Cellulose-based plastic film wrap offers superior biodegradability and compostability compared to polypropylene, which is petroleum-derived and non-biodegradable. Polypropylene provides higher moisture resistance and mechanical strength, making it more durable for long-term food packaging.
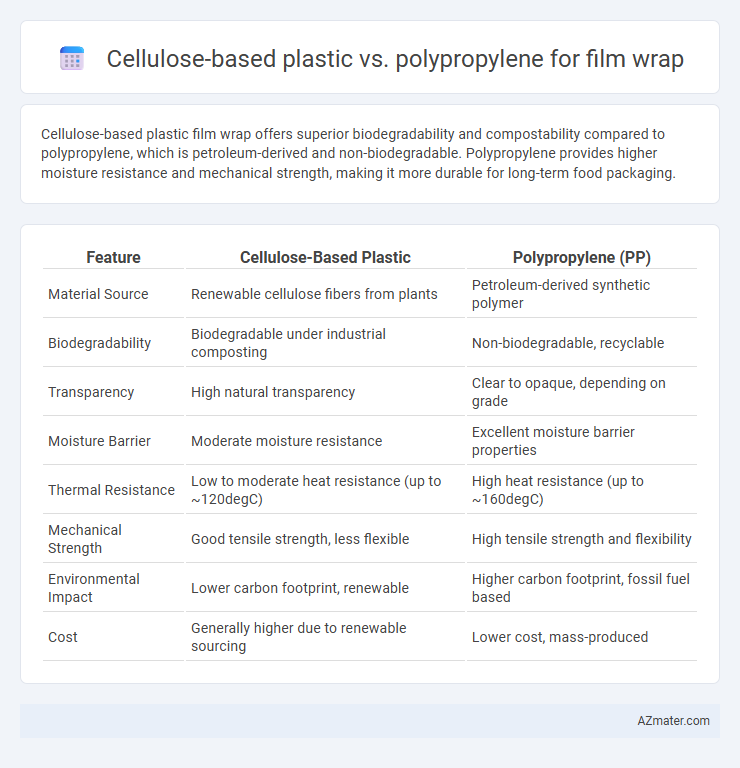
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellulose-Based Plastic | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable cellulose fibers from plants | Petroleum-derived synthetic polymer |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable under industrial composting | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Transparency | High natural transparency | Clear to opaque, depending on grade |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture resistance | Excellent moisture barrier properties |
| Thermal Resistance | Low to moderate heat resistance (up to ~120degC) | High heat resistance (up to ~160degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, less flexible | High tensile strength and flexibility |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, renewable | Higher carbon footprint, fossil fuel based |
| Cost | Generally higher due to renewable sourcing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Film Wrap Materials
Cellulose-based plastic and polypropylene are key materials used in film wrap production, each offering distinct environmental and functional benefits. Cellulose-based plastic, derived from renewable plant fibers, provides biodegradability and compostability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics. Polypropylene, a synthetic polymer, stands out for its strength, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring durable and versatile film wrap applications.
Overview of Cellulose-Based Plastic
Cellulose-based plastic, derived from renewable plant fibers such as wood pulp or cotton, offers a biodegradable and compostable alternative to conventional plastics like polypropylene used in film wrap applications. This bioplastic exhibits excellent oxygen and moisture barrier properties, making it suitable for food packaging that requires freshness preservation. Unlike polypropylene, cellulose-based films have a lower carbon footprint and contribute to reduced plastic pollution due to their natural origin and enhanced environmental compatibility.
Understanding Polypropylene Film Wrap
Polypropylene film wrap offers superior moisture resistance and tensile strength compared to cellulose-based plastic, making it ideal for preserving freshness in food packaging. Its chemical inertness and low oxygen permeability enhance shelf life while supporting recyclability through established polypropylene recycling streams. Understanding polypropylene's heat sealability and clarity aids in selecting optimal film wraps for durability and visualization in various packaging applications.
Key Properties Comparison
Cellulose-based plastic film wrap offers superior biodegradability and compostability compared to polypropylene, making it an eco-friendly alternative in packaging applications. Polypropylene film wrap exhibits higher tensile strength, moisture resistance, and thermal stability, which ensures better performance in extending product shelf life and withstanding varied storage conditions. The choice between cellulose-based and polypropylene films depends on balancing environmental impact with mechanical durability and barrier properties required for specific use cases.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Cellulose-based plastic film wrap offers significant environmental advantages over polypropylene, primarily due to its biodegradability and renewable source from plant fibers, which reduces reliance on fossil fuels and decreases landfill waste. Polypropylene, while durable and recyclable, is derived from petrochemicals and contributes to microplastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions during production and disposal. Life cycle analyses indicate cellulose films have a lower carbon footprint and greater potential for composting, making them a more sustainable choice for reducing plastic pollution in packaging applications.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Cellulose-based plastic offers superior biodegradability and compostability compared to polypropylene, as it naturally decomposes through microbial activity within weeks in industrial composting conditions. Polypropylene, a petroleum-based polymer, is resistant to biodegradation and can persist in the environment for decades, contributing to plastic pollution. Choosing cellulose-based film wrap significantly reduces environmental impact by breaking down into non-toxic organic matter, aligning with sustainable packaging goals.
Barrier Performance and Shelf Life
Cellulose-based plastic offers excellent oxygen barrier properties, reducing oxidation and extending the shelf life of food products compared to polypropylene, which has moderate gas permeability. Polypropylene provides superior moisture resistance but lower oxygen barrier performance, making it less effective in preventing spoilage caused by air exposure. Combining cellulose-based films with moisture barriers can optimize overall protection and prolong shelf life in food packaging applications.
Cost and Production Considerations
Cellulose-based plastic film wrap offers biodegradable advantages but typically incurs higher production costs due to raw material processing and lower economies of scale compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene, widely used in film wrap manufacturing, benefits from established large-scale production techniques, resulting in lower unit costs and faster production rates. Cost efficiency and manufacturing infrastructure make polypropylene the preferred choice for high-volume, cost-sensitive applications despite environmental concerns.
Typical Applications and Market Trends
Cellulose-based plastic film is widely used in eco-friendly packaging for food products and pharmaceutical wraps due to its biodegradability and compostability, appealing to sustainable market demands. Polypropylene film dominates the market in applications requiring high moisture resistance and mechanical strength, such as industrial packaging, retail bags, and agricultural films. Growing consumer preference for sustainable solutions is driving increased adoption of cellulose-based films, while polypropylene maintains strong market presence due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Future Prospects in Sustainable Packaging
Cellulose-based plastic offers significant advantages for sustainable film wraps due to its biodegradability and renewable raw material base, reducing environmental impact compared to polypropylene. Emerging innovations in enhancing cellulose film durability and moisture resistance could drive broader adoption in packaging markets seeking eco-friendly alternatives. Polypropylene remains widely used for its cost-effectiveness and mechanical strength, but growing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener options point toward a transition favoring cellulose-based films in the future.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Polypropylene for Film wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com