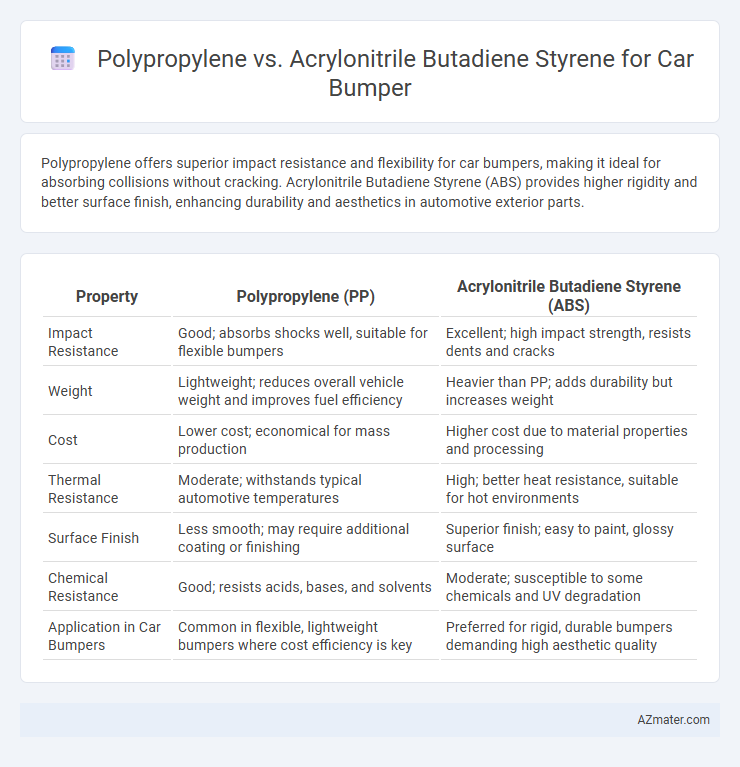
Polypropylene offers superior impact resistance and flexibility for car bumpers, making it ideal for absorbing collisions without cracking. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides higher rigidity and better surface finish, enhancing durability and aesthetics in automotive exterior parts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Good; absorbs shocks well, suitable for flexible bumpers | Excellent; high impact strength, resists dents and cracks |
| Weight | Lightweight; reduces overall vehicle weight and improves fuel efficiency | Heavier than PP; adds durability but increases weight |
| Cost | Lower cost; economical for mass production | Higher cost due to material properties and processing |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; withstands typical automotive temperatures | High; better heat resistance, suitable for hot environments |
| Surface Finish | Less smooth; may require additional coating or finishing | Superior finish; easy to paint, glossy surface |
| Chemical Resistance | Good; resists acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate; susceptible to some chemicals and UV degradation |
| Application in Car Bumpers | Common in flexible, lightweight bumpers where cost efficiency is key | Preferred for rigid, durable bumpers demanding high aesthetic quality |
Introduction to Car Bumper Materials
Car bumpers commonly utilize polypropylene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) due to their excellent impact resistance and durability. Polypropylene offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for absorbing low-speed impacts, while ABS provides higher rigidity and better paint adhesion, enhancing aesthetic appeal and structural support. Selecting between polypropylene and ABS depends on desired performance characteristics, manufacturing processes, and cost efficiency in automotive applications.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight thermoplastic polymer widely used in car bumper manufacturing due to its excellent chemical resistance, impact strength, and flexibility. Its low density and high fatigue resistance make it an ideal material for automotive exterior components, providing durability and energy absorption during collisions. PP also offers cost-effective production with good recyclability, making it a preferred choice in sustainable car bumper applications.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in car bumpers due to its excellent impact resistance and toughness. Its combination of acrylonitrile for chemical resistance, butadiene for impact strength, and styrene for rigidity makes ABS ideal for absorbing collision energy while maintaining structural integrity. ABS offers superior aesthetic finish and ease of manufacturing through injection molding, which contributes to its extensive use in automotive exterior components compared to polypropylene.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) offers high impact resistance and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for energy absorption in car bumpers, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior tensile strength and rigidity, ensuring structural integrity under stress. PP typically exhibits elongation at break values of 200-600%, compared to ABS's 20-50%, indicating greater ductility and ability to deform without breaking. ABS's tensile strength ranges around 40 MPa, higher than PP's 30 MPa, making ABS better suited for applications where stiffness and dimensional stability are critical.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polypropylene offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it highly effective in absorbing low to moderate collision forces for car bumpers, while maintaining durability under various environmental conditions. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior rigidity and toughness, delivering enhanced resistance to high-impact forces and maintaining structural integrity over time. Both materials exhibit strong durability, but ABS typically offers better long-term performance against physical wear and heat exposure in automotive applications.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Polypropylene offers a lightweight solution for car bumpers, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. Its exceptional design flexibility allows for complex shapes and seamless integrations, enhancing aesthetic appeal and impact absorption. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), while heavier, provides rigid structural strength but lacks the same versatility in molding intricate designs or achieving significant weight reduction.
Cost Analysis: PP vs ABS
Polypropylene (PP) offers a lower raw material cost compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it a cost-effective choice for car bumpers. Manufacturing processes for PP typically require less energy and shorter cycle times, further reducing production expenses. However, ABS provides superior impact resistance and surface finish, which may justify its higher cost in applications demanding enhanced durability and aesthetics.
Environmental Considerations and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior recyclability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), as it can be reprocessed multiple times without significant degradation, reducing automotive plastic waste. ABS contains styrene and acrylonitrile compounds that pose greater environmental disposal challenges and lower recycling rates due to its complex polymer structure. The lower carbon footprint and chemical stability of polypropylene contribute to its preference in eco-friendly car bumper manufacturing.
Industry Applications and Preferences
Polypropylene (PP) is widely favored in car bumper manufacturing due to its excellent impact resistance, lightweight nature, and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for mass production and cost efficiency in the automotive industry. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers higher rigidity, better surface finish, and enhanced heat resistance, preferred in premium vehicle models requiring durable aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. Industry trends show PP dominates in economy and mid-range cars for its recyclability and affordability, while ABS is chosen for luxury segments demanding higher mechanical strength and refined appearance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Car Bumpers
Polypropylene offers excellent impact resistance, low cost, and good chemical resistance, making it a popular choice for car bumpers designed for everyday use and minor collisions. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior strength, rigidity, and better surface finish, ideal for vehicles requiring enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, cost constraints, and the specific environmental conditions the bumper will face.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Car Bumper
 azmater.com
azmater.com