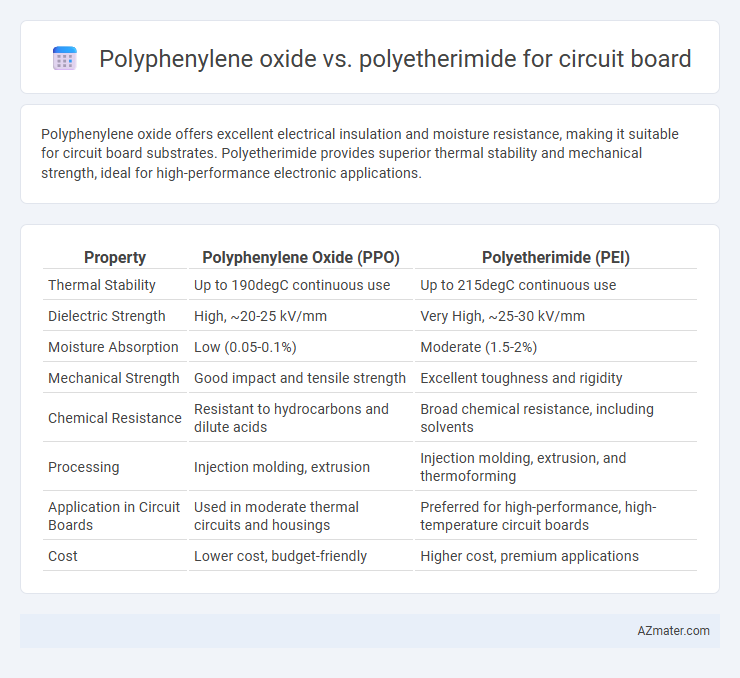
Polyphenylene oxide offers excellent electrical insulation and moisture resistance, making it suitable for circuit board substrates. Polyetherimide provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, ideal for high-performance electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyetherimide (PEI) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 190degC continuous use | Up to 215degC continuous use |
| Dielectric Strength | High, ~20-25 kV/mm | Very High, ~25-30 kV/mm |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.05-0.1%) | Moderate (1.5-2%) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact and tensile strength | Excellent toughness and rigidity |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to hydrocarbons and dilute acids | Broad chemical resistance, including solvents |
| Processing | Injection molding, extrusion | Injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming |
| Application in Circuit Boards | Used in moderate thermal circuits and housings | Preferred for high-performance, high-temperature circuit boards |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium applications |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polyetherimide
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and polyetherimide (PEI) are high-performance thermoplastics widely used in circuit board applications due to their excellent electrical insulation properties and thermal stability. PPO offers superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for environments with fluctuating humidity, while PEI provides higher mechanical strength and continuous use temperatures up to 170degC, ensuring durability in high-heat electronic assemblies. Both materials exhibit low dielectric constants and excellent chemical resistance, critical for maintaining signal integrity and longevity in advanced printed circuit boards.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with ether linkages, providing high thermal stability and excellent electrical insulation for circuit boards. Polyetherimide (PEI) contains imide groups coupled with aromatic rings, resulting in superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to PPO. The imide functionality in PEI enhances its dimensional stability and dielectric properties, making it more suitable for high-performance electronic applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), with a higher continuous use temperature typically around 170-200degC versus PPO's 120-130degC. PEI's glass transition temperature (Tg) can reach approximately 215-220degC, enabling better performance in high-temperature circuit board applications. PPO provides good dimensional stability but is less capable of maintaining structural integrity under prolonged thermal stress compared to PEI.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties with a high dielectric strength and low dissipation factor, making it ideal for high-frequency circuit board applications. Polyetherimide (PEI) also offers strong electrical insulation but surpasses PPO in thermal stability and mechanical strength, supporting higher operating temperatures in demanding environments. Both polymers provide reliable insulation, but PEI is preferred where enhanced thermal endurance and flame resistance are critical for circuit board performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making it suitable for circuit board substrates requiring rigidity and resistance to deformation. Polyetherimide (PEI) provides superior thermal durability and impact resistance, ensuring prolonged performance under high thermal cycling and mechanical stress conditions. Comparing both, PEI typically outperforms PPO in durability for demanding electronic applications, while PPO excels in maintaining mechanical strength at moderate thermal levels.
Flame Retardancy and Safety
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides inherent flame retardancy, making it a reliable choice for circuit boards requiring high safety standards without additional flame-retardant additives. Polyetherimide (PEI) offers exceptional thermal stability and self-extinguishing properties, ensuring robust flame retardancy under extreme operating conditions. Both materials meet stringent UL 94 V-0 ratings, but PEI typically offers superior performance in high-temperature safety applications due to its higher glass transition temperature and chemical resistance.
Processability in PCB Manufacturing
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, making it easier to process in PCB manufacturing with consistent layer adhesion and minimal warpage. Polyetherimide (PEI) presents higher thermal resistance and mechanical strength but requires more precise temperature control and longer curing cycles during PCB fabrication, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity. Selecting PPO favors streamlined processing and reduced thermal stress, while PEI suits high-performance PCBs demanding elevated temperature endurance despite tighter process parameters.
Cost and Availability for Circuit Boards
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a lower-cost option compared to Polyetherimide (PEI) for circuit board manufacturing, making it suitable for budget-sensitive applications. PPO is widely available with robust supply chains, ensuring consistent procurement for high-volume production runs. PEI, while more expensive and less readily available, provides higher thermal stability and mechanical strength, often justifying its cost in demanding electronic environments.
Typical Applications in Electronics
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is commonly used in circuit boards due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and dimensional stability, making it ideal for connectors, switches, and housings. Polyetherimide (PEI) offers superior thermal resistance and flame retardancy, preferred in high-performance electronic components such as connectors, insulators, and printed circuit boards requiring higher operating temperatures. Both materials are valued for their dielectric strength, but PEI's ability to withstand continuous use above 150degC distinguishes it in advanced electronics applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your PCB
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent dimensional stability and high thermal resistance, making it ideal for circuit boards requiring consistent performance under moderate heat. Polyetherimide (PEI) provides superior mechanical strength, higher temperature tolerance up to 217degC, and excellent flame retardancy, suitable for high-performance or harsh environment PCBs. Selecting the right material depends on balancing thermal requirements, mechanical durability, and cost-effectiveness to optimize PCB reliability and functionality.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyetherimide for Circuit board
 azmater.com
azmater.com