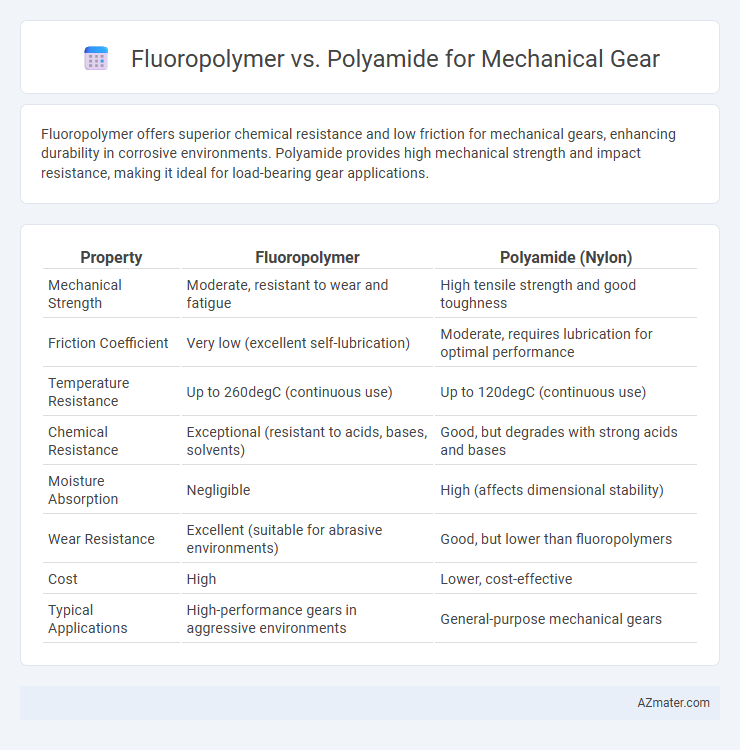
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance and low friction for mechanical gears, enhancing durability in corrosive environments. Polyamide provides high mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for load-bearing gear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, resistant to wear and fatigue | High tensile strength and good toughness |
| Friction Coefficient | Very low (excellent self-lubrication) | Moderate, requires lubrication for optimal performance |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (continuous use) | Up to 120degC (continuous use) |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional (resistant to acids, bases, solvents) | Good, but degrades with strong acids and bases |
| Moisture Absorption | Negligible | High (affects dimensional stability) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent (suitable for abrasive environments) | Good, but lower than fluoropolymers |
| Cost | High | Lower, cost-effective |
| Typical Applications | High-performance gears in aggressive environments | General-purpose mechanical gears |
Introduction to Fluoropolymers and Polyamides
Fluoropolymers, known for their exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high-temperature stability, are widely utilized in mechanical gears requiring durability and minimal wear. Polyamides, commonly referred to as nylons, offer excellent mechanical strength, toughness, and good thermal resistance, making them suitable for gears exposed to moderate mechanical stress. Understanding the fundamental properties of these polymers helps in selecting the optimal material for specific gear applications based on environmental conditions and performance demands.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Fluoropolymers consist of carbon-fluorine bonds, giving mechanical gears exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high thermal stability suitable for harsh environments. Polyamides, composed of repeating amide linkages in their molecular chains, offer superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability under load. The crystalline structure of polyamides contributes to their toughness and abrasion resistance, while fluoropolymers' semi-crystalline or amorphous structures provide enhanced flexibility and reduced surface energy, critical for low-friction gear applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Fluoropolymers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, but generally have lower tensile strength and mechanical durability compared to polyamides, which offer superior wear resistance and higher tensile strength ideal for mechanical gears. Polyamide materials, such as Nylon, provide excellent toughness, impact resistance, and long-term dimensional stability under load, making them more suitable for high-stress gear applications. Fluoropolymers excel in corrosive environments but are less mechanically robust, limiting their use where strength and durability are critical.
Wear and Friction Performance in Gears
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior wear resistance and low friction coefficients compared to polyamides, making them ideal for mechanical gears operating under high-speed or chemically aggressive environments. Polyamides offer good mechanical strength and wear durability but tend to have higher friction and are more susceptible to moisture absorption, which can degrade performance over time. Fluoropolymer gears maintain dimensional stability and reduce energy loss due to their inherently low sliding resistance and excellent chemical inertness.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polyamides, effectively withstanding exposure to aggressive solvents, acids, and bases without degradation, making them ideal for mechanical gears in harsh chemical environments. Polyamides, while mechanically strong, are more susceptible to hydrolysis and environmental stress cracking, leading to reduced durability in moisture-rich or chemically challenging conditions. Fluoropolymer gears offer enhanced environmental stability, including resistance to ultraviolet radiation and extreme temperatures, ensuring longer operational life in demanding applications.
Thermal Resistance: Operating Temperature Range
Fluoropolymers exhibit a superior thermal resistance with an operating temperature range typically between -200degC to 260degC, making them ideal for high-heat mechanical gear applications. Polyamides generally operate within a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 120degC, which limits their use in environments requiring elevated thermal stability. The extended thermal tolerance of fluoropolymers enhances gear durability and performance in demanding temperature conditions.
Machinability and Manufacturing Considerations
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance and low friction, but their machinability is challenging due to their low thermal conductivity and tendency to deform under cutting stresses, requiring specialized tooling and slower machining speeds. Polyamides, by contrast, exhibit better machinability with higher dimensional stability and ease of cutting, making them more cost-effective for complex gear geometries. Manufacturing considerations also favor polyamides for high-volume production due to faster cycle times and less stringent temperature control compared to fluoropolymers.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Fluoropolymer gears generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced material properties like chemical resistance and low friction, making them suitable for harsh environments. Polyamide gears offer a cost-effective solution with satisfactory mechanical strength and wear resistance, but may require more frequent replacement under high stress or chemical exposure. Long-term value favors fluoropolymers in applications demanding durability and minimal maintenance, while polyamides serve well in budget-sensitive projects with moderate operational conditions.
Typical Applications in Mechanical Gear Systems
Fluoropolymer gears excel in chemical resistance and low friction, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments such as pumps, valves, and chemical processing equipment. Polyamide gears offer superior toughness and wear resistance, commonly used in automotive transmissions, conveyor systems, and precision robotic actuators. Both materials enhance mechanical gear system performance but selection depends on operating temperature, load, and environmental exposure.
Choosing the Right Polymer: Key Decision Factors
Selecting the right polymer for mechanical gears involves evaluating factors such as wear resistance, friction coefficient, and temperature tolerance. Fluoropolymers offer exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, making them ideal for high-performance applications with aggressive environments. Polyamides provide superior mechanical strength and impact resistance, suitable for load-bearing gear systems requiring durability and toughness.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyamide for Mechanical Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com