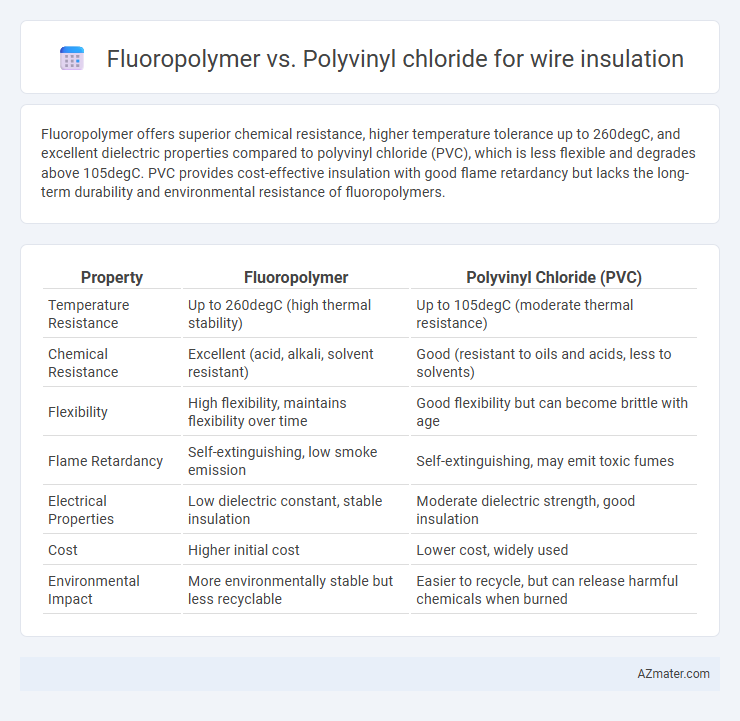
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent dielectric properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is less flexible and degrades above 105degC. PVC provides cost-effective insulation with good flame retardancy but lacks the long-term durability and environmental resistance of fluoropolymers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (high thermal stability) | Up to 105degC (moderate thermal resistance) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acid, alkali, solvent resistant) | Good (resistant to oils and acids, less to solvents) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, maintains flexibility over time | Good flexibility but can become brittle with age |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing, low smoke emission | Self-extinguishing, may emit toxic fumes |
| Electrical Properties | Low dielectric constant, stable insulation | Moderate dielectric strength, good insulation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely used |
| Environmental Impact | More environmentally stable but less recyclable | Easier to recycle, but can release harmful chemicals when burned |
Introduction to Wire Insulation Materials
Fluoropolymer and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are two widely used materials for wire insulation, each offering distinct properties critical to electrical performance and durability. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE and FEP, provide exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 260degC, and low dielectric constants, making them ideal for demanding environments. PVC, known for its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and flame retardant characteristics, is suitable for general-purpose wiring but has lower temperature resistance and chemical stability compared to fluoropolymers.
Overview of Fluoropolymer Insulation
Fluoropolymer insulation offers exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent electrical properties, making it ideal for demanding wire insulation applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. Its low dielectric constant and superior resistance to UV radiation and moisture extend wire lifespan and performance under extreme environmental conditions. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), fluoropolymers provide enhanced flame retardance and lower smoke emission, critical for safety-sensitive uses.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Insulation
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation is widely used in wire and cable applications due to its excellent balance of flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PVC offers good resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and flame, making it suitable for general-purpose electrical insulation in residential and commercial wiring. Its inherent flame-retardant properties and ability to withstand temperatures up to approximately 105degC contribute to its widespread adoption in low- to medium-voltage cable insulation.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Fluoropolymer wire insulation offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent electrical insulation properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which melts around 80-85degC and degrades when exposed to harsh chemicals. Fluoropolymers exhibit low dielectric constants and exceptional UV and weather resistance, enhancing performance in demanding environments, whereas PVC tends to be more rigid and less resistant to environmental stress cracking. The non-stick, hydrophobic surface of fluoropolymers also reduces contamination risks, while PVC insulation is easier to process and more cost-effective but with limited chemical and thermal durability.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Fluoropolymer wire insulation outperforms polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in extreme temperature conditions, maintaining stability and flexibility from -200degC to 260degC, whereas PVC typically degrades above 105degC. Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance and low flammability, making them ideal for aerospace and industrial applications requiring high thermal endurance. PVC insulation is cost-effective but becomes brittle and prone to cracking under severe cold or sustained heat exposure, limiting its use in harsh environments.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior electrical insulation capabilities compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to their high dielectric strength, chemical inertness, and excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance wire insulation in harsh environments. PVC offers adequate insulation for standard applications with good flexibility and flame retardance but has lower resistance to electrical breakdown and chemical exposure. The intrinsic low dielectric constant and minimal moisture absorption of fluoropolymers reduce signal loss and improve long-term reliability in critical electrical wiring systems.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Fluoropolymer wire insulation offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), withstanding extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments without degradation. It resists UV radiation, acids, solvents, and oils, making it ideal for industrial and aerospace applications requiring long-term performance. PVC insulation is less resistant to chemicals and heat, aging faster when exposed to environmental stressors, thus limiting its use in demanding conditions.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Fluoropolymer wire insulation offers superior flexibility and exceptional mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under dynamic conditions or extreme temperatures. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) provides moderate flexibility and adequate mechanical strength but tends to become brittle over time, especially when exposed to harsh environmental factors. Fluoropolymer's chemical resistance and thermal stability further enhance its mechanical performance compared to PVC in demanding wire insulation roles.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Fluoropolymers used in wire insulation exhibit superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, reducing environmental degradation and extending product lifespan compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC manufacturing and disposal release harmful dioxins and toxic additives like phthalates, posing significant environmental and health concerns. Fluoropolymer insulation offers enhanced safety due to lower smoke emission and flame retardancy, minimizing toxic exposure during fires.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Fluoropolymer wire insulation excels in high-temperature, chemical-resistant applications such as aerospace, automotive, and medical industries due to its superior thermal stability and low friction properties. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is widely used in residential wiring, consumer electronics, and general-purpose industrial cables because of its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and flame-retardant qualities. Industries requiring durability in harsh environments favor fluoropolymers, while PVC remains the standard choice for everyday electrical insulation tasks.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyvinyl chloride for Wire Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com