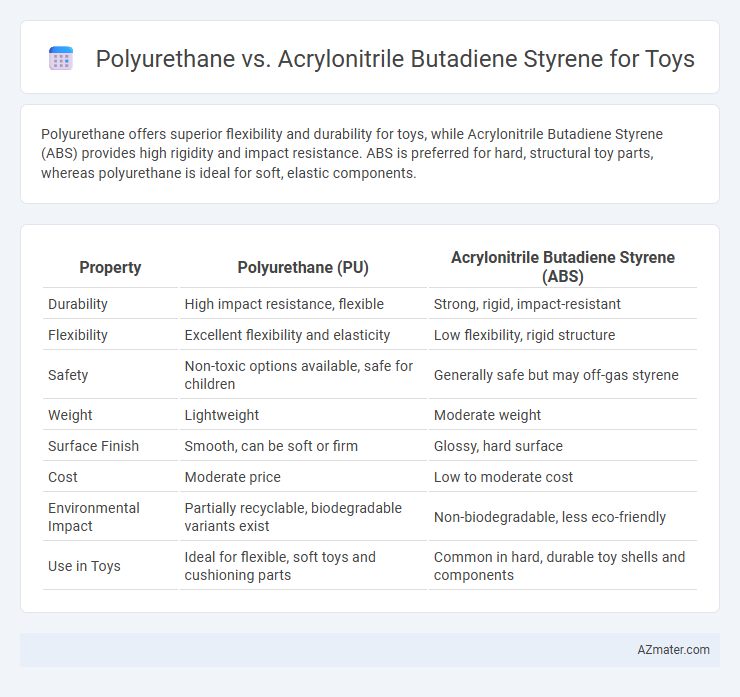
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and durability for toys, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides high rigidity and impact resistance. ABS is preferred for hard, structural toy parts, whereas polyurethane is ideal for soft, elastic components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High impact resistance, flexible | Strong, rigid, impact-resistant |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility and elasticity | Low flexibility, rigid structure |
| Safety | Non-toxic options available, safe for children | Generally safe but may off-gas styrene |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, can be soft or firm | Glossy, hard surface |
| Cost | Moderate price | Low to moderate cost |
| Environmental Impact | Partially recyclable, biodegradable variants exist | Non-biodegradable, less eco-friendly |
| Use in Toys | Ideal for flexible, soft toys and cushioning parts | Common in hard, durable toy shells and components |
Introduction to Polyurethane and ABS in Toy Manufacturing
Polyurethane (PU) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are widely used polymers in toy manufacturing due to their distinct mechanical properties and safety profiles. Polyurethane offers excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and cushioning, making it ideal for soft, durable toy parts that require elasticity and toughness. ABS is favored for its rigidity, high impact resistance, and ease of molding, providing durable, hard plastic components with smooth finishes commonly found in construction toys and action figures.
Material Composition: Polyurethane vs ABS
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer composed of organic units linked by carbamate (urethane) bonds, offering flexibility, impact resistance, and abrasion durability ideal for soft and flexible toy parts. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a rigid thermoplastic composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, providing high strength, rigidity, and good impact resistance suitable for hard, structural toy components. The material composition of polyurethane allows for more elasticity and cushioning, while ABS delivers superior toughness and dimensional stability for durable toy manufacturing.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polyurethane exhibits superior impact resistance and elasticity, making it ideal for toys requiring high durability against drops and rough handling. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent toughness and rigidity, providing strong structural integrity but lower flexibility compared to polyurethane. For toys subject to frequent impact and deformation, polyurethane outperforms ABS in maintaining shape and resisting cracks.
Safety Standards and Non-Toxicity
Polyurethane and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are widely used materials in toy manufacturing, with ABS often preferred for its superior compliance with international safety standards such as ASTM F963 and EN71, ensuring non-toxic and durable playthings. Polyurethane, while versatile and flexible, requires rigorous testing to meet these safety benchmarks due to potential risks of chemical residue and off-gassing. Both materials must conform to regulations that restrict harmful substances like phthalates and heavy metals to guarantee child safety and non-toxicity in toys.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Appeal
Polyurethane offers a smooth, glossy surface finish with excellent flexibility, enhancing the tactile and visual appeal of toys. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides a rigid, matte finish that resists scratches and maintains vibrant color integrity over time. The choice between polyurethane and ABS impacts the toy's durability, surface texture, and overall aesthetic quality.
Flexibility and Hardness Comparison
Polyurethane and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) differ significantly in flexibility and hardness, key factors in toy manufacturing. Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, making it ideal for toys requiring elasticity and impact resistance, while ABS provides higher hardness and rigidity, suitable for structural components needing durability and shape retention. The choice between polyurethane and ABS hinges on the toy's functional requirements, balancing flexibility against hardness for optimal performance.
Cost Efficiency and Production Scalability
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and durability for toys but generally comes with higher raw material costs and more complex processing requirements, impacting cost efficiency. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides a balance of strength, rigidity, and ease of molding, resulting in lower production costs and faster scalability for mass manufacturing. Manufacturers seeking cost-effective, scalable toy production often prefer ABS for its efficient injection molding capabilities and consistent material performance.
Suitability for Different Toy Types
Polyurethane offers exceptional flexibility and durability, making it ideal for soft, squeezable toys and those requiring shock absorption, such as plush-like action figures and interactive sensory toys. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides rigidity, impact resistance, and a smooth surface finish, making it suitable for hard toys like building blocks, dolls, and vehicle models that require structural strength and detailed molding. The choice between polyurethane and ABS depends on the toy's functional requirements, with polyurethane favored for softness and resilience, while ABS excels in precise shape retention and toughness.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyurethane (PU) used in toys offers durability but poses environmental challenges due to its complex chemical composition and limited recyclability, often ending up in landfills or incineration. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), a common thermoplastic in toy manufacturing, is more readily recyclable through mechanical recycling processes, reducing plastic waste. ABS also has a lower environmental footprint in production and disposal phases compared to PU, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious toy design.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Material for Toys
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and cushioning, making it ideal for soft, impact-absorbing toys, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides high rigidity, strength, and durability, perfect for hard toys requiring precise molding and surface finish. For toys demanding toughness and resistance to wear, ABS is preferred due to its excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. In contrast, polyurethane suits toys prioritizing comfort and elasticity, influencing the final choice based on toy design, safety, and user interaction requirements.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com