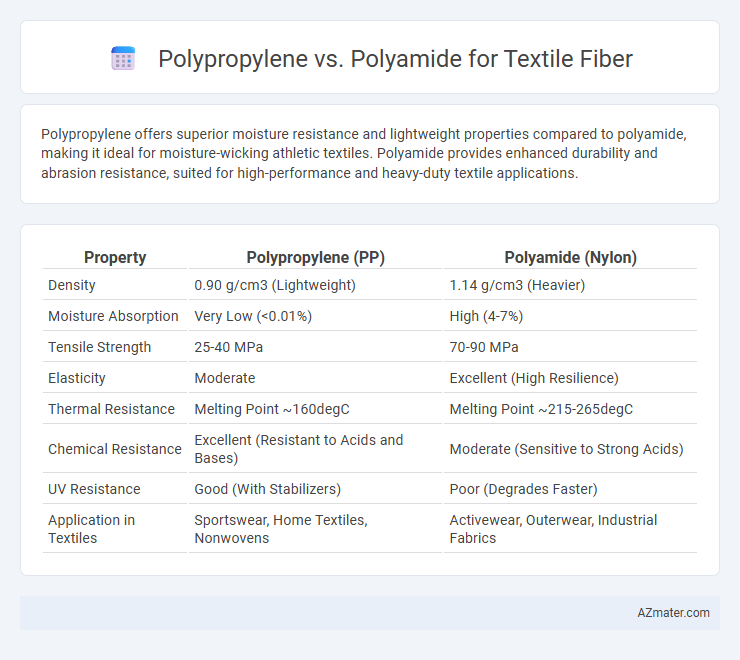
Polypropylene offers superior moisture resistance and lightweight properties compared to polyamide, making it ideal for moisture-wicking athletic textiles. Polyamide provides enhanced durability and abrasion resistance, suited for high-performance and heavy-duty textile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 1.14 g/cm3 (Heavier) |
| Moisture Absorption | Very Low (<0.01%) | High (4-7%) |
| Tensile Strength | 25-40 MPa | 70-90 MPa |
| Elasticity | Moderate | Excellent (High Resilience) |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting Point ~160degC | Melting Point ~215-265degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Resistant to Acids and Bases) | Moderate (Sensitive to Strong Acids) |
| UV Resistance | Good (With Stabilizers) | Poor (Degrades Faster) |
| Application in Textiles | Sportswear, Home Textiles, Nonwovens | Activewear, Outerwear, Industrial Fabrics |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyamide Fibers
Polypropylene fibers are lightweight, chemical-resistant, and hydrophobic, making them ideal for moisture-wicking textiles and outdoor apparel. Polyamide fibers, commonly known as nylon, offer excellent strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, widely used in performance wear and industrial applications. Both fibers differ significantly in their molecular structure, resulting in distinct mechanical properties and applications within the textile industry.
Molecular Structure and Composition
Polypropylene fibers consist of long chains of propylene molecules, characterized by a non-polar, linear hydrocarbon structure that imparts hydrophobic properties and high chemical resistance. In contrast, polyamide fibers, such as nylon, feature amide linkages (-CONH-) within their molecular chains, creating polar sites that enhance moisture absorption and intermolecular hydrogen bonding, resulting in greater strength and elasticity. The distinct molecular structures influence their respective fiber qualities, with polypropylene offering lightweight and moisture-wicking performance, while polyamide provides durability and higher tensile strength in textile applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polypropylene offers excellent mechanical strength with high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for lightweight and durable textile fibers. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, surpasses polypropylene in toughness and abrasion resistance, providing superior elasticity and impact strength for demanding textile applications. Both fibers deliver durability, but polyamide's enhanced mechanical properties suit high-performance fabrics requiring long-term resilience under stress.
Moisture Absorption and Comfort
Polypropylene exhibits low moisture absorption, typically less than 0.1%, which results in quick-drying properties and enhanced moisture-wicking capabilities, making it ideal for activewear and performance textiles. Polyamide (nylon) absorbs more moisture, ranging from 4% to 7%, offering better breathability and a softer hand feel but potentially feeling clammy during high sweat activity. The choice between polypropylene and polyamide fibers impacts textile comfort significantly, with polypropylene emphasizing dryness and thermal insulation, while polyamide balances moisture retention with tactile softness.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Polypropylene fibers exhibit lower thermal conductivity and higher heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity up to approximately 160degC, making them suitable for applications requiring insulation and heat retention. In contrast, polyamide (nylon) fibers demonstrate superior tensile strength but begin to degrade at lower temperatures around 130degC, limiting their use in high-temperature environments. The choice between polypropylene and polyamide in textile fibers depends largely on balancing thermal stability and mechanical performance for specific end-use conditions.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Polyamide fibers exhibit superior dyeability compared to polypropylene due to their polar molecular structure, which allows better absorption and retention of a wide range of dyes, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors. Polypropylene's non-polar, hydrophobic nature limits its dye affinity, often requiring specialized dyes or surface treatments to achieve acceptable color intensity and durability. Consequently, polyamide is preferred for applications demanding excellent color retention and fastness after repeated washing and exposure to sunlight.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene fibers exhibit lower environmental impact compared to polyamide, as they require less energy during production and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Polyamide is derived from petroleum and is not biodegradable, whereas polypropylene offers better recyclability and resistance to chemical degradation, enhancing its sustainability profile. Both materials pose challenges regarding microplastic pollution, but innovations in recycling and bio-based alternatives increasingly improve their environmental performance.
Cost Efficiency in Textile Production
Polypropylene fibers offer significant cost efficiency in textile production due to their lower raw material price and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing compared to polyamide. Polyamide fibers, while providing superior strength and elasticity, typically incur higher costs from complex polymerization and dyeing processes. Selecting polypropylene enhances overall production affordability, especially for high-volume textiles requiring durability and moisture resistance.
Common Applications in the Textile Industry
Polypropylene fibers are widely used in activewear, sportswear, and industrial textiles due to their lightweight, moisture-wicking, and quick-drying properties, making them ideal for performance garments and geotextiles. Polyamide fibers, commonly known as nylon, dominate in hosiery, swimwear, and outerwear because of their high strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, providing durability and comfort in everyday wear. Both fibers serve distinct roles in the textile industry, with polypropylene preferred for moisture management and polyamide valued for its resilience and versatility.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Polypropylene vs Polyamide
Polypropylene fibers offer excellent moisture-wicking properties and high resistance to chemicals, making them ideal for performance textiles and activewear. Polyamide fibers, known for their superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, provide durability and comfort in applications like hosiery and sportswear. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing polypropylene's lightweight, moisture management advantages with polyamide's toughness and enhanced wear resistance for the intended textile use.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyamide for Textile Fiber
 azmater.com
azmater.com