Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and higher thermal stability compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for reusable food containers requiring durability. PET provides better clarity and is widely used for single-use food packaging due to its excellent barrier properties and recyclability.
Table of Comparison
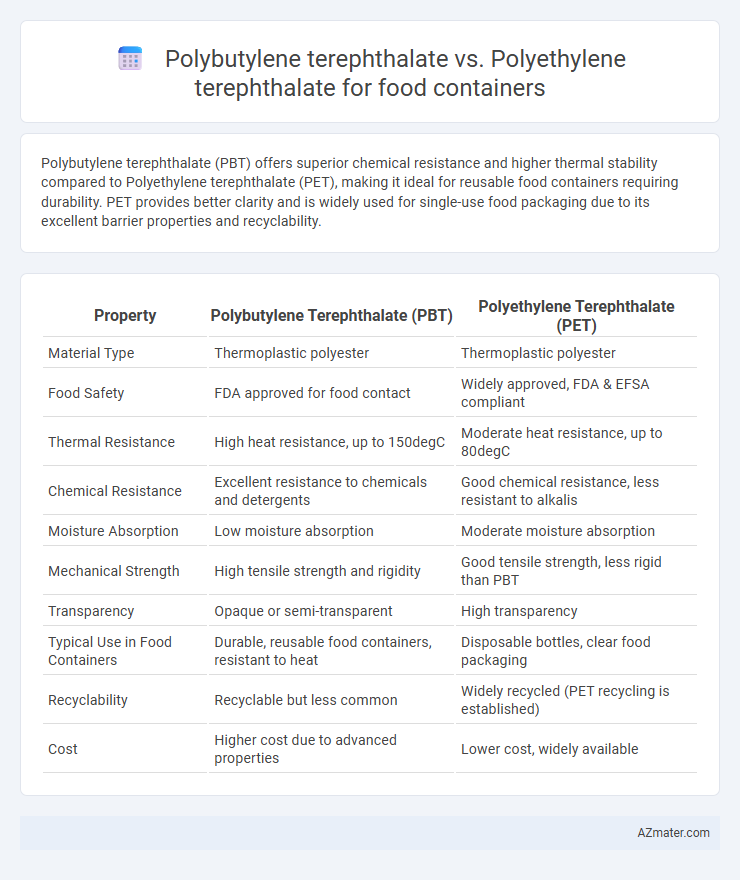
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | Widely approved, FDA & EFSA compliant |
| Thermal Resistance | High heat resistance, up to 150degC | Moderate heat resistance, up to 80degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and detergents | Good chemical resistance, less resistant to alkalis |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Good tensile strength, less rigid than PBT |
| Transparency | Opaque or semi-transparent | High transparency |
| Typical Use in Food Containers | Durable, reusable food containers, resistant to heat | Disposable bottles, clear food packaging |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but less common | Widely recycled (PET recycling is established) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to PBT and PET in Food Packaging
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are both thermoplastic polymers widely used in food packaging due to their durability and resistance to chemicals. PET is favored for its excellent clarity, strong barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, and high recyclability, making it ideal for clear food containers and bottles. PBT offers superior toughness, heat resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for food containers requiring higher temperature tolerance and mechanical strength.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PBT vs PET
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) features a repeating unit with a butylene glycol segment, offering increased flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which contains an ethylene glycol segment. The longer alkylene chain in PBT results in lower crystallinity and a lower melting point than PET, affecting thermal stability and processing conditions for food containers. PET's higher crystallinity and melting temperature provide better barrier properties and chemical resistance, making it more suitable for applications requiring enhanced durability and food safety.
Mechanical Properties Relevant to Food Containers
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior impact resistance and higher dimensional stability compared to polyethytene terephthalate (PET), enhancing durability in food container applications. PET, while having excellent tensile strength and clarity, is less resistant to repeated thermal cycling and mechanical stress, which can lead to deformation or cracking under heavy use. Both polymers exhibit good chemical resistance, but PBT's enhanced toughness and resistance to deformation under load make it a preferable choice for durable, reusable food containers requiring long-term mechanical stability.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits higher thermal resistance and superior heat tolerance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making PBT more suitable for food containers subjected to elevated temperatures such as microwave and dishwasher use. PBT maintains structural integrity and resists deformation at temperatures up to approximately 150degC, whereas PET tends to soften around 70-80degC, limiting its application in high-heat scenarios. The enhanced thermal stability of PBT contributes to safer, longer-lasting containers that withstand repeated heating cycles without compromising food safety or container performance.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior moisture barrier properties compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it more effective at preventing water vapor transmission in food containers. PET exhibits lower oxygen permeability, which enhances its ability to protect food products from oxidation and spoilage. Selecting the appropriate polymer depends on the specific barrier requirements of moisture retention versus gas protection for optimal food preservation.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely preferred over Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) for food containers due to its superior food safety profile and extensive regulatory approvals from agencies like the FDA and EFSA. PET exhibits excellent chemical resistance and low permeability, minimizing the risk of contaminant migration into food products, which is critical for maintaining food quality and safety standards. PBT, while durable, has limited food-grade certifications and higher leaching potential, making PET the industry standard for compliant, safe food packaging applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely preferred for food containers due to its extensive availability and competitive cost, supported by a mature manufacturing infrastructure and high demand in the packaging industry. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), while offering superior mechanical and thermal properties, is less commonly used in food packaging, making it generally more expensive and harder to source in large quantities. The cost-efficiency and abundant supply chain of PET make it the dominant choice for food container applications where affordability and mass production are crucial.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits greater chemical resistance and mechanical strength, which extends the lifespan of food containers and reduces waste generation compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET). PET is more widely recycled globally, with established recycling streams yielding flakes and pellets for new containers, while PBT recycling is less common, often requiring specialized facilities. The lower recycling infrastructure for PBT results in higher environmental impact due to limited reuse options and potential landfill accumulation.
Typical Applications in the Food Industry
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is often utilized in food container components requiring high mechanical strength and heat resistance, such as closures and lids, where durability during thermal processing is essential. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) dominates the food packaging industry with its excellent clarity, lightweight properties, and superior gas barrier performance, making it ideal for beverage bottles, trays, and blister packaging. Both polymers comply with FDA regulations for food contact but are selected based on specific performance needs like flexibility, moisture barrier, and thermal stability in applications such as ready-to-eat meal containers and carbonated drink bottles.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PBT and PET for Food Containers
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is generally preferred for food containers due to its excellent clarity, superior chemical resistance, and strong barrier properties against moisture and gases, ensuring longer shelf life. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers higher thermal stability and impact resistance but lacks the transparency and gas barrier effectiveness required for many food packaging applications. Choosing between PBT and PET depends on the specific needs of the food product, with PET being optimal for clear, lightweight containers and PBT suited for durable, high-temperature resistant applications.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com