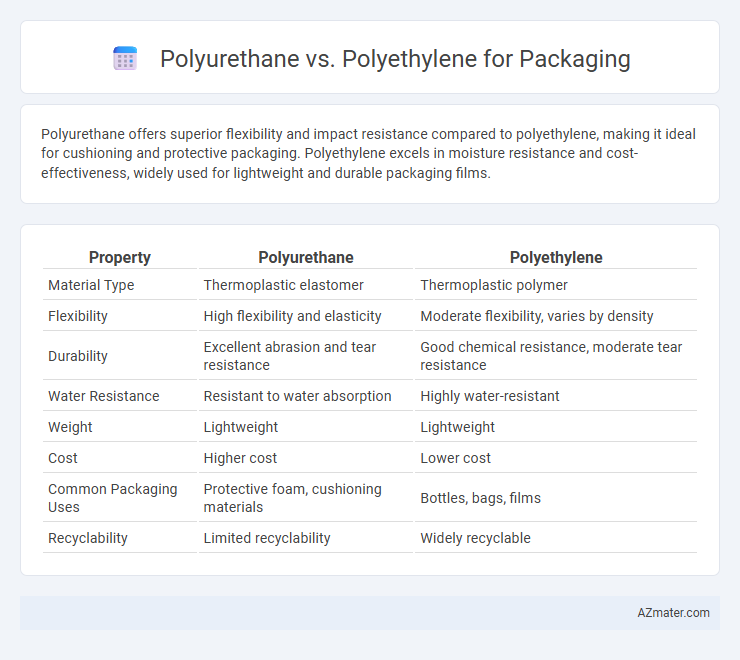
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for cushioning and protective packaging. Polyethylene excels in moisture resistance and cost-effectiveness, widely used for lightweight and durable packaging films.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, varies by density |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance | Good chemical resistance, moderate tear resistance |
| Water Resistance | Resistant to water absorption | Highly water-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Packaging Uses | Protective foam, cushioning materials | Bottles, bags, films |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyethylene Packaging
Polyurethane packaging is valued for its exceptional flexibility, durability, and impact resistance, making it ideal for protective cushioning and insulation. Polyethylene packaging, widely used due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties, excels in films, bags, and containers. Both materials offer unique advantages that cater to diverse packaging requirements, with polyurethane suited for high-performance protection and polyethylene favored for cost-effective, versatile applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Polyurethane consists of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links, formed through the reaction of diisocyanates and polyols, resulting in a versatile polymer with varying rigidity based on its chemical formulation. Polyethylene is a simple thermoplastic polymer composed of long chains of ethylene monomers (-CH2-CH2-) with a saturated hydrocarbon backbone, known for its high chemical resistance and flexibility. The presence of urethane linkages in polyurethane provides enhanced mechanical properties and adhesion, whereas polyethylene's non-polar, linear or branched structure offers superior moisture barrier and chemical inertness for packaging applications.
Key Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and impact absorbance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), excels in chemical resistance, moisture barrier properties, and tensile strength, suited for rigid packaging solutions. Both materials provide excellent durability, but polyurethane's elastic recovery contrasts with polyethylene's higher stiffness and ease of thermoforming.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polyurethane offers superior durability and tensile strength compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for packaging requiring robust impact resistance and flexibility. Polyethylene, while less durable, provides excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness for lightweight applications. Choosing between polyurethane and polyethylene depends on the packaging's demand for mechanical strength versus economic efficiency.
Flexibility and Cushioning Performance
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and cushioning performance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for packaging fragile or delicate items. Its open-cell structure allows better shock absorption and impact resistance, reducing the risk of damage during transit. Polyethylene, while more rigid, provides adequate protection for heavier or less sensitive goods but lacks the same level of pliability and cushioning as polyurethane.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane packaging offers excellent durability and insulation properties but poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling, often relying on petrochemical sources. Polyethylene is widely used in packaging for its recyclability and lower carbon footprint; however, conventional polyethylene still contributes to plastic pollution unless managed with effective recycling systems or replaced by bio-based alternatives. Sustainable packaging decisions increasingly favor recyclable polyethylene variants and innovations in biodegradable polyurethane composites to reduce ecological impact and support circular economy goals.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Polyethylene offers lower production costs and greater availability, making it a cost-efficient choice for large-scale packaging applications. Polyurethane provides superior durability and cushioning properties but typically involves higher material and processing expenses. Evaluating the balance between upfront investment and product protection is essential for economic decision-making in packaging solutions.
Applications in Packaging Industries
Polyurethane and polyethylene serve distinct roles in packaging industries due to their unique properties; polyurethane excels in cushioning and protective packaging with its high resilience and flexibility, making it ideal for fragile or electronics items. Polyethylene offers excellent moisture resistance and durability, widely used in films, bags, and containers for food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods packaging. The choice between polyurethane and polyethylene depends on the specific application requirements such as impact absorption versus barrier protection.
Pros and Cons of Polyurethane vs Polyethylene
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, durability, and excellent resistance to abrasion and chemicals, making it ideal for protective packaging that requires cushioning and impact absorption. Polyethylene, on the other hand, is highly cost-effective, lightweight, and resistant to moisture and many chemicals, commonly used in films, bags, and containers. While polyurethane provides better mechanical strength and versatility, polyethylene stands out for its recyclability, lower production costs, and widespread availability, which influence packaging choices based on specific application needs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Packaging Needs
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for protective packaging of delicate or high-value items. Polyethylene, known for its lightweight, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties, suits applications requiring cost-effective, durable packaging with moisture protection. Selecting the right packaging material depends on factors such as product fragility, environmental exposure, and budget constraints, ensuring optimal protection and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com