucial, as PMMA's longer lifespan often offsets its upfront price advantage over polystyrene in lighting applications.
Ease of Fabrication and Design Flexibility
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior design flexibility and ease of fabrication compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its excellent thermoforming properties and ability to achieve complex shapes with high optical clarity. PMMA's resistance to thermal deformation and ability to be precisely machined or molded make it ideal for intricate lighting diffuser designs, while polystyrene often faces limitations in durability and dimensional stability under heat. Engineering lighting diffusers with PMMA ensures enhanced durability, higher light transmission, and smoother finishes, outperforming PS in applications requiring detailed customization and consistent optical performance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior recyclability compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its ability to be recycled multiple times without significant degradation in optical properties, making it a more sustainable choice for lighting diffusers. PMMA's environmental impact is lower because it is derived from methacrylic acid, which can be produced from renewable resources, whereas polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic, contributes more to fossil fuel depletion and generates harmful styrene monomers during degradation. Moreover, PMMA's higher durability and resistance to yellowing extend the product lifecycle, reducing waste and environmental burden in lighting applications.
Optimal Applications for Each Material
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is ideal for lighting diffusers requiring high light transmission, excellent clarity, and UV resistance, making it optimal for outdoor and architectural lighting applications. Polystyrene (PS), with its cost-effectiveness and ease of molding, suits indoor lighting diffusers where impact resistance and lightweight properties are less critical. PMMA offers superior weatherability and optical properties, while PS is preferred for budget-friendly, short-lifecycle lighting solutions.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polystyrene for Lighting Diffuser
 azmater.com
azmater.com