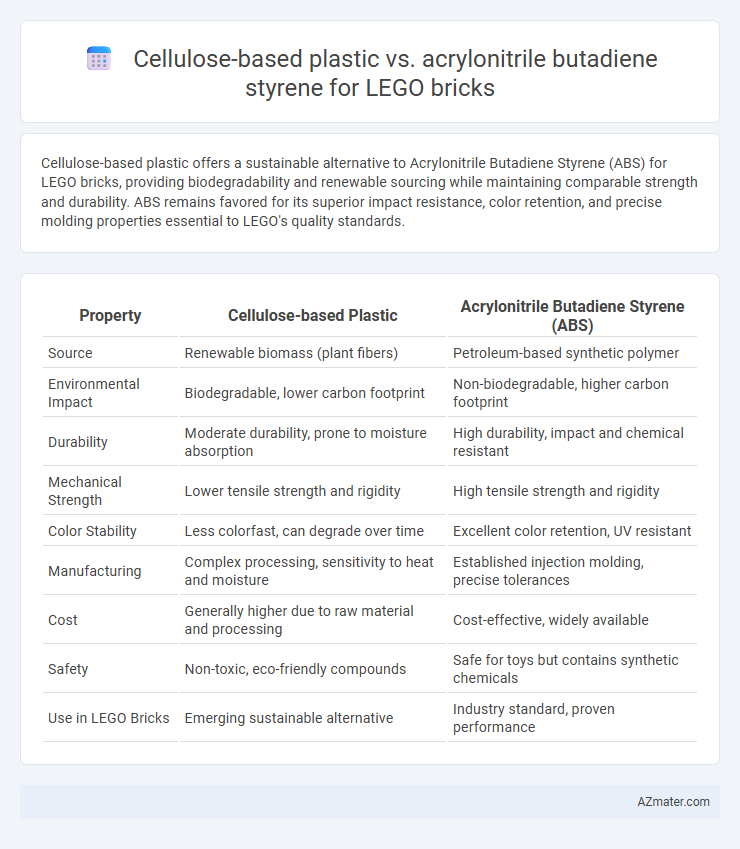
Cellulose-based plastic offers a sustainable alternative to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) for LEGO bricks, providing biodegradability and renewable sourcing while maintaining comparable strength and durability. ABS remains favored for its superior impact resistance, color retention, and precise molding properties essential to LEGO's quality standards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose-based Plastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable biomass (plant fibers) | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate durability, prone to moisture absorption | High durability, impact and chemical resistant |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength and rigidity | High tensile strength and rigidity |
| Color Stability | Less colorfast, can degrade over time | Excellent color retention, UV resistant |
| Manufacturing | Complex processing, sensitivity to heat and moisture | Established injection molding, precise tolerances |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material and processing | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Safety | Non-toxic, eco-friendly compounds | Safe for toys but contains synthetic chemicals |
| Use in LEGO Bricks | Emerging sustainable alternative | Industry standard, proven performance |
Introduction to Sustainable Materials for LEGO Bricks
Cellulose-based plastics offer a renewable, biodegradable alternative to traditional petroleum-based materials like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) used in LEGO bricks. These bioplastics reduce carbon footprint by utilizing plant-derived fibers, promoting circular economy principles in toy manufacturing. Despite ABS's durability and ease of molding, cellulose-based alternatives demonstrate growing potential for sustainable, environmentally friendly LEGO components.
Overview of Cellulose-Based Plastics
Cellulose-based plastics, derived from renewable plant fibers such as wood pulp or cotton, offer a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based polymers like Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). These bioplastics provide biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint while maintaining adequate durability and strength suitable for LEGO bricks. Innovations in cellulose extraction and polymer modification enhance clarity, impact resistance, and molding performance, positioning cellulose-based plastics as promising candidates in eco-friendly toy manufacturing.
Understanding Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, durability, and impact resistance, making it ideal for LEGO bricks that require precise molding and long-lasting performance. Unlike cellulose-based plastics, ABS offers superior dimensional stability and resistance to heat and chemicals, ensuring LEGO bricks maintain their shape and color over time. The material's ability to withstand repeated assembly and disassembly without degradation supports the high standards of LEGO's quality and playability.
Environmental Impact: Cellulose-Based Plastics vs ABS
Cellulose-based plastics significantly reduce environmental impact compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to their renewable origin and biodegradability, leading to lower carbon footprints and less persistent plastic waste. ABS, derived from petroleum, contributes to higher greenhouse gas emissions and generates durable plastic pollution that resists natural degradation. The use of cellulose-based materials in LEGO bricks supports circular economy principles by enabling compostability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Mechanical Properties and Durability Comparison
Cellulose-based plastics exhibit lower impact resistance and tensile strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making ABS more suitable for LEGO bricks that require high durability and mechanical stability. ABS offers superior toughness, resistance to deformation, and better dimensional stability under stress, contributing to LEGO's iconic snap-fit performance and long-lasting use. While cellulose-based plastics are more sustainable, their mechanical properties currently limit their effectiveness in high-performance applications like LEGO bricks.
Color, Texture, and Aesthetic Considerations
Cellulose-based plastic offers a matte finish with a natural, slightly fibrous texture that enhances LEGO bricks' eco-friendly appeal but may limit vibrant color intensity compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS provides a glossy, smooth surface ideal for bright, consistent colors and sharp detailing, ensuring LEGO bricks maintain their iconic aesthetic. The choice between cellulose-based plastic and ABS impacts the visual vibrancy and tactile experience, balancing sustainability with traditional LEGO aesthetics.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Cellulose-based plastic for LEGO bricks leverages renewable biomass sources, requiring specialized compounding and extrusion techniques to maintain durability and precision in molding, with challenges in achieving mass-production scale consistent with traditional plastics. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) benefits from well-established injection molding processes, enabling high-throughput manufacturing with excellent mechanical properties and consistent color fidelity. Scalability favors ABS due to widespread industrial infrastructure and cost efficiency, although advances in bioplastic processing are improving cellulose-based alternatives' feasibility for large-scale LEGO production.
Safety, Non-Toxicity, and Child-Friendliness
Cellulose-based plastic offers a non-toxic, biodegradable alternative to traditional acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) used in LEGO bricks, reducing chemical exposure risks for children. ABS, while durable and impact-resistant, contains synthetic compounds that may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), raising concerns about long-term safety and environmental impact. The cellulose-based variant enhances child-friendliness by utilizing renewable materials with minimal toxic additives, aligning with growing demands for safer, eco-conscious toys.
Cost Analysis and Market Feasibility
Cellulose-based plastic for LEGO bricks offers a renewable alternative with potentially lower raw material costs but faces higher processing expenses and scalability challenges compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which benefits from established supply chains and manufacturing efficiency. ABS maintains a cost advantage due to mature production methods and consistent material properties, driving stronger market feasibility despite environmental concerns. Market adoption of cellulose-based plastics hinges on overcoming production cost barriers and consumer willingness to pay premiums for sustainability.
Future Outlook: Evolving LEGO Brick Materials
Cellulose-based plastics offer a sustainable alternative to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) for LEGO bricks by utilizing renewable resources and providing biodegradability, aligning with global environmental goals. Advances in cellulose nanofiber reinforcement enhance mechanical strength, making these materials increasingly viable for maintaining the durability and precision crucial in LEGO products. Continued innovation in bio-based polymer formulations and scalable manufacturing processes positions cellulose-based plastics as a promising future material for eco-friendly, high-performance LEGO bricks.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for LEGO brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com