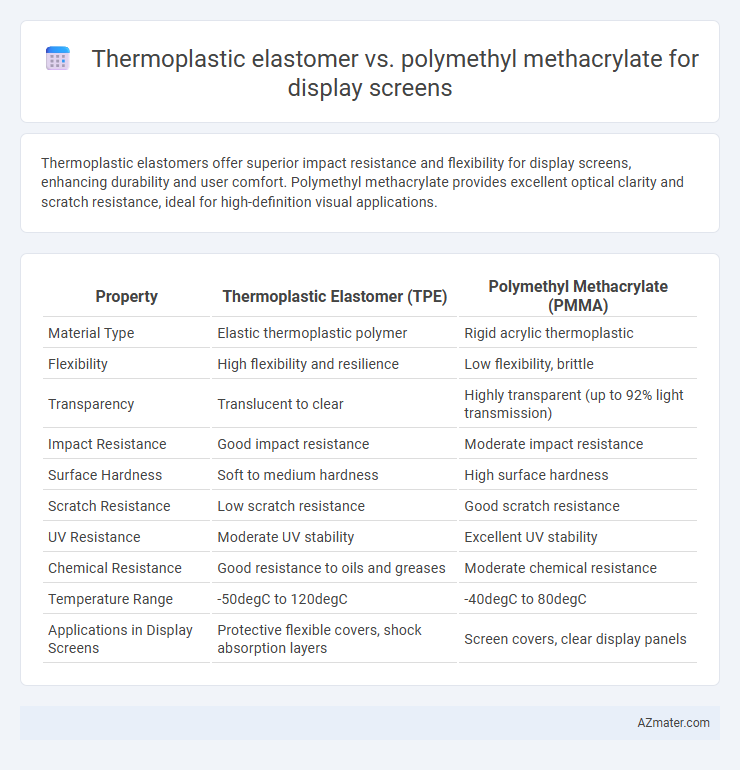
Thermoplastic elastomers offer superior impact resistance and flexibility for display screens, enhancing durability and user comfort. Polymethyl methacrylate provides excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance, ideal for high-definition visual applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Elastic thermoplastic polymer | Rigid acrylic thermoplastic |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and resilience | Low flexibility, brittle |
| Transparency | Translucent to clear | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Surface Hardness | Soft to medium hardness | High surface hardness |
| Scratch Resistance | Low scratch resistance | Good scratch resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV stability | Excellent UV stability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and greases | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 120degC | -40degC to 80degC |
| Applications in Display Screens | Protective flexible covers, shock absorption layers | Screen covers, clear display panels |
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) and Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the elasticity of rubber with the recyclability of plastics, offering flexibility, impact resistance, and durability for display screens. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), known as acrylic glass, provides excellent optical clarity, high scratch resistance, and UV stability, making it ideal for high-visual quality screens. TPE is favored for protective, flexible displays, whereas PMMA is preferred for rigid, transparent screen covers with superior light transmission.
Material Composition and Chemical Structure
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are composed of a block copolymer structure combining rubber-like elasticity with thermoplastic processability, featuring flexible polymer chains such as styrene, ethylene, or propylene segments. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) consists of a rigid, glassy amorphous polymer formed by the polymerization of methyl methacrylate monomers, characterized by a backbone of carbon atoms with pendant methacrylate groups providing high transparency and hardness. The flexible molecular architecture of TPE offers superior impact resistance and flexibility in display screens, whereas PMMA provides excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance but less elasticity.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer flexible transparency with moderate optical clarity but lower light transmission rates, typically around 85-90%, which can result in slight visual distortion for display screens. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), known as acrylic, boasts superior optical clarity with light transmission exceeding 92%, making it ideal for high-performance display screens requiring sharp image quality and minimal light diffusion. PMMA's inherent rigidity and excellent UV resistance enhance display longevity, whereas TPE's flexibility may compromise sustained optical performance under extended exposure.
Impact Resistance and Durability Comparison
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) due to their flexible, rubber-like properties that absorb shocks effectively, making TPE ideal for display screens prone to drops and impacts. PMMA, also known as acrylic glass, provides excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance but is more brittle and susceptible to cracking under impact, reducing its durability in high-stress environments. For long-term durability and impact resilience in display screen applications, TPE outperforms PMMA by maintaining structural integrity under repeated mechanical stress.
Flexibility and Hardness of TPE vs. PMMA
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit superior flexibility compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making TPE ideal for display screens requiring bending and impact resistance. PMMA offers significantly higher hardness, providing excellent scratch resistance and clarity but lacks the elasticity of TPE. The balance between TPE's flexibility and PMMA's hardness determines their suitability for various display screen applications, with TPE favored in flexible displays and PMMA chosen for rigid, transparent panels.
Surface Scratch Resistance Performance
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) typically exhibit lower surface scratch resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) when used for display screens due to their softer, more flexible polymer chains. PMMA offers superior hardness and abrasion resistance, making it more durable against scratches and maintaining visual clarity over time. Consequently, PMMA is preferred in applications demanding high surface scratch resistance and sustained optical performance in display technologies.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer flexible molding and shorter cycle times in display screen manufacturing due to their rubber-like elasticity and thermoplastic processability, enabling efficient injection and extrusion methods. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), characterized by its rigidity and optical clarity, requires precise casting or injection molding with longer cooling phases to avoid stress-induced defects. TPE's reusability and lower processing temperatures contrast with PMMA's higher thermal stability and resistance to UV degradation, influencing production costs and equipment choices in display screen fabrication.
Cost Implications for Display Screen Applications
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer lower material and processing costs compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in display screen applications due to their flexible manufacturing and recyclability. PMMA, while providing superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, involves higher raw material expenses and more energy-intensive production steps, leading to increased overall costs. Cost-sensitive display manufacturers favor TPE for impact-resistant screens, whereas premium displays prioritize PMMA despite its higher price point.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit superior recyclability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) due to their ability to be repeatedly melted and reshaped without significant degradation, reducing environmental impact through lowered plastic waste. PMMA, a rigid thermoplastic, faces challenges in recycling processes and often ends up in landfills, where its resistance to biodegradation contributes to long-term environmental pollution. The life cycle analysis of TPE demonstrates lower carbon footprint and energy consumption during recycling, making it a more sustainable choice for display screen applications focused on environmental responsibility.
Best Use Cases for Display Screens: TPE vs. PMMA
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for display screens requiring shock absorption and durability in portable devices. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, suited for high-visibility displays in outdoor or brightly lit environments. TPE is best for flexible or rugged displays, while PMMA excels in rigid, scratch-resistant screens demanding high transparency.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Display screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com