Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and durability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for reusable medical devices. Polystyrene is typically used for disposable medical items due to its lower cost and ease of molding but lacks the thermal and sterilization capabilities of polysulfone.
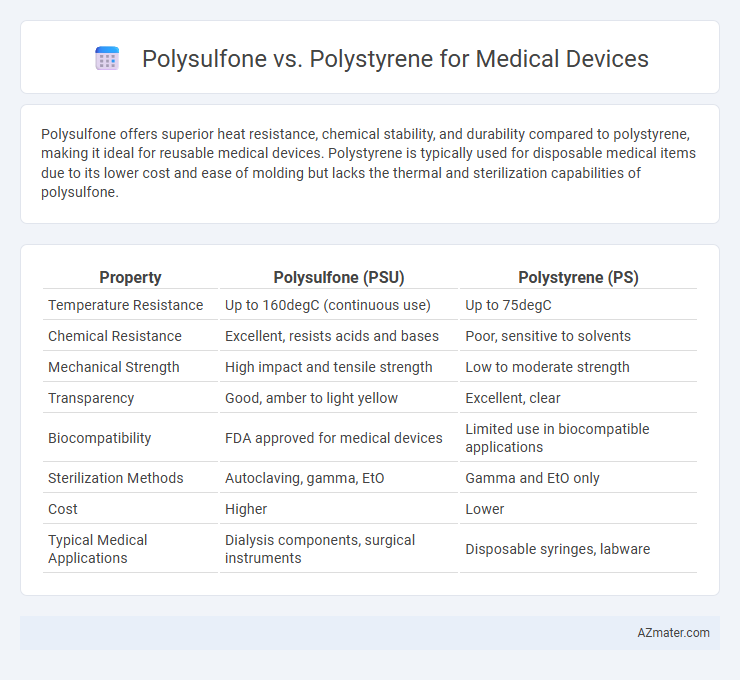
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 160degC (continuous use) | Up to 75degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists acids and bases | Poor, sensitive to solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact and tensile strength | Low to moderate strength |
| Transparency | Good, amber to light yellow | Excellent, clear |
| Biocompatibility | FDA approved for medical devices | Limited use in biocompatible applications |
| Sterilization Methods | Autoclaving, gamma, EtO | Gamma and EtO only |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Medical Applications | Dialysis components, surgical instruments | Disposable syringes, labware |
Introduction to Medical Device Materials
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for demanding medical device applications. Polystyrene is commonly used for disposable medical items due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of molding but lacks the durability required for long-term use. Material selection depends on device function, sterilization processes, and regulatory compliance, with polysulfone favored for reusable or implantable components.
Overview of Polysulfone
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic characterized by excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it highly suitable for demanding medical device applications. Its inherent transparency and biocompatibility allow for precise, safe use in sterilizable components such as fluid-handling devices and surgical instruments. Compared to polystyrene, polysulfone offers superior durability and resistance to repeated sterilization cycles, enhancing the longevity and reliability of medical devices.
Overview of Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in medical devices due to its excellent clarity, rigidity, and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for disposable diagnostic components and laboratory ware. Its biocompatibility and low cost contribute to its prevalence in single-use applications such as petri dishes, test tubes, and culture plates. However, polystyrene's limited chemical resistance and lower thermal stability compared to polysulfone restrict its use in high-temperature or harsh chemical environments within medical device manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength and higher impact resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for demanding medical device applications requiring durability. Polysulfone maintains its mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures up to 160degC, while polystyrene tends to become brittle and lose strength around 80degC. The flexibility and fatigue resistance of polysulfone surpass polystyrene, providing longer service life for medical devices exposed to repetitive stress.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, maintaining stability in exposure to harsh solvents, acids, and alkalis commonly encountered in medical environments. Polystyrene tends to degrade or swell when exposed to aggressive chemicals such as alcohols and certain disinfectants, limiting its application in sterilizable medical devices. The enhanced chemical resistance of polysulfone makes it a preferred choice for components requiring repeated sterilization and chemical exposure without compromising material integrity.
Sterilization Compatibility
Polysulfone exhibits superior sterilization compatibility compared to polystyrene, withstanding high-temperature steam autoclaving up to 135degC without significant degradation. Polystyrene is more prone to deformation and loss of mechanical integrity under heat-based sterilization methods, limiting its use primarily to ethylene oxide or gamma radiation sterilization. Polysulfone's enhanced chemical resistance enables multiple sterilization cycles, making it ideal for reusable medical devices requiring reliable sterilization performance.
Biocompatibility Considerations
Polysulfone offers superior biocompatibility compared to polystyrene, featuring enhanced thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis, making it suitable for long-term medical device applications. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and biocompatible for short-term use, tends to exhibit lower chemical resistance and potential cytotoxicity concerns in prolonged contact with biological tissues. Medical devices requiring sterilization and sustained bodily exposure benefit from polysulfone's durability and minimal leachables, ensuring safer patient outcomes.
Applications in Medical Devices
Polysulfone exhibits superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for sterilizable medical devices such as surgical instruments, blood oxygenators, and dialysis components. Polystyrene is commonly used for disposable medical items like petri dishes, test tubes, and diagnostic trays due to its clarity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability for repeated sterilization. The choice between polysulfone and polystyrene hinges on application requirements for sterilization, mechanical strength, and long-term exposure to bodily fluids.
Cost and Manufacturing Factors
Polysulfone offers higher thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, making it suitable for sterilizable medical devices, but comes with increased raw material costs and more complex processing requirements. Polystyrene is more cost-effective and easier to mold due to its lower melting point and simpler polymer structure, which can reduce manufacturing time and expenses. However, its lower durability and limited resistance to heat and chemicals may lead to higher long-term costs in medical applications requiring frequent sterilization or extended device lifespan.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for reusable medical devices requiring sterilization. Polystyrene excels in cost-effectiveness and ease of molding, suitable for disposable applications with minimal exposure to harsh conditions. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability, sterilization needs, and budget constraints within the medical device design process.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polystyrene for Medical Device
 azmater.com
azmater.com