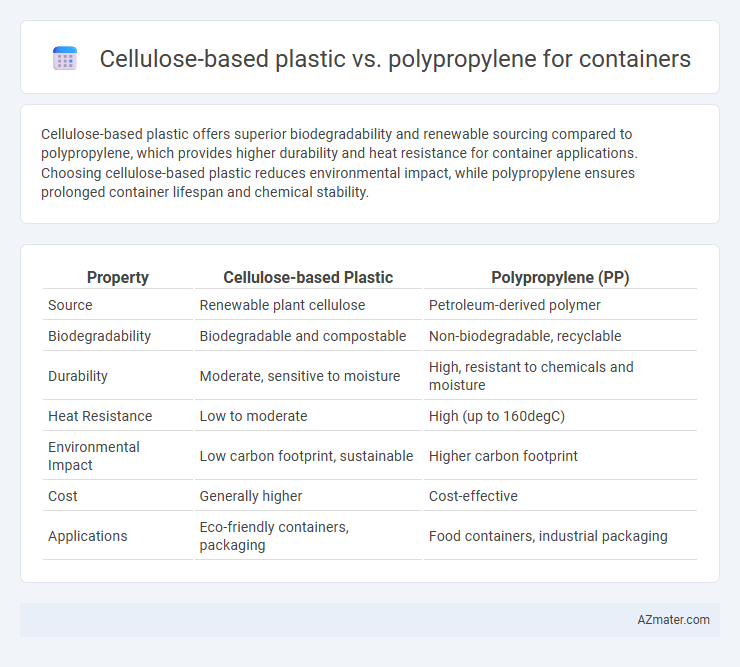
Cellulose-based plastic offers superior biodegradability and renewable sourcing compared to polypropylene, which provides higher durability and heat resistance for container applications. Choosing cellulose-based plastic reduces environmental impact, while polypropylene ensures prolonged container lifespan and chemical stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose-based Plastic | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant cellulose | Petroleum-derived polymer |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to moisture | High, resistant to chemicals and moisture |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate | High (up to 160degC) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | Higher carbon footprint |
| Cost | Generally higher | Cost-effective |
| Applications | Eco-friendly containers, packaging | Food containers, industrial packaging |
Overview of Cellulose-Based Plastic and Polypropylene
Cellulose-based plastic, derived from natural fibers like wood pulp, offers biodegradability and compostability, making it an eco-friendly option for containers. Polypropylene, a petroleum-based thermoplastic polymer, is known for its durability, chemical resistance, and low production cost, widely used in packaging for its lightweight and strong properties. The choice between cellulose-based plastic and polypropylene depends on environmental impact priorities and performance requirements such as strength and reusability.
Material Composition and Sources
Cellulose-based plastic is derived from natural polymers found in plant cell walls, primarily sourced from wood pulp, cotton, or other renewable biomass, making it biodegradable and environmentally friendly. Polypropylene is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer composed of repeating propylene monomers obtained from petroleum or natural gas, known for its durability and resistance to heat and chemicals. The renewable origin of cellulose-based plastics contrasts with the fossil fuel dependency of polypropylene, influencing their environmental impact and end-of-life options.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose-based plastics are derived from renewable plant fibers, making them biodegradable and compostable, which significantly reduces landfill waste and microplastic pollution compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene, a petroleum-based polymer, has a longer degradation time and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions throughout its lifecycle, posing challenges for sustainable waste management. The shift to cellulose-based containers supports circular economy principles by enhancing biodegradability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cellulose-based plastics exhibit moderate mechanical strength but tend to have lower durability compared to polypropylene, which offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance ideal for containers subjected to heavy use. Polypropylene's high fatigue resistance and chemical stability enhance its longevity in various environmental conditions, while cellulose-based plastics may degrade faster due to moisture sensitivity and lower thermal stability. Selecting polypropylene ensures enhanced container performance in demanding applications, whereas cellulose-based plastics provide eco-friendly alternatives with moderate mechanical properties.
Chemical Resistance and Safety
Cellulose-based plastic containers exhibit superior biodegradability and are derived from renewable resources, offering enhanced environmental safety compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene containers provide excellent chemical resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, making them suitable for storing aggressive substances without degradation. While cellulose-based plastics have moderate chemical resistance and may degrade with prolonged exposure to strong chemicals, their non-toxic, compostable nature ensures safer disposal and minimal environmental impact.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Cellulose-based plastics exhibit superior biodegradability compared to polypropylene, breaking down naturally in composting environments within months, reducing landfill accumulation significantly. Polypropylene containers, while durable and recyclable, persist in the environment for centuries unless processed through specialized recycling facilities, which are limited. End-of-life options for cellulose plastics include industrial composting and anaerobic digestion, whereas polypropylene typically relies on mechanical recycling or energy recovery, impacting overall environmental footprint.
Performance in Food Packaging
Cellulose-based plastics offer excellent biodegradability and oxygen barrier properties, making them ideal for preserving food freshness in packaging applications. Polypropylene provides superior moisture resistance, mechanical strength, and heat tolerance, ensuring durability and performance during storage and transportation. Both materials suit food packaging, but cellulose-based plastics excel in sustainability, whereas polypropylene delivers enhanced protection against environmental factors.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Cellulose-based plastic containers typically incur higher production costs due to raw material sourcing and limited manufacturing scale, which affects overall cost effectiveness compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene containers benefit from widespread market availability, established supply chains, and lower material costs, enhancing their affordability for mass production. Despite cellulose-based plastics offering eco-friendly advantages, polypropylene remains the preferred choice for cost-sensitive applications due to its economic efficiency and extensive market presence.
Consumer Preferences and Perception
Consumers increasingly prefer cellulose-based plastics for containers due to their biodegradability and eco-friendly appeal, aligning with growing environmental awareness. Polypropylene remains favored for its durability, lightweight nature, and resistance to chemicals, which appeals to consumers prioritizing functionality and cost-effectiveness. Perception studies indicate that while polypropylene is trusted for practicality, cellulose-based plastics gain positive consumer perception for sustainability and reducing plastic pollution.
Future Trends and Innovations in Container Materials
Cellulose-based plastics are increasingly favored for container materials due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing, aligning with global sustainability goals and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Innovations in molecular engineering are enhancing cellulose plastic's barrier properties and thermal resistance, making them more competitive with polypropylene's durability and chemical resistance. Future trends highlight hybrid composites combining cellulose with polypropylene to optimize strength, environmental impact, and recyclability in container applications.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Polypropylene for Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com