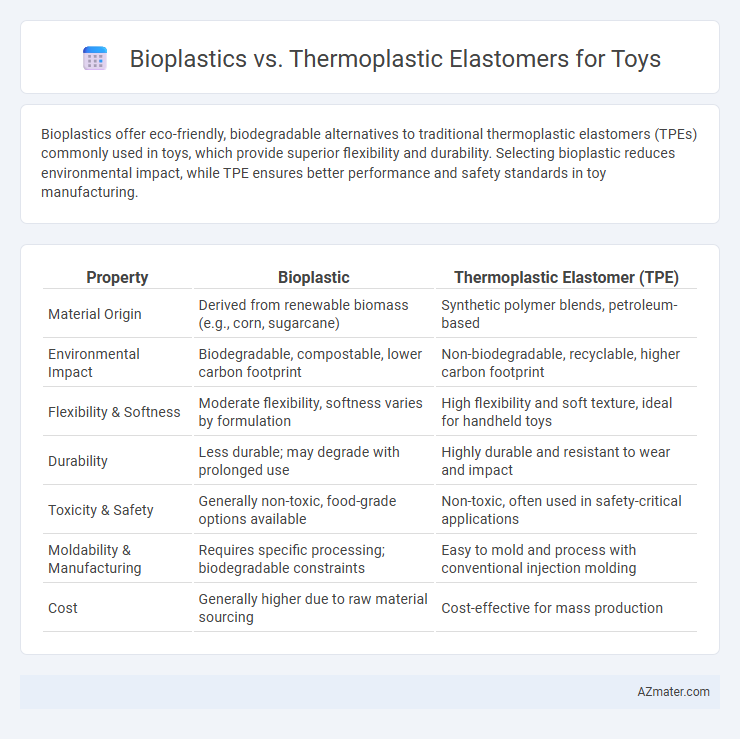
Bioplastics offer eco-friendly, biodegradable alternatives to traditional thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) commonly used in toys, which provide superior flexibility and durability. Selecting bioplastic reduces environmental impact, while TPE ensures better performance and safety standards in toy manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Derived from renewable biomass (e.g., corn, sugarcane) | Synthetic polymer blends, petroleum-based |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, recyclable, higher carbon footprint |
| Flexibility & Softness | Moderate flexibility, softness varies by formulation | High flexibility and soft texture, ideal for handheld toys |
| Durability | Less durable; may degrade with prolonged use | Highly durable and resistant to wear and impact |
| Toxicity & Safety | Generally non-toxic, food-grade options available | Non-toxic, often used in safety-critical applications |
| Moldability & Manufacturing | Requires specific processing; biodegradable constraints | Easy to mold and process with conventional injection molding |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material sourcing | Cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction to Bioplastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers
Bioplastics, derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch and sugarcane, offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics by being biodegradable or compostable, making them increasingly popular in sustainable toy manufacturing. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) combine the properties of rubber and thermoplastics, providing flexibility, durability, and recyclability, which are essential for safe, soft-touch toy components. Choosing between bioplastics and TPEs depends on factors like environmental impact, performance requirements, and production cost in the toy industry.
Material Composition: Bioplastic vs Thermoplastic Elastomer
Bioplastic for toys is primarily derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offering biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) consist of a blend of rubber and plastic polymers, providing flexibility, durability, and easy processing but rely on petroleum-based raw materials. The choice between bioplastic and TPE hinges on balancing eco-friendly material composition against mechanical performance and cost-effectiveness in toy manufacturing.
Safety and Non-Toxicity for Children’s Toys
Bioplastic and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) both offer safety advantages for children's toys, with bioplastics being derived from natural, renewable sources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals. Thermoplastic elastomers provide durability and flexibility while being free from phthalates and BPA, commonly found in traditional plastics, ensuring non-toxicity during prolonged child use. Both materials comply with strict safety standards like ASTM F963 and EN71, confirming their suitability for non-toxic, child-safe toys.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastics in toys offer reduced carbon footprints and biodegradability, supporting eco-friendly waste management compared to traditional thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), which rely on fossil fuels and persist longer in landfills. The production of bioplastics often involves renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, enhancing sustainability through lower greenhouse gas emissions and circular economy benefits. However, TPEs provide superior durability and recyclability in some systems, making them a viable option when paired with advanced recycling technologies to mitigate environmental impact.
Durability and Longevity in Toy Applications
Bioplastics, derived from renewable sources, generally exhibit lower durability and limited resistance to mechanical stress compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), which offer superior elasticity and resilience ideal for toys subjected to frequent handling and stretching. Thermoplastic elastomers retain their shape and performance over extended periods, ensuring longevity in high-use toy applications, whereas bioplastics may degrade faster due to environmental exposure and repeated use. Choosing TPEs enhances the toy's lifespan through robust wear resistance and sustained flexibility, critical for both safety and user satisfaction.
Cost Comparison: Bioplastic vs Thermoplastic Elastomer
Bioplastics generally have higher production costs compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) due to raw material expenses and processing complexities, affecting overall toy manufacturing budgets. Thermoplastic elastomers offer cost advantages with lower material prices and more efficient molding processes, enabling mass production scalability. Despite higher upfront costs, bioplastics present long-term value through sustainability, but thermoplastic elastomers remain preferred for cost-sensitive toy markets.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Bioplastics for toys are produced through processes like injection molding and extrusion, utilizing renewable raw materials such as polylactic acid (PLA), which may require adjustments in standard equipment due to their lower melting points and thermal stability. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) benefit from established manufacturing techniques, including injection molding and blow molding, offering high scalability and fast cycle times suitable for mass production. The scalability of TPE is superior due to consistent material properties and compatibility with existing industrial infrastructure, while bioplastics face challenges in uniformity and equipment adaptation that can affect large-scale production efficiency.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Bioplastics offer sustainable customization options with biodegradable properties but generally have limited design flexibility compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs). TPEs enable extensive design versatility through easy molding, varied hardness, and color adaptability, making them ideal for intricate toy designs requiring durability and elasticity. Manufacturers prioritize TPEs when flexibility and detailed customization are critical, while bioplastics are chosen for eco-friendly toy applications with simpler design needs.
Market Trends in Toy Material Selection
Bioplastic and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are gaining traction in the toy industry due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable and non-toxic materials. Market trends indicate a growing preference for bioplastics derived from renewable resources, offering biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional TPEs. However, TPEs maintain a strong presence due to their superior flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness, driving manufacturers to innovate hybrid solutions to meet evolving regulatory and eco-conscious standards.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Toy Materials
Bioplastics in toy manufacturing are advancing rapidly due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing, addressing environmental concerns while maintaining safety standards. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer enhanced flexibility and durability, with ongoing innovations improving recyclability and performance in toys. Future trends emphasize hybrid materials combining bioplastics and TPE to optimize sustainability, safety, and playability in next-generation toys.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Thermoplastic elastomer for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com