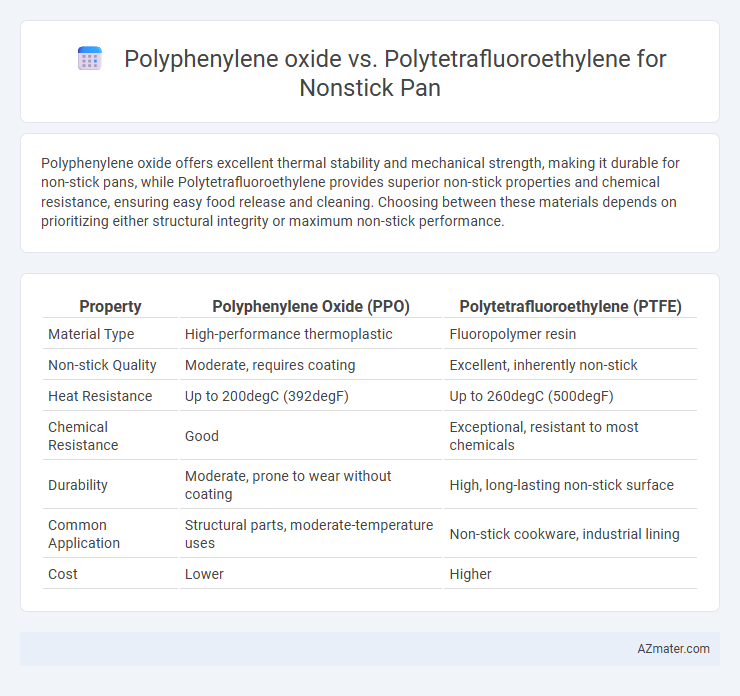
Polyphenylene oxide offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it durable for non-stick pans, while Polytetrafluoroethylene provides superior non-stick properties and chemical resistance, ensuring easy food release and cleaning. Choosing between these materials depends on prioritizing either structural integrity or maximum non-stick performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic | Fluoropolymer resin |
| Non-stick Quality | Moderate, requires coating | Excellent, inherently non-stick |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 200degC (392degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Exceptional, resistant to most chemicals |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear without coating | High, long-lasting non-stick surface |
| Common Application | Structural parts, moderate-temperature uses | Non-stick cookware, industrial lining |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Non-Stick Pan Materials
Non-stick pans primarily utilize materials like Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for their coating properties. PPO offers excellent thermal stability and durability, enhancing the pan's resistance to heat and wear. PTFE is renowned for its superior non-stick characteristics and chemical inertness, providing easy food release and straightforward cleaning.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making it a suitable material for non-stick pan coatings. Unlike polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), PPO offers better heat resistance up to around 260degC without significant degradation, which contributes to durable non-stick surfaces. Its superior rigidity and dimensional stability enhance the overall lifespan of cookware, while maintaining low friction properties essential for non-stick performance.
Overview of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional non-stick properties, chemical resistance, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for cookware coatings. PTFE offers a smooth, low-friction surface that prevents food from adhering, ensuring easy cleaning and long-lasting performance in non-stick pans. Compared to polyphenylene oxide, PTFE provides superior heat resistance up to approximately 260degC (500degF) and enhanced durability against abrasion and chemical corrosion.
Thermal Stability: PPO vs PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), maintaining integrity at temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) without degradation, making it ideal for non-stick pans exposed to high cooking heat. PPO, while offering good thermal resistance up to approximately 190-200degC, tends to degrade and lose mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, limiting its use in high-heat cookware applications. The enhanced thermal endurance of PTFE ensures non-stick coatings remain effective and safe during intense cooking processes, setting a higher standard over PPO in thermal stability performance.
Non-Stick Performance Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits moderate non-stick properties with good thermal stability but tends to wear faster under high-heat cooking compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which is renowned for its superior non-stick performance and resistance to sticking even at elevated temperatures. PTFE coatings provide a smoother surface that significantly reduces food adhesion, enabling easier cleaning and enhanced cooking efficiency. While PPO-based coatings offer durability and heat resistance, PTFE remains the preferred choice for premium non-stick pans due to its unmatched release capabilities and longevity.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers moderate durability with good thermal stability but tends to degrade faster under high heat compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which exhibits exceptional heat resistance and chemical inertness, leading to superior lifespan in non-stick pans. PTFE coatings can withstand temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) without significant breakdown, whereas PPO-based coatings generally lose integrity around 150-170degC (302-338degF). The robust molecular structure of PTFE ensures prolonged non-stick performance and resistance to scratching, making it the preferred material for long-lasting non-stick cookware.
Safety and Food Contact Compliance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior non-stick properties and exceptional chemical resistance, making it widely used in cookware with proven food contact safety and FDA compliance. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits high thermal stability and mechanical strength but is less common in non-stick applications due to limited non-stick efficacy and fewer established food contact certifications. Choosing PTFE ensures optimal safety and regulatory adherence for non-stick pans, while PPO may require additional processing to meet food contact compliance standards.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) non-stick pans require gentle cleaning with mild detergents and soft sponges to maintain their surface integrity, whereas polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) pans are generally more resistant to chemical damage and can tolerate slightly more abrasive wiping without significant wear. PPO coatings tend to have lower thermal stability, making them more sensitive to high temperatures during cleaning routines, while PTFE's superior heat resistance facilitates easier removal of burnt residues with proper care. Both materials benefit from hand washing and avoiding metal utensils, but PTFE typically offers longer durability under frequent cleaning and maintenance cycles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in non-stick pans due to its lower emission of harmful fluorochemicals during manufacturing and disposal. PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, releases persistent per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) that degrade slowly in the environment, raising concerns about bioaccumulation and toxicity. Choosing PPO enhances sustainability by reducing the ecological footprint associated with non-stick cookware production and end-of-life contamination.
Final Recommendations: Choosing the Right Material
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent heat resistance and durability, making it a strong contender for non-stick cookware that requires frequent high-temperature usage. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides superior non-stick performance and ease of cleaning but may degrade at very high temperatures above 260degC. For longevity and robust heat tolerance, PPO is recommended, while PTFE remains ideal for everyday cooking with moderate heat and effortless food release.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com