Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior stiffness and chemical resistance, making it ideal for durable eyeglass frames, while Polycarbonate (PC) provides exceptional impact resistance and lightweight comfort, preferred for lens material. Polycarbonate lenses also feature inherent UV protection, enhancing eye safety compared to Polyoxymethylene.
Table of Comparison
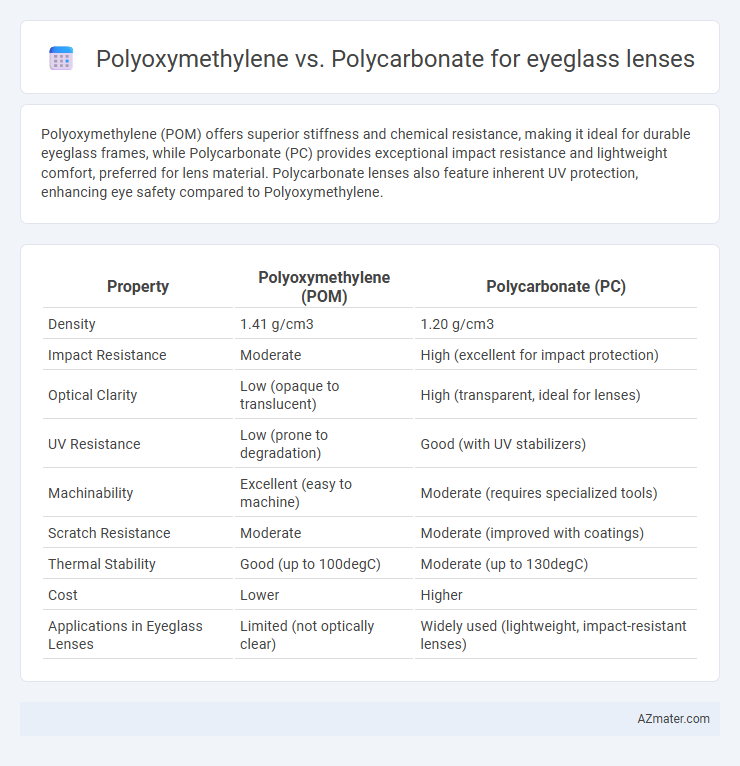
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High (excellent for impact protection) |
| Optical Clarity | Low (opaque to translucent) | High (transparent, ideal for lenses) |
| UV Resistance | Low (prone to degradation) | Good (with UV stabilizers) |
| Machinability | Excellent (easy to machine) | Moderate (requires specialized tools) |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Moderate (improved with coatings) |
| Thermal Stability | Good (up to 100degC) | Moderate (up to 130degC) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications in Eyeglass Lenses | Limited (not optically clear) | Widely used (lightweight, impact-resistant lenses) |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and polycarbonate are prominent materials used in eyeglass lens manufacturing, with each offering distinct optical and mechanical properties. Polycarbonate lenses are highly valued for their impact resistance and lightweight nature, making them ideal for active lifestyles and children's eyewear. In contrast, polyoxymethylene lenses provide superior dimensional stability and chemical resistance, although they are less common in mainstream eyeglass production due to limited optical clarity compared to polycarbonate.
What is Polyoxymethylene (POM)?
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic widely used for its exceptional stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. In eyeglass lenses, POM offers superior impact resistance and lightweight properties, making it an alternative to polycarbonate, especially in applications where mechanical durability is critical. Compared to polycarbonate, POM exhibits greater resistance to wear and chemicals, although it is less transparent, which limits its use in standard optical lenses but suits protective and specialized eyewear components.
What is Polycarbonate (PC)?
Polycarbonate (PC) is a highly durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used for eyeglass lenses due to its lightweight nature and superior shatter protection. It offers excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for everyday eyewear and safety glasses. Compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), polycarbonate provides better transparency and resistance to impact, while POM is more suited for mechanical parts rather than optical applications.
Optical Clarity: POM vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior optical clarity compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), with a higher light transmittance of approximately 88-90%, making them ideal for eyeglass applications where clear vision is critical. Polyoxymethylene's optical clarity is lower due to its semi-crystalline structure, resulting in slightly more light scattering and less transparency. The refractive index of polycarbonate is around 1.586, enhancing visual sharpness and reducing distortions compared to POM, which typically has a refractive index near 1.52.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate lenses exhibit significantly higher impact resistance than polyoxymethylene, making them the preferred choice for eyeglass lenses in safety and sports applications. Polycarbonate's impact strength typically exceeds 250 ft-lbs/in, while polyoxymethylene's impact resistance is considerably lower due to its rigidity and brittleness. This superior durability ensures polycarbonate lenses better withstand drops and impacts, reducing the likelihood of cracks or shattering during everyday use.
Weight and Comfort for Eyewear
Polyoxymethylene (POM) lenses are significantly lighter than polycarbonate lenses, enhancing overall comfort during prolonged wear. Polycarbonate lenses, while slightly heavier, offer superior impact resistance but may cause more fatigue due to their increased weight. Choosing POM can improve daily comfort for eyeglass users prioritizing lightweight design without compromising lens durability.
Scratch Resistance and Durability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits high scratch resistance and excellent durability, making it less prone to surface damage compared to polycarbonate lenses. Polycarbonate lenses are impact-resistant but tend to scratch more easily without additional coatings. For eyeglass lenses prioritizing longevity and scratch prevention, POM offers superior performance, while polycarbonate provides better impact-related durability.
Cost Considerations for Lens Manufacturing
Polyoxymethylene (POM) lenses generally offer a lower material cost compared to polycarbonate, making them an attractive choice for budget-conscious eyeglass manufacturers. Polycarbonate, while more expensive, provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity that justify the higher price for premium eyewear. Cost considerations also include manufacturing processes, where POM's ease of molding can reduce production time and expenses, while polycarbonate requires more precise handling and finishing.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Polyoxymethylene (POM) eyeglass lenses offer high chemical resistance and durability, but their production involves formaldehyde release, raising environmental concerns. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and UV protection while being BPA-free and recyclable, making them a safer and more eco-friendly choice. Polycarbonate's lower carbon footprint and compliance with safety standards position it as the preferred material for sustainable eyewear lenses.
Which Material is Best for Eyeglass Lenses?
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance and UV protection compared to polyoxymethylene, making them a safer and more durable choice for eyeglass lenses. Polyoxymethylene, while lightweight and dimensionally stable, lacks the optical clarity and scratch resistance critical for daily eyewear use. For robust performance and safety in eyeglass applications, polycarbonate remains the preferred material.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com