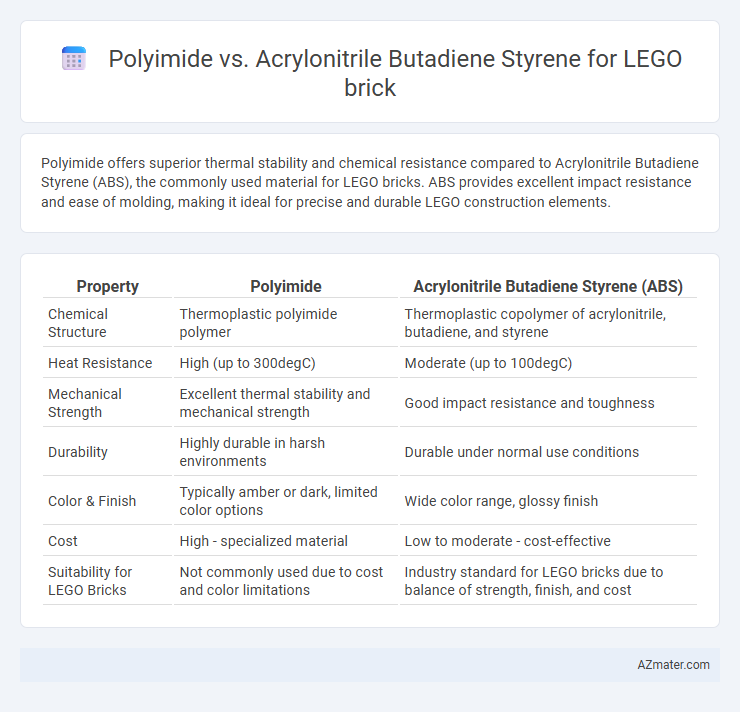
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), the commonly used material for LEGO bricks. ABS provides excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, making it ideal for precise and durable LEGO construction elements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Thermoplastic polyimide polymer | Thermoplastic copolymer of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene |
| Heat Resistance | High (up to 300degC) | Moderate (up to 100degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength | Good impact resistance and toughness |
| Durability | Highly durable in harsh environments | Durable under normal use conditions |
| Color & Finish | Typically amber or dark, limited color options | Wide color range, glossy finish |
| Cost | High - specialized material | Low to moderate - cost-effective |
| Suitability for LEGO Bricks | Not commonly used due to cost and color limitations | Industry standard for LEGO bricks due to balance of strength, finish, and cost |
Introduction: Understanding LEGO Brick Materials
Polyimide and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are key materials in evaluating LEGO brick durability and performance. ABS provides excellent impact resistance, color retention, and ease of molding, making it the industry standard for LEGO bricks. Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength but is less commonly used due to higher cost and processing complexity compared to ABS in toy manufacturing.
Overview of Polyimide: Properties and Applications
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for demanding applications such as electronics insulation and aerospace components. Unlike Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), commonly used in LEGO bricks for its toughness and ease of molding, polyimide offers greater durability under extreme temperatures and harsh environments. These superior properties position polyimide as a potential material for advanced LEGO bricks requiring enhanced heat resistance and longevity.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Key Characteristics
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, excellent toughness, and superior dimensional stability, making it ideal for LEGO bricks that require durability and precise interlocking. Its resistance to heat and chemicals ensures LEGO pieces can withstand repeated use and environmental stress without deforming or fading. ABS's ease of molding allows for consistent color vibrancy and smooth finishes, enhancing both the aesthetic and functional qualities of LEGO bricks compared to polyimide.
Mechanical Strength: Polyimide vs ABS in LEGO Bricks
Polyimide offers superior mechanical strength with higher tensile strength and thermal stability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it more resistant to deformation under stress in LEGO bricks. ABS provides adequate strength and impact resistance, but polyimide's enhanced durability and heat resistance improve long-term performance and structural integrity in demanding environments. The use of polyimide in LEGO bricks can significantly reduce wear and maintain precise interlocking capabilities over extended use.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), withstanding temperatures up to 400degC without degradation, whereas ABS typically melts around 220degC and begins to deform near 105degC. This makes polyimide a preferred choice for applications requiring high-temperature resistance and dimensional stability. ABS, while more cost-effective and easier to mold, may experience warping or melting under prolonged heat exposure, limiting its use in high-thermal environments.
Chemical Resistance: Polyimide and ABS Evaluation
Polyimide exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), effectively withstanding exposure to solvents, acids, and bases without significant degradation. ABS, while durable and impact-resistant, is more susceptible to chemical attack, particularly from organic solvents and strong alkalis, which can cause surface swelling or weakening. For LEGO bricks, polyimide's chemical stability offers enhanced longevity in harsh environments, whereas ABS remains preferred for its balance of mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness in typical play conditions.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), enabling manufacturing processes that involve higher temperature molding and longer cycle times without degradation. ABS is favored in LEGO brick production for its ease of injection molding, faster cooling rates, and cost-effectiveness due to lower processing temperatures and better flow characteristics. The choice between polyimide and ABS impacts manufacturing efficiency, with polyimide requiring specialized equipment and handling protocols to manage its higher processing temperatures and viscosity.
Color and Surface Finish in LEGO Bricks
Polyimide offers superior color stability and heat resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), ensuring LEGO bricks maintain vibrant hues over extended periods and under varying environmental conditions. ABS provides a glossy surface finish with excellent gloss retention, giving LEGO bricks a smooth, shiny appearance favored in consumer products. Polyimide's surface finish tends to be more matte and less reflective, which can affect the tactile feel and visual brightness of LEGO components.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and durability for LEGO bricks, contributing to longer product lifespans that reduce waste and environmental impact. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), the traditional material, poses challenges in recycling due to its complex chemical structure, leading to higher carbon footprints. Sustainable alternatives and advanced recycling methods for polyimide enhance its appeal by lowering emissions and promoting circular economy principles in LEGO manufacturing.
Conclusion: Best Polymer Choice for LEGO Bricks
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making it highly durable for LEGO bricks exposed to extended wear and environmental stress. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) remains the industry standard due to its excellent impact resistance, ease of molding, and cost-effectiveness for mass production. The best polymer choice for LEGO bricks balances performance and manufacturing efficiency, with ABS dominating current applications while polyimide serves niche uses requiring enhanced durability and heat resistance.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for LEGO brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com