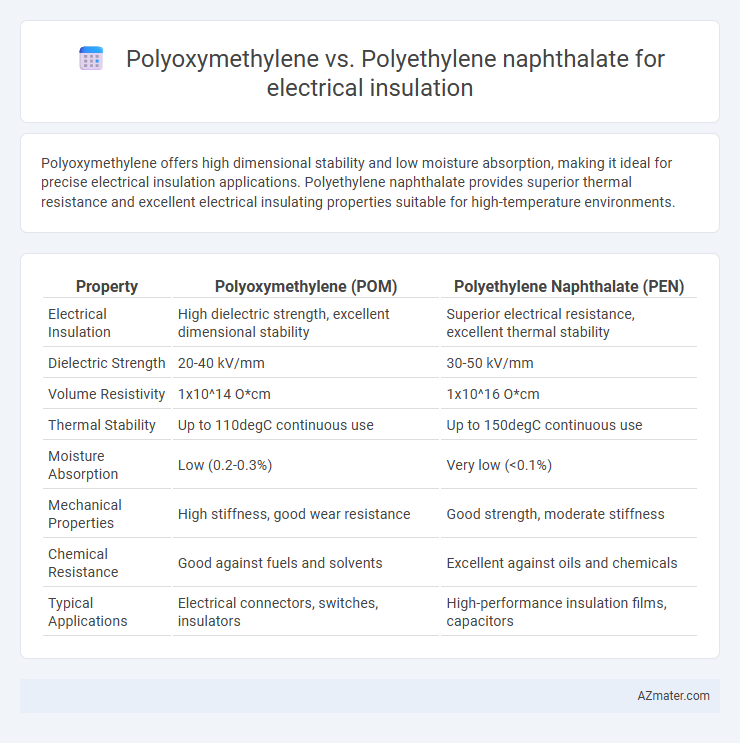
Polyoxymethylene offers high dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for precise electrical insulation applications. Polyethylene naphthalate provides superior thermal resistance and excellent electrical insulating properties suitable for high-temperature environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, excellent dimensional stability | Superior electrical resistance, excellent thermal stability |
| Dielectric Strength | 20-40 kV/mm | 30-50 kV/mm |
| Volume Resistivity | 1x10^14 O*cm | 1x10^16 O*cm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 110degC continuous use | Up to 150degC continuous use |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.2-0.3%) | Very low (<0.1%) |
| Mechanical Properties | High stiffness, good wear resistance | Good strength, moderate stiffness |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against fuels and solvents | Excellent against oils and chemicals |
| Typical Applications | Electrical connectors, switches, insulators | High-performance insulation films, capacitors |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) are prominent materials used in electrical insulation due to their distinct dielectric properties. POM offers high mechanical strength, low moisture absorption, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision components in electrical devices. PEN provides superior thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and low dielectric constant, ensuring reliable insulation performance in high-temperature and demanding electrical environments.
Overview of Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic featuring excellent mechanical strength, low friction, and high dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision electrical insulation components. Its superior dielectric properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals enhance durability and electrical performance in demanding environments. Compared to Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN), POM offers better machinability and structural integrity, although PEN provides higher thermal stability and moisture resistance.
Overview of Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN)
Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) is a high-performance polyester known for its excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and superior electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for advanced electrical applications. Compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), PEN offers greater resistance to moisture, higher dimensional stability, and improved dielectric constant, enhancing its reliability in harsh environments. PEN's exceptional barrier properties and chemical resistance contribute to long-lasting insulation performance in demanding electronic components.
Chemical Structure Comparison: POM vs PEN
Polyoxymethylene (POM) features a linear polymer chain composed of repeating -CH2-O- units, which provide high crystallinity and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for precise electrical insulation applications. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) contains rigid aromatic naphthalene rings in its backbone, enhancing thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to POM, ideal for high-temperature insulation environments. The absence of aromatic structures in POM limits its thermal endurance relative to PEN, which leverages its semicrystalline polyester structure for superior dielectric performance under thermal stress.
Dielectric Properties and Electrical Performance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits excellent dielectric properties with a high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, making it suitable for precision electrical insulation applications where dimensional stability is critical. In contrast, Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) offers superior electrical performance with higher thermal resistance and stable dielectric behavior under varying environmental conditions, enhancing long-term insulation reliability. PEN's robust resistance to moisture and thermal aging provides better performance in high-frequency electrical components compared to POM, which can degrade faster under prolonged thermal stress.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent dimensional stability and mechanical strength but has lower thermal stability with a maximum continuous use temperature around 100degC, making it less ideal for high-heat electrical insulation applications. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance with continuous service temperatures exceeding 150degC and a higher glass transition temperature, ensuring reliable insulation performance under elevated thermal stress. PEN's enhanced heat deflection temperature and lower thermal expansion coefficients make it more suitable for demanding electrical insulation environments requiring prolonged durability and thermal endurance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength with high stiffness and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for precise electrical insulation components. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) provides enhanced durability under thermal stress and exhibits excellent moisture resistance, ensuring long-term performance in harsh electrical environments. PEN's higher glass transition temperature and chemical stability contribute to better insulation reliability compared to POM in demanding applications.
Application Suitability in Electrical Insulation
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits excellent dimensional stability, mechanical strength, and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for precision electrical insulation components in connectors and switches. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) offers superior thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and excellent chemical resistance, which enhances its application in high-temperature electrical insulation films and flexible printed circuit boards. The choice between POM and PEN depends on specific operational requirements such as temperature range, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure in electrical insulation applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers lower material costs and easier machining compared to Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), making it a cost-effective choice for electrical insulation in high-volume manufacturing. PEN provides superior thermal stability and dielectric properties but generally requires more complex processing techniques, which increase production expenses. Manufacturers must balance POM's affordability and manufacturability against PEN's enhanced performance and higher cost when selecting materials for electrical insulation applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between POM and PEN
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent mechanical strength, low moisture absorption, and good dielectric properties, making it suitable for precision electrical insulation components requiring dimensional stability. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) excels in thermal resistance, electrical insulation at high temperatures, and chemical resistance, ideal for demanding electrical insulation applications exposed to harsh environments. Selecting between POM and PEN depends on the application's temperature requirements and mechanical stress, with POM favored for structural stability and PEN preferred for thermal endurance and chemical durability.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyethylene naphthalate for Electrical insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com