Polyamide offers high mechanical strength and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for durable sealants in harsh environments. Polydimethylsiloxane provides superior flexibility and thermal stability, ensuring effective sealing in applications requiring elasticity and temperature resilience.
Table of Comparison
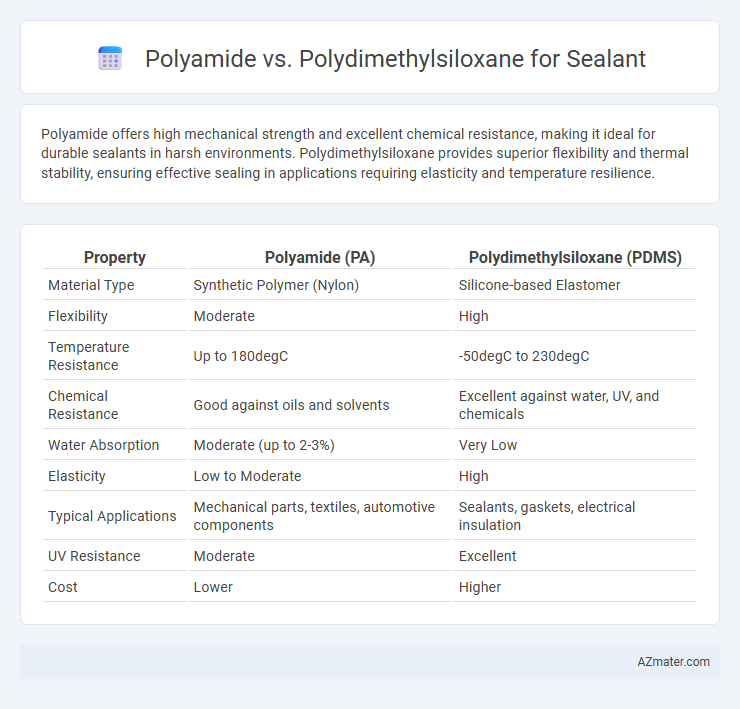
| Property | Polyamide (PA) | Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Polymer (Nylon) | Silicone-based Elastomer |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 180degC | -50degC to 230degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against oils and solvents | Excellent against water, UV, and chemicals |
| Water Absorption | Moderate (up to 2-3%) | Very Low |
| Elasticity | Low to Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Mechanical parts, textiles, automotive components | Sealants, gaskets, electrical insulation |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyamide and Polydimethylsiloxane
Polyamide is a synthetic polymer known for its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability, often used in industrial and automotive sealants to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), a silicone-based polymer, offers superior flexibility, thermal stability, and water repellency, making it ideal for sealants requiring elasticity and weather resistance. Comparing their properties, polyamide excels in structural applications, whereas PDMS is preferred for flexible sealing solutions.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polyamide sealants consist of repeating amide (-CONH-) groups, forming strong hydrogen bonds that provide high tensile strength and chemical resistance. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), a silicone-based polymer, features a flexible Si-O-Si backbone with methyl side groups, offering excellent thermal stability and low surface energy. The distinct chemical structures lead to polyamide's rigid and durable nature while PDMS exhibits superior elasticity and hydrophobicity in sealing applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyamide sealants exhibit superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), making them ideal for high-stress mechanical applications. PDMS offers exceptional flexibility and elongation at break, which enhances its performance in dynamic sealing environments subject to frequent movement or thermal expansion. The choice between polyamide and PDMS sealants depends on the required balance between rigidity and elasticity in specific mechanical contexts.
Adhesion and Bonding Capabilities
Polyamide sealants exhibit strong adhesion to a variety of substrates, including metals, glass, and plastics, due to their excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sealants offer superior flexibility and moisture resistance but generally have lower surface energy, resulting in weaker bonding to non-silicone surfaces without primer treatment. For applications requiring robust, durable bonds to diverse materials, polyamide sealants typically outperform PDMS in adhesion and long-term bonding reliability.
Resistance to Chemicals and Temperature
Polyamide sealants exhibit excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including oils, fuels, and solvents, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sealants offer superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and stability across extreme temperature ranges from -50degC to 200degC. The choice between polyamide and PDMS depends on the specific chemical exposure and thermal requirements of the sealing environment.
Durability and Longevity in Sealant Applications
Polyamide sealants exhibit exceptional durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term mechanical stability. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sealants provide superior flexibility and excellent resistance to UV radiation and extreme temperatures, which significantly enhances their longevity in outdoor and dynamic environments. The choice between polyamide and PDMS depends on application-specific demands; polyamide excels in robust structural sealants while PDMS is preferred for flexible, weather-resistant sealing solutions.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Polyamide sealants offer moderate flexibility with good mechanical strength but limited elasticity, making them suitable for applications requiring durable, rigid joints. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sealants exhibit superior flexibility and high elasticity, allowing them to withstand significant deformation without cracking or losing adhesion. The inherent silicone-based structure of PDMS provides exceptional elongation and recovery properties, ideal for dynamic environments with frequent movement or temperature fluctuations.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Polyamide sealants exhibit lower environmental impact due to their biodegradability and reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sealants, which are synthetic silicones with limited biodegradability. Polyamide formulations generally pose less health risk since they release fewer hazardous substances during curing and degradation, enhancing workplace safety. PDMS sealants, while chemically inert and non-toxic, persist longer in the environment and may contribute to microplastic pollution, raising concerns about their long-term ecological effects.
Cost and Availability
Polyamide sealants typically cost more due to their specialized chemical structure and higher performance in adhesive strength, but they are less widely available compared to polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), which is commonly used and mass-produced for industrial applications. Polydimethylsiloxane sealants offer cost efficiency and broad availability, making them suitable for general-purpose sealing where moderate durability is sufficient. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in varied environmental conditions.
Best Use Cases for Polyamide vs Polydimethylsiloxane Sealants
Polyamide sealants provide excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications involving metal, glass, and plastics where durability under mechanical stress is essential. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sealants offer superior flexibility, UV resistance, and temperature stability, which suits outdoor sealing, electronics encapsulation, and applications requiring long-term weatherproofing. Choosing between polyamide and PDMS sealants depends primarily on the environment's exposure conditions and the mechanical demands of the sealing application.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polydimethylsiloxane for Sealant
 azmater.com
azmater.com