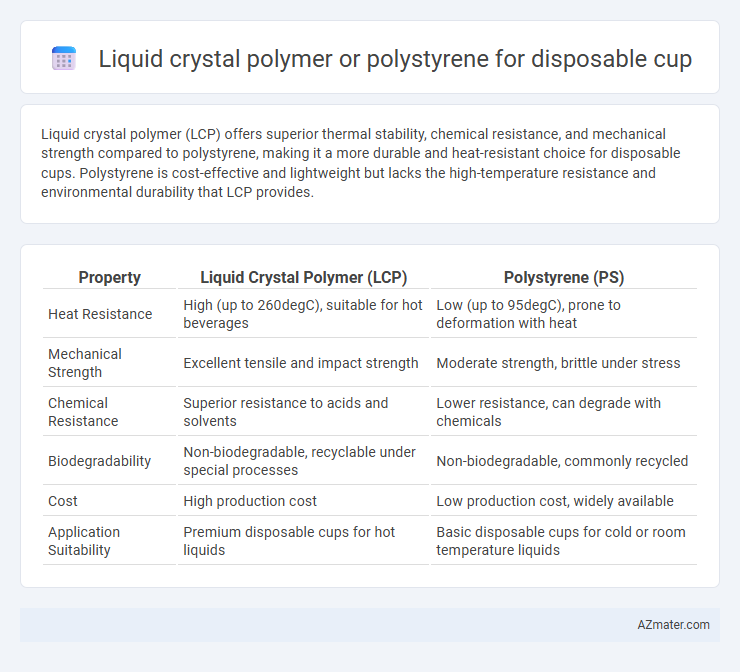
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polystyrene, making it a more durable and heat-resistant choice for disposable cups. Polystyrene is cost-effective and lightweight but lacks the high-temperature resistance and environmental durability that LCP provides.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High (up to 260degC), suitable for hot beverages | Low (up to 95degC), prone to deformation with heat |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile and impact strength | Moderate strength, brittle under stress |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to acids and solvents | Lower resistance, can degrade with chemicals |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable, recyclable under special processes | Non-biodegradable, commonly recycled |
| Cost | High production cost | Low production cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability | Premium disposable cups for hot liquids | Basic disposable cups for cold or room temperature liquids |
Introduction to Disposable Cup Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent mechanical strength compared to polystyrene (PS), making it a premium choice for disposable cup applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Polystyrene, known for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in disposable cups primarily for cold beverages but lacks the thermal endurance and environmental resistance of LCP. The selection between LCP and polystyrene hinges on factors such as usage temperature, environmental impact, and performance requirements, with LCP providing enhanced performance for hot liquids and extended shelf life.
What is Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)?
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic characterized by its unique molecular structure that aligns in an ordered, crystalline phase, providing exceptional mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Compared to Polystyrene, LCP offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it suitable for disposable cups requiring high-temperature liquids without deformation or leaching. The advanced properties of LCP reduce environmental impact by enabling thinner, lighter designs while maintaining functionality and safety in food contact applications.
What is Polystyrene (PS)?
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer styrene, widely used in disposable cups due to its lightweight, rigidity, and excellent insulation properties. Compared to liquid crystal polymer (LCP), polystyrene offers cost-effective production and ease of molding but has lower heat resistance and mechanical strength. Its thermal stability typically ranges around 90-100degC, making it suitable for cold or warm beverages but less ideal for high-temperature applications.
Manufacturing Processes: LCP vs Polystyrene
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers advanced manufacturing processes such as precision injection molding and extrusion, allowing for high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance in disposable cups. Polystyrene, on the other hand, utilizes simpler techniques like thermoforming and injection molding, which enable cost-effective mass production but result in lower heat tolerance and reduced durability. The choice between LCP and polystyrene manufacturing impacts product quality, cycle time, and environmental sustainability in the disposable cup industry.
Mechanical and Thermal Properties Comparison
Liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) exhibit superior mechanical strength and higher thermal stability compared to polystyrene, making them more suitable for disposable cups exposed to hot liquids. LCPs maintain rigidity and resist deformation at temperatures exceeding 250degC, while polystyrene typically softens around 100degC to 120degC, limiting its thermal resilience. The enhanced tensile strength and heat resistance of LCPs reduce the risk of cup failure under thermal stress, providing a more durable and reliable disposable cup material.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior environmental impact and sustainability compared to polystyrene (PS) for disposable cups due to its higher strength-to-weight ratio, enabling reduced material use and waste generation. LCP's enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance allow for better recyclability and lower emissions during disposal, contrasting with polystyrene's significant contribution to non-biodegradable waste and toxic leachates. The biodegradability challenges and energy-intensive production of polystyrene further exacerbate its environmental footprint, positioning LCP as a more sustainable alternative for single-use applications.
Cost Efficiency and Pricing Analysis
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), but its higher raw material and processing costs make it less cost-efficient for disposable cup production. Polystyrene remains the more affordable option due to its low material cost and ease of manufacturing, enabling large-scale production at competitive prices. Pricing analysis reveals that while LCP cups may deliver enhanced durability, polystyrene cups dominate the market where cost efficiency and price sensitivity are critical factors.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polystyrene, making it safer for disposable cups in high-temperature applications. LCP does not leach harmful substances into food or beverages, ensuring excellent food compatibility and compliance with FDA regulations. In contrast, polystyrene may release styrene monomers and other potentially toxic compounds, especially when exposed to hot liquids, raising concerns about consumer safety in food contact use.
Applications in Food and Beverage Industry
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for disposable cups used in hot beverages and acidic foods. Polystyrene is widely used for cold drink cups and foam insulation due to its low cost, lightweight nature, and ease of molding, but it lacks the heat resistance of LCP. In the food and beverage industry, LCP ensures safer performance for hot liquid applications, while polystyrene remains dominant for cost-effective cold beverage cups and single-use convenience.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to Polystyrene, positioning it as a promising material for future disposable cup manufacturing focused on sustainability and durability. Emerging trends favor LCP's recyclability and reduced environmental impact, aligning with global efforts to minimize plastic waste. Manufacturers are recommended to invest in LCP technology development and supply chain adaptation to meet increasing regulatory demands and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polystyrene for Disposable cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com