Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and gas barrier properties, making it ideal for transparent, carbonated water bottles. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) provides excellent chemical resistance and durability, suitable for opaque, heavy-duty water containers.
Table of Comparison
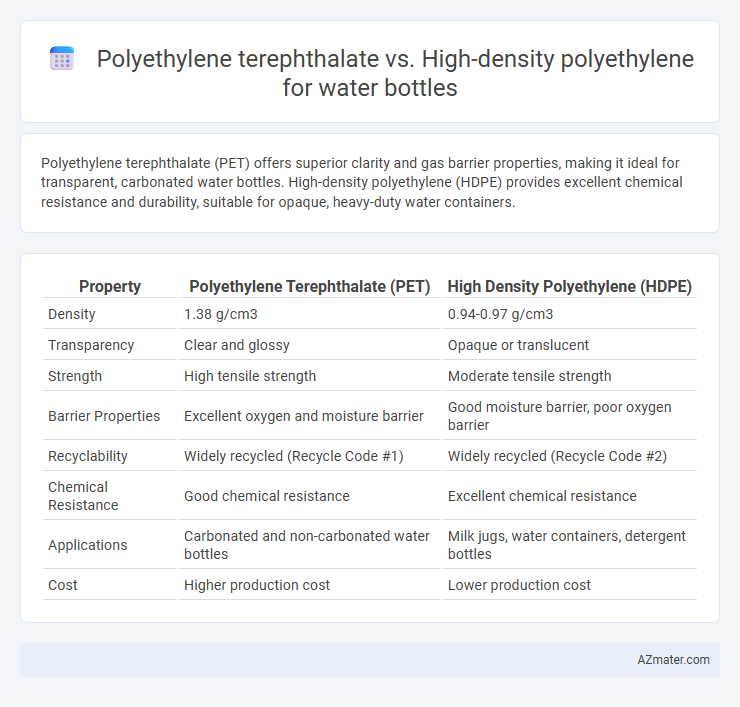
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 0.94-0.97 g/cm3 |
| Transparency | Clear and glossy | Opaque or translucent |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier | Good moisture barrier, poor oxygen barrier |
| Recyclability | Widely recycled (Recycle Code #1) | Widely recycled (Recycle Code #2) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good chemical resistance | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Applications | Carbonated and non-carbonated water bottles | Milk jugs, water containers, detergent bottles |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Water Bottle Plastics: PET vs HDPE
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) dominate the water bottle market due to their distinct properties and environmental impact. PET offers excellent clarity, lightweight strength, and superior gas barrier capabilities, making it ideal for single-use water bottles that preserve freshness and carbonation. HDPE provides high chemical resistance, durability, and recyclability, favoring reusable and opaque bottles that support long-term water storage and environmental sustainability.
Chemical Composition: PET and HDPE Explained
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a polyester polymer characterized by repeating units of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, providing excellent transparency and strength for water bottles. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) consists of long chains of ethylene monomers with minimal branching, resulting in a rigid, opaque material with superior chemical resistance. PET's ester linkages contribute to its clarity and barrier properties, while HDPE's saturated hydrocarbon structure offers enhanced durability and resistance to impact and moisture.
Manufacturing Processes for PET and HDPE Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are typically manufactured using injection stretch blow molding, which involves heating PET preforms before stretching and blowing them into bottle molds, resulting in clear, lightweight containers with excellent strength and barrier properties. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles are produced through injection molding followed by blow molding, creating opaque, durable bottles with high chemical resistance and flexibility. The differences in manufacturing processes impact the material properties, recyclability, and suitability of PET for carbonated beverages versus HDPE for milk or detergent containers.
Physical Properties: Strength, Weight, and Durability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior strength and clarity compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it ideal for water bottles requiring rigidity and transparency. PET is lighter than HDPE, enhancing portability and user convenience. Despite HDPE's higher impact resistance and chemical durability, PET's balance of strength and lightweight qualities makes it the preferred choice for single-use and recyclable water bottles.
Barrier Performance: Oxygen and Moisture Protection
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior barrier performance against oxygen and moisture compared to high density polyethylene (HDPE), making it the preferred choice for water bottles requiring enhanced freshness preservation. PET's crystalline structure significantly reduces oxygen permeability, effectively preventing oxidation and extending product shelf life. In contrast, HDPE's higher oxygen and moisture transmission rates result in less protection, limiting its suitability for applications demanding stringent barrier requirements.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used for water bottles due to its strong barrier properties and BPA-free composition, making it generally safe for single use but potentially prone to leaching antimony when exposed to heat or prolonged storage. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior chemical resistance and durability, often regarded as safer for repeated use and recycling, with minimal risk of harmful chemical migration. Both materials meet regulatory standards, but HDPE's higher resistance to cracking and chemical leaching provides an advantage for long-term health safety in water bottle applications.
Environmental Impact: Recyclability and Sustainability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely favored in water bottle production due to its high recyclability and strong recycling infrastructure, reducing environmental impact by enabling efficient material recovery and reuse. High density polyethylene (HDPE) offers robust durability and is also recyclable, but its lower market demand for recycled HDPE can limit closed-loop recycling efforts compared to PET. PET's lighter weight and transparent quality enhance its sustainability profile by reducing transportation emissions and facilitating consumer recycling participation.
Cost Comparison: PET vs HDPE Water Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) water bottles generally have a higher production cost compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles due to PET's superior clarity and barrier properties. HDPE bottles offer a more cost-effective solution, especially for opaque or less visually demanding applications, with raw material costs and manufacturing processes being less expensive. The choice between PET and HDPE frequently hinges on budget constraints balanced against desired product qualities and consumer preferences.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely preferred for water bottles due to its excellent clarity, lightweight nature, and strong barrier properties that effectively preserve water freshness and prevent contamination. High density polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior chemical resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for opaque bottles and applications requiring durability over transparency. Selecting between PET and HDPE depends on the desired bottle clarity, strength requirements, and environmental considerations such as recyclability and production footprint.
Conclusion: Which Plastic is Best for Water Bottles?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, lightweight properties, and excellent gas barrier performance, making it ideal for maintaining water freshness. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) provides higher chemical resistance and durability but lacks the transparency and carbonation retention of PET. For most consumer water bottles, PET is the preferred choice due to its balance of safety, performance, and recyclability.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs High density polyethylene for Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com