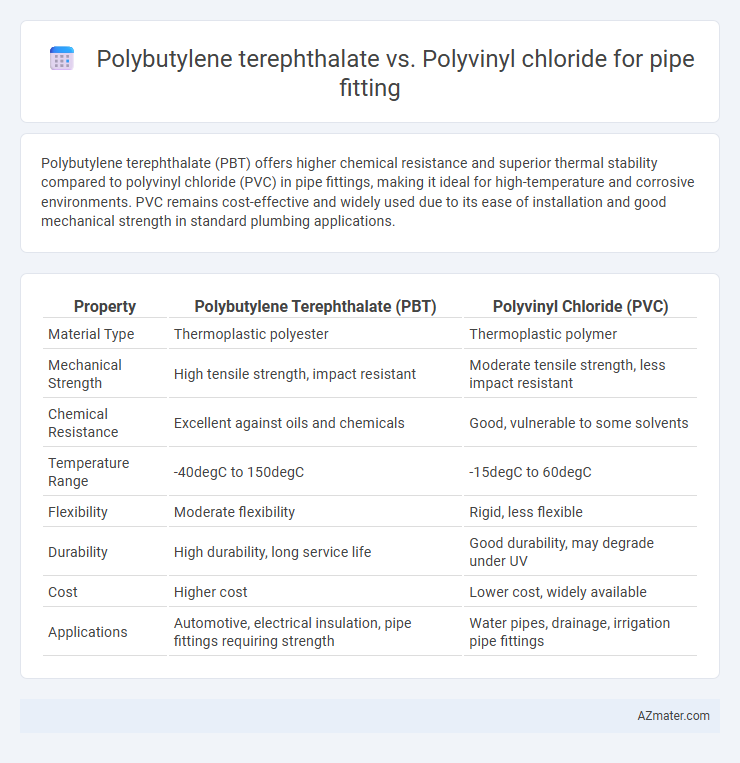
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers higher chemical resistance and superior thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in pipe fittings, making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments. PVC remains cost-effective and widely used due to its ease of installation and good mechanical strength in standard plumbing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, impact resistant | Moderate tensile strength, less impact resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils and chemicals | Good, vulnerable to some solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -15degC to 60degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Rigid, less flexible |
| Durability | High durability, long service life | Good durability, may degrade under UV |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Automotive, electrical insulation, pipe fittings requiring strength | Water pipes, drainage, irrigation pipe fittings |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer known for its high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision pipe fittings in automotive and industrial applications. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used plastic characterized by its durability, affordability, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals, commonly employed for water supply and drainage pipe systems. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with PBT providing superior heat resistance and toughness, while PVC excels in cost-effectiveness and widespread availability for standard piping solutions.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits a semicrystalline polyester structure composed of repeating units of butylene glycol and terephthalic acid, giving it strong resistance to chemicals and heat. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of vinyl chloride monomers with a linear polymer structure rich in chlorine atoms, providing rigidity and excellent chemical resistance, especially to acids and alkalis. The ester linkages in PBT's composition result in superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to PVC, which relies on chlorine substituents for enhanced chemical inertness and flame retardance in pipe fittings.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Differences
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more resistant to impact and stress under high pressure in pipe fittings. PBT exhibits greater flexibility, allowing for better absorption of vibrations and thermal expansion without cracking, whereas PVC tends to be more rigid and brittle under similar conditions. These differences make PBT ideal for dynamic and high-stress piping applications, while PVC is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation in static systems.
Thermal Resistance and Operating Temperature Ranges
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with an operating temperature range typically from -40degC to 150degC, while PVC ranges from -15degC to 60degC. PBT's higher glass transition temperature around 22degC and melting point near 223degC enable it to withstand elevated temperatures and repeated thermal cycling without deformation. PVC's lower thermal stability limits its use in high-temperature pipe fittings, making PBT more suitable for applications requiring enhanced heat resistance and long-term durability.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance Properties
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for pipe fittings exposed to harsh environments. PBT resists acids, bases, and solvents more effectively, reducing degradation and extending service life in chemically aggressive applications. In contrast, PVC, while resistant to many chemicals, can degrade under strong solvents and elevated temperatures, limiting its durability in certain corrosive conditions.
Installation and Fabrication Methods
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior ease of installation and fabrication for pipe fittings due to its excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, allowing for precise injection molding and rapid assembly. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes require solvent welding or mechanical joining, which can be less flexible and more time-consuming compared to PBT's thermal welding and ultrasonic bonding capabilities. The enhanced fabrication versatility of PBT reduces labor costs and installation time while maintaining strong mechanical performance in various industrial applications.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers higher cost efficiency in pipe fitting applications due to its superior durability and resistance to chemical corrosion, reducing long-term maintenance expenses compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC). While PVC pipes typically have a lower upfront cost, their shorter lifespan and susceptibility to degradation under harsh environmental conditions often lead to increased replacement and repair costs over time. Economic considerations favor PBT in industrial and high-performance settings, where initial investments are offset by enhanced longevity and reduced total cost of ownership.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior environmental benefits over polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in pipe fittings due to its higher recyclability and lower toxicity during production and disposal. PBT is a thermoplastic polyester that can be efficiently recycled without releasing harmful dioxins, unlike PVC, which often requires complex handling to avoid environmental contamination from chlorine-based compounds. The biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint of PBT make it a more sustainable choice in applications demanding eco-friendly materials.
Common Applications in Pipe Fitting
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is commonly used in pipe fittings for applications requiring excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability, and electrical insulation properties, such as in automotive fuel systems and industrial fluid handling. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipe fittings are widely utilized in plumbing, irrigation, and sewage systems due to their affordability, rigid structure, and resistance to corrosion and abrasion. Both materials offer specific advantages: PBT excels in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments, while PVC is preferred for general water supply and drainage applications.
Choosing Between PBT and PVC: Key Factors to Consider
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for applications involving hot water or aggressive chemicals. PVC, known for its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, is widely used in residential and irrigation piping due to its durability and corrosion resistance. When choosing between PBT and PVC for pipe fittings, consider factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, mechanical strength, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Pipe fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com