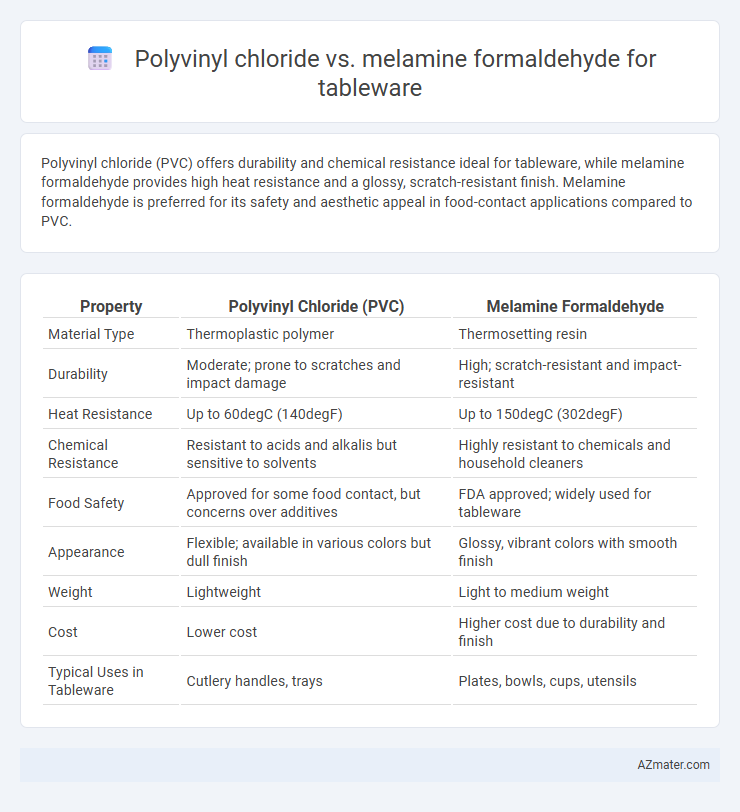
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers durability and chemical resistance ideal for tableware, while melamine formaldehyde provides high heat resistance and a glossy, scratch-resistant finish. Melamine formaldehyde is preferred for its safety and aesthetic appeal in food-contact applications compared to PVC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Melamine Formaldehyde |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermosetting resin |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to scratches and impact damage | High; scratch-resistant and impact-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60degC (140degF) | Up to 150degC (302degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis but sensitive to solvents | Highly resistant to chemicals and household cleaners |
| Food Safety | Approved for some food contact, but concerns over additives | FDA approved; widely used for tableware |
| Appearance | Flexible; available in various colors but dull finish | Glossy, vibrant colors with smooth finish |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to medium weight |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to durability and finish |
| Typical Uses in Tableware | Cutlery handles, trays | Plates, bowls, cups, utensils |
Introduction to Tableware Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and melamine formaldehyde are popular materials for manufacturing durable tableware, each offering distinct properties suited for different applications. PVC provides flexibility, water resistance, and affordability, making it suitable for casual and outdoor use, whereas melamine formaldehyde is prized for its hardness, scratch resistance, and heat stability, ideal for formal dining and high-use environments. Understanding the chemical composition and performance characteristics of these materials helps manufacturers and consumers select tableware that balances durability, aesthetics, and safety.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used synthetic plastic polymer known for its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness in tableware manufacturing. PVC exhibits excellent moisture resistance, making it suitable for reusable or disposable plates, cups, and cutlery, while its flexibility allows for varied designs and colors. However, concerns about the release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal have impacted its acceptance compared to alternatives like Melamine Formaldehyde.
Overview of Melamine Formaldehyde
Melamine formaldehyde is a thermosetting plastic known for its high durability, heat resistance, and glossy finish, making it ideal for tableware like plates and bowls. Unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC), melamine formaldehyde offers superior hardness and scratch resistance while being non-toxic and BPA-free, ensuring food safety. Its lightweight and shatterproof properties combined with easy maintenance contribute to its popularity in both residential and commercial dining settings.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits high flexibility, excellent chemical resistance, and moderate heat tolerance, making it suitable for lightweight tableware that requires durability and low maintenance. Melamine formaldehyde offers superior hardness, higher heat resistance up to 160degC, and enhanced scratch resistance, ideal for rigid, long-lasting dishware with a glossy finish. While PVC tends to be softer and more impact-resistant, melamine formaldehyde provides better dimensional stability and resistance to staining under regular use.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits high chemical resistance against acids and alkalis, making it suitable for various tableware applications, but may release harmful plasticizers affecting food safety. Melamine formaldehyde offers superior heat resistance and does not leach chemicals into food, ensuring higher safety standards for tableware use. For food safety, melamine formaldehyde is generally preferred due to its inert nature and compliance with regulatory standards, whereas PVC requires careful formulation to minimize toxic exposure.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers moderate durability but is prone to scratching and deformation over time, reducing its lifespan for tableware applications. Melamine formaldehyde exhibits superior hardness and resistance to heat, chemicals, and impact, resulting in longer-lasting, durable tableware. The lifespan of melamine formaldehyde tableware often exceeds that of PVC, making it a preferred choice for high-use environments.
Design and Aesthetic Options
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers versatile design possibilities with its ability to be easily molded into various shapes and tinted in a wide palette of colors, making it popular for vibrant and customizable tableware. Melamine formaldehyde excels in providing a high-gloss, polished finish that mimics ceramic or porcelain, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of tableware with elegant patterns and sophisticated textures. Both materials are durable, but melamine's resistance to scratches and heat supports long-lasting visual appeal, whereas PVC allows more flexibility in intricate or playful designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits significant environmental challenges due to its production process releasing toxic chemicals like dioxins and its difficulty in recycling, contributing to long-term pollution and landfill accumulation. Melamine formaldehyde, a thermosetting plastic, offers better durability and lower toxicity upon disposal but poses sustainability concerns because it is derived from fossil fuels and is not biodegradable, complicating waste management. Choosing between the two requires prioritizing either reduced chemical hazards (melamine formaldehyde) or lower lifecycle pollution and recyclability, where both materials have inherent environmental trade-offs.
Cost Analysis for Manufacturers and Consumers
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tableware offers a lower production cost for manufacturers due to its inexpensive raw materials and ease of processing, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers. Melamine formaldehyde, while more costly to produce because of its complex resin synthesis and higher durability standards, provides greater longevity and resistance to heat and scratches, potentially reducing replacement frequency for users. Manufacturers must balance PVC's affordability with melamine formaldehyde's premium quality features when targeting different market segments and price points.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Tableware
Melamine formaldehyde is the best choice for tableware due to its superior heat resistance, durability, and non-toxic properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Unlike PVC, which can release harmful chemicals when heated, melamine formaldehyde maintains safety and structural integrity under high temperatures. This makes melamine formaldehyde optimal for everyday use and long-term durability in tableware applications.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Melamine formaldehyde for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com