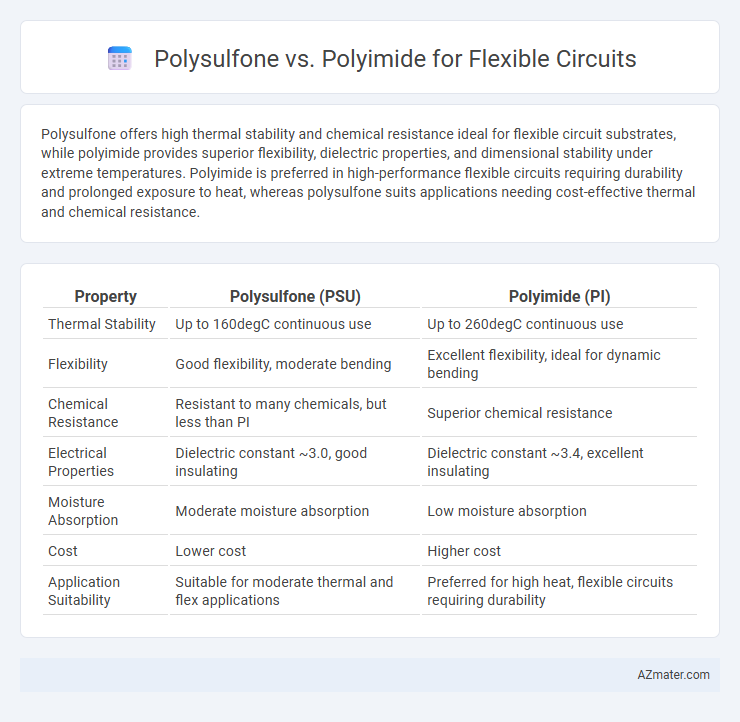
Polysulfone offers high thermal stability and chemical resistance ideal for flexible circuit substrates, while polyimide provides superior flexibility, dielectric properties, and dimensional stability under extreme temperatures. Polyimide is preferred in high-performance flexible circuits requiring durability and prolonged exposure to heat, whereas polysulfone suits applications needing cost-effective thermal and chemical resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyimide (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 160degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, moderate bending | Excellent flexibility, ideal for dynamic bending |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals, but less than PI | Superior chemical resistance |
| Electrical Properties | Dielectric constant ~3.0, good insulating | Dielectric constant ~3.4, excellent insulating |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Application Suitability | Suitable for moderate thermal and flex applications | Preferred for high heat, flexible circuits requiring durability |
Introduction to Flexible Circuit Materials
Polysulfone and polyimide are prominent materials used in flexible circuits due to their excellent thermal stability and mechanical flexibility. Polyimide exhibits superior heat resistance up to 400degC and excellent electrical insulation, making it a preferred choice for high-performance flexible circuits. Polysulfone offers good chemical resistance and dimensional stability but generally operates at lower temperatures compared to polyimide, making it suitable for applications with moderate thermal requirements.
Overview of Polysulfone
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 180degC, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for flexible circuit substrates. Its inherent toughness and transparency, combined with good dimensional stability, ensure reliable performance in harsh environments and repeated flexing applications. Polysulfone's dielectric properties support signal integrity, making it an effective material for flexible circuits requiring durability and consistent electrical insulation.
Overview of Polyimide
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer widely used in flexible circuits due to its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical flexibility. It maintains structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 400degC, making it ideal for advanced electronic applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Compared to polysulfone, polyimide offers superior electrical insulation and flexibility, enhancing the reliability of flexible circuit substrates in demanding environments.
Material Properties Comparison
Polysulfone offers high thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to 150degC and excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for flexible circuits exposed to moderate heat and harsh environments. Polyimide surpasses polysulfone with superior thermal endurance, tolerating continuous use temperatures above 200degC and providing exceptional dielectric strength and mechanical flexibility, ideal for high-performance flexible circuits. Both materials exhibit low moisture absorption and dimensional stability, but polyimide's enhanced heat resistance and electrical insulation make it the preferred choice for demanding flexible circuit applications.
Thermal Stability: Polysulfone vs Polyimide
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polysulfone, maintaining integrity at temperatures up to 400degC, while polysulfone typically withstands up to 180degC. This high thermal resistance makes polyimide the preferred choice for flexible circuits operating in high-temperature environments such as aerospace and automotive electronics. Polysulfone's lower thermal tolerance limits its application to less demanding thermal conditions where flexibility and moderate heat resistance are sufficient.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polysulfone offers excellent mechanical strength with high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for durable flexible circuits that require robust performance under stress. Polyimide excels in flexibility and thermal stability, maintaining mechanical integrity in extreme temperature environments, which is critical for flexible circuits subject to bending and thermal cycling. Choosing between polysulfone and polyimide depends on the application's mechanical strength requirements versus the need for flexibility and thermal endurance.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Polysulfone demonstrates superior chemical resistance in flexible circuits, offering excellent stability against acids, bases, and solvents, maintaining performance in harsh chemical environments. Polyimide provides high chemical resistance as well but can degrade under prolonged exposure to strong alkalis and certain solvents, limiting its use in aggressive chemical applications. Therefore, polysulfone is preferred in flexible circuits requiring enhanced durability and consistent chemical stability in corrosive settings.
Processability and Manufacturing Considerations
Polysulfone offers superior processability for flexible circuits due to its excellent thermal stability and ease of extrusion, enabling efficient mass production with consistent film thickness. Polyimide, while providing higher thermal resistance and mechanical strength, presents more complex processing requirements such as longer curing times and sensitivity to moisture during manufacturing. Manufacturers often select polysulfone for cost-effective, rapid fabrication, whereas polyimide is preferred for high-performance applications demanding enhanced durability and thermal endurance.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polysulfone offers a more cost-effective solution for flexible circuits due to its lower manufacturing expenses and widespread commercial availability, making it an attractive option for budget-sensitive projects. Polyimide, while more expensive, provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, which justifies its higher price in high-performance applications. Availability of polysulfone is generally better across global markets, whereas polyimide may require sourcing from specialized suppliers, impacting lead times and overall project costs.
Applications in Flexible Circuit Design
Polysulfone offers high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for flexible circuits used in automotive sensors and medical devices. Polyimide excels in electrical insulation and flexibility, suited for high-density interconnects and aerospace flexible circuits. Both materials support diverse flexible circuit designs, with polysulfone preferred for moderate flexibility and polyimide favored for extreme flexibility and thermal endurance.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyimide for Flexible Circuit
 azmater.com
azmater.com