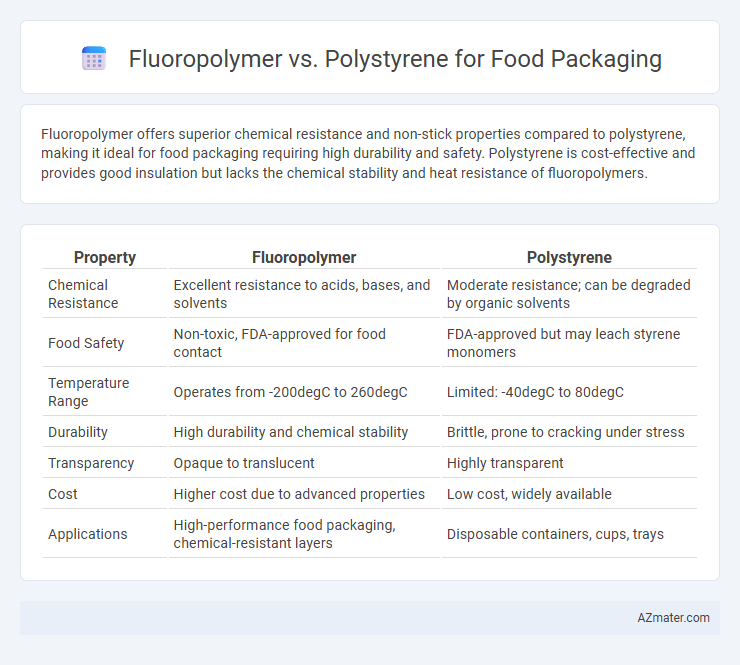
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for food packaging requiring high durability and safety. Polystyrene is cost-effective and provides good insulation but lacks the chemical stability and heat resistance of fluoropolymers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate resistance; can be degraded by organic solvents |
| Food Safety | Non-toxic, FDA-approved for food contact | FDA-approved but may leach styrene monomers |
| Temperature Range | Operates from -200degC to 260degC | Limited: -40degC to 80degC |
| Durability | High durability and chemical stability | Brittle, prone to cracking under stress |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Low cost, widely available |
| Applications | High-performance food packaging, chemical-resistant layers | Disposable containers, cups, trays |
Introduction to Food Packaging Materials
Fluoropolymers in food packaging offer superior chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and high-temperature stability compared to polystyrene, making them ideal for packaging acidic or greasy foods. Polystyrene, widely used for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness, provides excellent rigidity and clarity but lacks the barrier properties and durability of fluoropolymers. Selecting between these materials depends on the specific food product requirements including shelf life, safety standards, and environmental impact.
Overview of Fluoropolymers
Fluoropolymers, known for their exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties, offer superior barrier performance against moisture, oils, and gases in food packaging applications. Their molecular structure provides high thermal stability and prevents flavor contamination, making them ideal for maintaining food freshness and safety. Compared to polystyrene, fluoropolymers deliver enhanced durability and longevity, especially in demanding environments involving heat or aggressive substances.
Overview of Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a versatile, lightweight plastic commonly used in food packaging due to its excellent clarity, rigidity, and ease of molding. It offers good insulation properties, making it ideal for products like disposable cups, containers, and trays. However, its low resistance to heat and susceptibility to chemical leaching limit its use compared to fluoropolymers in applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical inertness.
Barrier Properties: Fluoropolymers vs Polystyrene
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior barrier properties compared to polystyrene, effectively preventing the permeation of gases, moisture, and oils, which is critical for maintaining food freshness and extending shelf life. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, offers lower resistance to oxygen and water vapor transmission, making it less ideal for packaging oxygen-sensitive or moisture-prone foods. The enhanced chemical inertness and hydrophobicity of fluoropolymers contribute to their exceptional performance in high-barrier food packaging applications where product protection and safety are paramount.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Fluoropolymer exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, effectively repelling oils, acids, and solvents, which significantly enhances food safety by preventing contamination and maintaining packaging integrity. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, is more susceptible to chemical degradation and migration of styrene monomers, raising concerns about potential food safety risks. Fluoropolymer's inert nature ensures minimal interaction with food products, making it a superior choice for applications demanding high chemical resistance and stringent food safety standards.
Thermal Stability and Application Range
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior thermal stability compared to polystyrene, with melting points often exceeding 250degC, enabling their use in high-temperature food packaging applications such as microwave-safe containers and heat-sealable films. Polystyrene, with a lower thermal resistance typically around 100degC, is more suited for cold or room-temperature packaging like disposable cups and food trays. The broader application range of fluoropolymers includes resistance to chemicals and grease, supporting extended shelf life and diverse food types, whereas polystyrene is favored for cost-effective, lightweight packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance and barrier properties, ensuring longer shelf life and reduced food waste, but their environmental impact is significant due to persistent bioaccumulation and challenges in recycling. Polystyrene, widely used for food packaging, poses environmental concerns from its non-biodegradability and potential release of toxic styrene monomers, yet advancements in recycling technologies and bio-based alternatives are improving its sustainability profile. Evaluating both materials requires balancing functional performance with end-of-life management and ecological footprint to optimize sustainable packaging solutions.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Fluoropolymer-based food packaging typically incurs higher costs due to advanced chemical properties like exceptional heat resistance and non-stick surfaces, which are less common in polystyrene options. Polystyrene remains more cost-effective and widely available in the food packaging market, favored for its low production cost and versatile molding capabilities. Market availability of polystyrene surpasses fluoropolymers given its widespread use in disposable containers, while fluoropolymers dominate niche markets requiring enhanced chemical resistance and durability.
Regulatory Compliance for Food Contact
Fluoropolymers offer superior regulatory compliance for food contact applications due to their excellent chemical resistance and low permeability, which reduces the risk of contaminant migration. Polystyrene, while widely used in food packaging, faces stricter limitations under FDA and EU food contact regulations because of potential styrene monomer migration. Fluoropolymer packaging materials consistently meet FDA 21 CFR 177 and EU Regulation No 10/2011 standards, ensuring safer use with a broad range of food types and conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Food Packaging
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for packaging acidic or oily foods that require extended shelf life. Polystyrene is cost-effective and provides excellent rigidity and clarity, suitable for dry or solid food items but may not withstand solvents or heat as effectively. Choosing the right material depends on the food type, storage conditions, and safety standards to ensure optimal preservation and consumer safety.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polystyrene for Food Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com