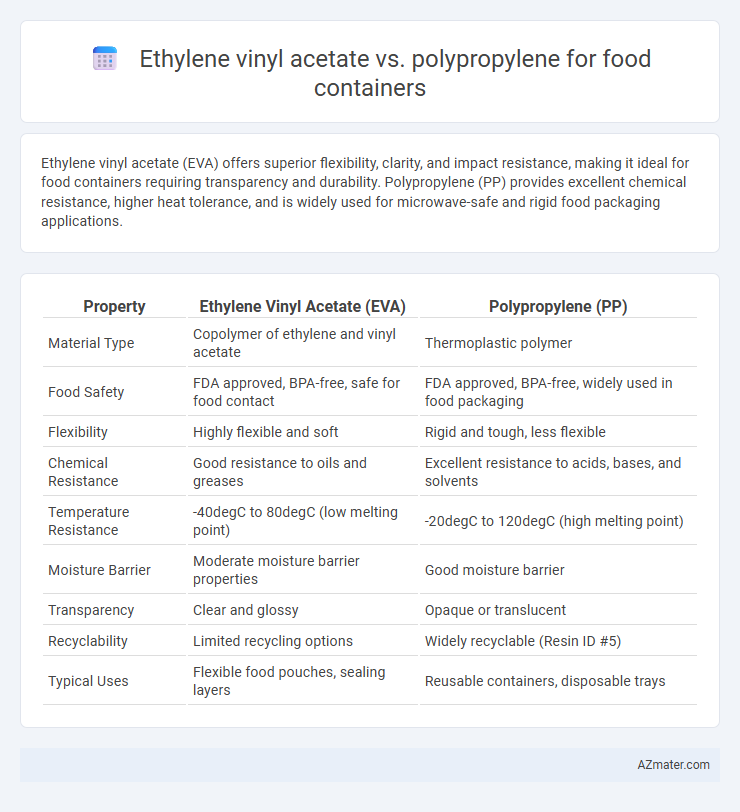
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, clarity, and impact resistance, making it ideal for food containers requiring transparency and durability. Polypropylene (PP) provides excellent chemical resistance, higher heat tolerance, and is widely used for microwave-safe and rigid food packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, BPA-free, safe for food contact | FDA approved, BPA-free, widely used in food packaging |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and soft | Rigid and tough, less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and greases | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 80degC (low melting point) | -20degC to 120degC (high melting point) |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture barrier properties | Good moisture barrier |
| Transparency | Clear and glossy | Opaque or translucent |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Widely recyclable (Resin ID #5) |
| Typical Uses | Flexible food pouches, sealing layers | Reusable containers, disposable trays |
Introduction to Food Container Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polypropylene (PP) are widely used materials in food container manufacturing due to their distinct properties. EVA offers excellent flexibility, clarity, and resistance to low temperatures, making it suitable for products requiring elasticity and transparency. Polypropylene is favored for its high chemical resistance, durability, and heat tolerance, which ensures safe storage and reheating of food while maintaining container integrity.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a flexible, transparent copolymer widely used in food containers due to its excellent clarity, impact resistance, and low-temperature toughness. EVA provides superior sealing properties and resistance to stress cracking compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for airtight packaging and prolonged food freshness. Its chemical stability and non-toxic nature comply with FDA regulations for food contact materials, ensuring safety for storing consumables.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight, durable thermoplastic widely used in food containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, high melting point around 160degC, and strong barrier properties against moisture. It is BPA-free and FDA-approved for food contact, making it safe for storing and reheating food without leaching harmful substances. Polypropylene also offers superior rigidity compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), ensuring better structural integrity and extended shelf life for packaged food products.
Chemical Properties Comparison: EVA vs PP
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance due to its copolymer structure, which combines ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, resulting in a softer and more elastic material compared to polypropylene (PP). Polypropylene exhibits higher chemical resistance, particularly against acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it less prone to degradation in contact with various food substances. EVA has a lower melting point (around 85-90degC) versus PP's melting range (160-170degC), impacting thermal stability and suitability for high-temperature food storage or microwave use.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polypropylene (PP) both meet food safety standards, but polypropylene is more commonly approved by FDA and EFSA for direct food contact due to its chemical stability and resistance to leaching. EVA offers flexibility and good transparency but may contain vinyl acetate monomers, raising regulatory concerns in certain regions regarding potential migration risks. Polypropylene's high melting point and inert nature make it preferred for applications requiring repeated heating and compliance with stringent global food contact regulations.
Durability and Lifespan in Food Storage
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits excellent flexibility and resistance to impact, making it durable for various food storage applications, though it may degrade faster under prolonged sunlight exposure compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene (PP) offers superior chemical resistance, higher melting point, and enhanced durability, resulting in a longer lifespan for food containers, especially when exposed to heat and repeated washing. The choice between EVA and PP depends on specific storage conditions, with PP generally preferred for long-term resilience and durability in food storage environments.
Heat Resistance: Microwave and Dishwasher Suitability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers moderate heat resistance, making it suitable for microwave use but with limitations on prolonged high-temperature exposure, whereas polypropylene (PP) boasts superior heat resistance, commonly withstanding temperatures up to 120degC, ideal for repeated microwave and dishwasher cycles. PP containers resist warping and chemical leaching under dishwasher conditions, ensuring safety and durability. Selecting polypropylene enhances food container performance for microwave reheating and dishwasher cleaning through its robust thermal stability and resistance to degradation.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits lower recyclability compared to polypropylene (PP) due to its complex copolymer structure, which challenges standard recycling processes. Polypropylene, widely valued for its high recyclability and lower environmental footprint due to ease of reprocessing, is often preferred for sustainable food container manufacturing. Both materials differ in biodegradability, with PP showing slightly better environmental impact metrics related to lifecycle emissions and material recovery rates.
Cost Analysis: EVA vs Polypropylene Containers
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) containers generally incur higher costs than polypropylene (PP) containers due to more complex production processes and raw material expenses. Polypropylene offers a cost-efficient alternative with lower material costs and ease of manufacturing, making it ideal for budget-sensitive food packaging. Despite EVA's slightly higher price, its superior flexibility and impact resistance can justify the investment for specialized food containers requiring durability.
Which Material is Best for Food Containers?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, transparency, and resistance to cracking, making it ideal for food containers requiring pliability and airtight seals. Polypropylene (PP) provides superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it best suited for containers exposed to high temperatures, such as microwave use or hot food storage. Choosing between EVA and PP depends on the specific food container application, with PP preferred for thermal resilience and food safety compliance, while EVA is suitable for flexible, lightweight packaging.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com