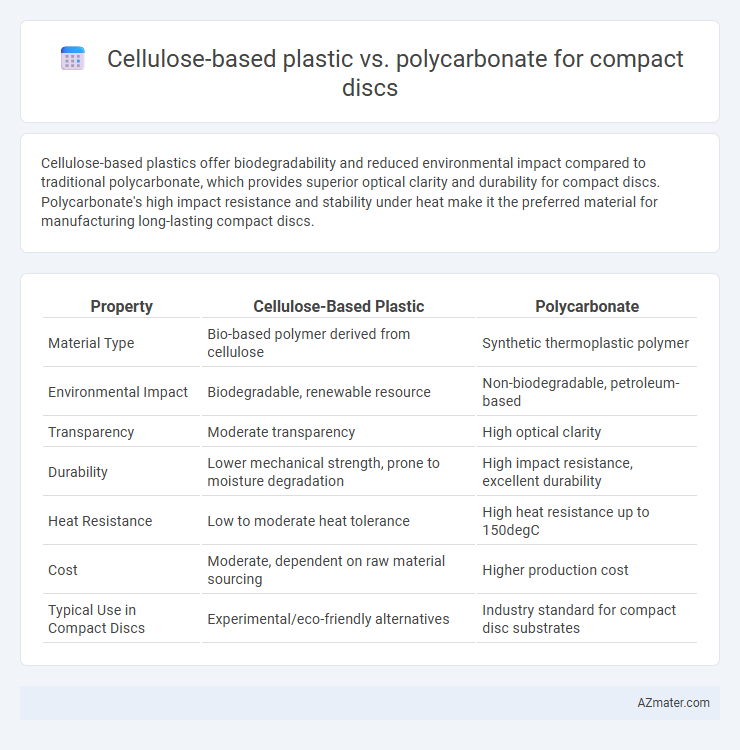
Cellulose-based plastics offer biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional polycarbonate, which provides superior optical clarity and durability for compact discs. Polycarbonate's high impact resistance and stability under heat make it the preferred material for manufacturing long-lasting compact discs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose-Based Plastic | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bio-based polymer derived from cellulose | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Transparency | Moderate transparency | High optical clarity |
| Durability | Lower mechanical strength, prone to moisture degradation | High impact resistance, excellent durability |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate heat tolerance | High heat resistance up to 150degC |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on raw material sourcing | Higher production cost |
| Typical Use in Compact Discs | Experimental/eco-friendly alternatives | Industry standard for compact disc substrates |
Introduction to Compact Disc Materials
Compact discs commonly utilize polycarbonate due to its high optical clarity, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, which ensure accurate data reading and durability. Cellulose-based plastics, although biodegradable and environmentally friendly, generally lack the mechanical strength and clarity required for reliable optical data storage. Advances in material science aim to enhance cellulose-based polymers for potential use in compact disc production, balancing sustainability with performance demands.
Overview of Cellulose-Based Plastics
Cellulose-based plastics, derived from natural polymers found in plant cell walls, provide a biodegradable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics like polycarbonate in compact disc manufacturing. These materials offer good transparency, mechanical strength, and resistance to heat, making them suitable for optical media applications while reducing reliance on petroleum-based resources. Their biodegradability and lower carbon footprint enhance sustainability efforts compared to polycarbonate, which is known for its durability but poses environmental disposal challenges.
Polycarbonate: The Standard for Compact Discs
Polycarbonate is the standard material for compact discs due to its exceptional clarity, durability, and resistance to physical and chemical damage, providing reliable data storage and playback performance. Unlike cellulose-based plastics, polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability, ensuring longevity and minimal data degradation over time. Its precise molding capabilities enable the accurate encoding of digital information, making polycarbonate the preferred choice in the optical disc industry.
Environmental Impact of Cellulose-Based Plastics
Cellulose-based plastics used in compact discs offer significant environmental advantages due to their biodegradability and renewable origin, reducing landfill accumulation and fossil fuel dependency compared to polycarbonate discs. The production of cellulose plastics involves lower carbon emissions and energy consumption, contributing to a smaller ecological footprint. Unlike polycarbonate, which is derived from petroleum and resistant to degradation, cellulose plastics decompose naturally, enhancing sustainability in media manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity: Cellulose vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate offers superior durability and longevity compared to cellulose-based plastic for compact discs due to its high impact resistance and resistance to cracking under stress. Cellulose-based plastics are more prone to degradation over time as they absorb moisture and are less resistant to environmental factors such as UV exposure. Polycarbonate's robust structure ensures consistent data integrity and a longer lifespan in various conditions, making it the preferred material for compact disc manufacturing.
Optical Clarity and Data Integrity
Cellulose-based plastics offer moderate optical clarity, which can cause slight signal distortion in compact discs, whereas polycarbonate provides superior transparency, enhancing laser read accuracy and reducing data errors. Polycarbonate's higher resistance to physical and environmental degradation maintains the integrity of the disc's data layer, ensuring reliable long-term storage. The molecular stability and minimal birefringence in polycarbonate optimize optical clarity, making it the preferred material for compact disc manufacturing over cellulose-based alternatives.
Production Costs and Manufacturing Processes
Cellulose-based plastics for compact discs offer lower production costs due to the use of abundant renewable biomass materials and simpler polymerization techniques compared to polycarbonate, which relies on petroleum-derived monomers and more complex, energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Manufacturing cellulose-based discs involves fewer hazardous chemicals and operates at lower temperatures, reducing overall environmental impact and operational expenses. Polycarbonate discs, while providing superior durability and optical clarity, require precise injection molding and polishing steps that increase production time and costs.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Disposal
Cellulose-based plastic offers superior biodegradability compared to polycarbonate, breaking down more efficiently in natural environments, which significantly reduces long-term waste accumulation from compact discs. In contrast, polycarbonate, a petroleum-based polymer widely used for CDs, resists degradation and poses challenges in recycling processes, often ending in landfill or incineration. The end-of-life disposal of cellulose-based CDs aligns better with sustainable waste management practices, promoting composting or eco-friendly degradation, whereas polycarbonate discs demand specialized recycling systems to mitigate environmental impact.
Market Adoption and Industry Trends
Cellulose-based plastics, valued for their biodegradability, have seen limited adoption in compact disc production due to durability concerns, whereas polycarbonate dominates the market with over 90% share because of its superior optical clarity and impact resistance. Recent industry trends emphasize sustainability, prompting research into enhanced cellulose composites, but polycarbonate remains preferred for mass production and long-term data storage reliability. Market forecasts predict steady demand for polycarbonate CDs despite digital media growth, with niche applications exploring cellulose-based alternatives for eco-friendly packaging and limited-run discs.
Future Prospects for Sustainable CD Materials
Cellulose-based plastics offer a renewable and biodegradable alternative to traditional polycarbonate, addressing the environmental concerns tied to CD production and disposal. Advances in bio-based polymers and improved durability of cellulose composites enhance their potential to meet performance standards required for optical media. Future prospects suggest a shift towards integrating sustainable materials like cellulose, reducing carbon footprint while maintaining the reliability and clarity essential for compact disc functionality.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Polycarbonate for Compact disc
 azmater.com
azmater.com